Difference between revisions of "Balduina uniflora"
HaleighJoM (talk | contribs) (→Ecology) |
|||
| (32 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
| range_map_caption = Natural range of ''Balduina uniflora'' from USDA NRCS [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=BAUN Plants Database]. | | range_map_caption = Natural range of ''Balduina uniflora'' from USDA NRCS [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=BAUN Plants Database]. | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | Common Names: | + | Common Names: Savanna Honeycomb-head; Yellow Balduina;<ref name="Weakley 2015">Weakley AS (2015) Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Herbarium.</ref> Oneflower Honeycombhead<ref name="USDA">USDA NRCS (2016) The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 26 January 2018). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.</ref> |
==Taxonomic Notes== | ==Taxonomic Notes== | ||
| − | + | Synonyms: ''Endorima uniflora'' (Nuttall) Rafinesque <ref name="Weakley 2015"/><ref name="weakley">Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> | |
| + | |||
| + | Varieties: none.<ref name="weakley">Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> | ||
==Description== <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ==Description== <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| − | ''Balduina uniflora'' is a dioecious perennial that grows as a forb/herb.<ref name=" | + | ''Balduina uniflora'' is a dioecious perennial that grows as a forb/herb,<ref name="USDA"/> possessses fleshy roots<ref name="Parker & Jones 1975"/> that have a mean depth of 15.75 cm and porosity of 0.0%,<ref name="Brewer et al 2011">Brewer JS, Baker DJ, Nero AS, Patterson AL, Robers RS, Turner LM (2011) Carnivoory in plants as a beneficial trait in wetlands. Aquatic Botany 94:62-70.</ref> and reproduces vegetatively from root stocks. This species can reach heights of 0.7 - 1.0 m. When in bloom there are 1 - 3 heads, each with 8 - 22 yellow ray flowers that are 5.5 - 8.2 mm long and 1 - 2 mm wide.<ref name="Parker & Jones 1975"/> |
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
| − | + | ''Balduina uniflora'' is endemic to the longleaf pine range<ref>Sorrie, B. A. and A. S. Weakley 2001. Coastal Plain valcular plant endemics: Phytogeographic patterns. Castanea 66: 50-82.</ref> found from eastern Louisiana, eastward throughout the panhandle of Florida and southeastern Georgia, and northward to southeastern North Carolina.<ref name="USDA"/> | |
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | This species is found in wet pine savannas and | + | This species is found in wet pine savannas, pine flatwoods,<ref name="Weakley 2015"/> and the margins of pitcher-plant bogs.<ref name="Parker & Jones 1975">Parker ES, Jones SB (1975) A systematic study of the genus ''Balduina'' (Compositae, Heliantheae). Brittonia 27(4):355-361.</ref> It has also been observed in moist sand roadsides, wet peaty soil in pocosin, swamps, and mesic disturbed sites.<ref name= "Herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: March 2019. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, L. E. Arnold, Wendy Casper, A. F. Clewell, A. H. Curtiss, M. Darst, Donald Davidson, M. Davis, R. K. Godfrey, Floyd Griffith, Bruce Hansen, JoAnn Hansen, Ann F. Johnson, Lisa Keppner, R. Kral, R. A. Norris, Katelin D. Pearson, R. E. Perdue, Jr., Paul R. Redfearn, Jr., Bob Rice, E. L. Tyson, D. B. Ward, Rodie White, and Lovett E. Williams. States and Counties: Florida: Bay, Calhoun, Duval, Escambia, Franklin, Jackson, Leon, Nassau, Okaloosa, Santa Rosa, St Johns, Volusia, Wakulla, Walton, and Washington. Georgia: Grady, Thomas, and Worth.</ref> ''B. uniflora'' does not respond to soil disturbance by clearcutting and chopping in North Florida flatwoods forests.<ref>Moore, W.H., B.F. Swindel, and W.S. Terry. (1982). Vegetative Response to Clearcutting and Chopping in a North Florida Flatwoods Forest. Journal of Range Management 35(2):214-218.</ref> |
| + | |||
| + | ''Balduina uniflora'' is an indicator species for the Panhandle Seepage Savannas community type as described in Carr et al. (2010).<ref>Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Associated species: ''Liatris'' sp., ''Sporobolus'' sp., ''Andropogon'' sp., ''Schizachyrium'' sp., ''Eupatorium'' sp., ''[[Pinus palustris]]'', ''Habenaria ciliaris'', ''[[Lilium catesbaei]]'', ''[[Eragrostis elliottii]]'', ''[[Eriocaulon decangulare]]'', ''Rhynchospora'' sp., ''Bigelowia'' sp., ''Hypericum'' sp., ''[[Serenoa repens]]'', ''Xyris flexuosa'', ''[[Sabatia brevifolia]]'', ''Kalmia hirsute'', ''[[Polygala lutea]]'', ''[[Sorghastrum secundum]]'', ''Quercus pumila'', ''[[Seymeria cassioides]]'', ''[[Helianthus heterophyllus]]'', ''Juncus'' sp., ''[[Ilex glabra]]'', ''Rhexia'' sp., ''Marshallia graminifolia'', ''Pityopsis'' sp., and ''Carex'' sp.<ref name= "Herbarium"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| + | In the southeastern and mid-Atlantic United States, flowering occurs from late July through September.<ref name="Weakley 2015"/> Another, study reports flowering starting in June.<ref name="Parker & Jones 1975"/> It has been observed to flower from November to Janurary, March and April, and July through September, with peak inflorescence in September.<ref name= "Panflora">Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 26 MAR 2019</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
| + | This species is thought to be dispersed by wind. <ref> Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.</ref> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | < | + | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> |
| − | + | In Mississippi pine barrens, flowering increased significantly from one year after a burn into the second year following a burn.<ref name="Hinman & Brewer 2007">Hinman SE, Brewer JS (2007) Responses of two frequently-burned wet pine savannas to an extended period without fire. Journal of the Torrey Botanical Society 134(4):512-526.</ref> | |
| + | |||
| + | ===Pollination=== | ||
| + | It attracts bumblebees and butterflies which pollinates it.<ref name="Pitts-Singer et al 2002">Pitts-Singer TL, Hanula JL, Walker JL (2002) Insect pollinators of three rare plants in a Florida longleaf pine forest. Florida Entomologist 85(2):308-316.</ref> Pollen grains are 40-45 µm in diameter.<ref name="Parker & Jones 1975"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Herbivory and toxicology=== | ||
| + | Henslow's sparrows were observed to eat ''B. uniflora'' as a part of their diet.<ref name= "DiMiceli">DiMiceli, J. K., et al. (2007). "Seed preferences of wintering Henslow's sparrows." Condor 109: 595-604.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
<!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | <!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | ||
| − | ==Conservation and | + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration=== |
| − | == | + | ==Cultural use== |
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
<gallery widths=180px> | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
Latest revision as of 19:51, 15 June 2022
| Balduina uniflora | |
|---|---|
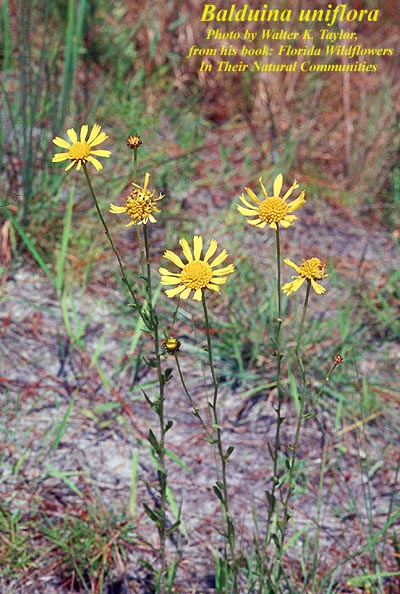

| |
| Photo by Altas of Florida Plants Database | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae |
| Genus: | Balduina |
| Species: | B. uniflora |
| Binomial name | |
| Balduina uniflora Nutt. | |
| |
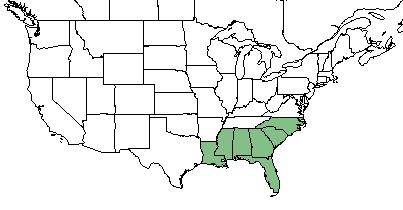
| Natural range of Balduina uniflora from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common Names: Savanna Honeycomb-head; Yellow Balduina;[1] Oneflower Honeycombhead[2]
Contents
[hide]Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: Endorima uniflora (Nuttall) Rafinesque [1][3]
Varieties: none.[3]
Description
Balduina uniflora is a dioecious perennial that grows as a forb/herb,[2] possessses fleshy roots[4] that have a mean depth of 15.75 cm and porosity of 0.0%,[5] and reproduces vegetatively from root stocks. This species can reach heights of 0.7 - 1.0 m. When in bloom there are 1 - 3 heads, each with 8 - 22 yellow ray flowers that are 5.5 - 8.2 mm long and 1 - 2 mm wide.[4]
Distribution
Balduina uniflora is endemic to the longleaf pine range[6] found from eastern Louisiana, eastward throughout the panhandle of Florida and southeastern Georgia, and northward to southeastern North Carolina.[2]
Ecology
Habitat
This species is found in wet pine savannas, pine flatwoods,[1] and the margins of pitcher-plant bogs.[4] It has also been observed in moist sand roadsides, wet peaty soil in pocosin, swamps, and mesic disturbed sites.[7] B. uniflora does not respond to soil disturbance by clearcutting and chopping in North Florida flatwoods forests.[8]
Balduina uniflora is an indicator species for the Panhandle Seepage Savannas community type as described in Carr et al. (2010).[9]
Associated species: Liatris sp., Sporobolus sp., Andropogon sp., Schizachyrium sp., Eupatorium sp., Pinus palustris, Habenaria ciliaris, Lilium catesbaei, Eragrostis elliottii, Eriocaulon decangulare, Rhynchospora sp., Bigelowia sp., Hypericum sp., Serenoa repens, Xyris flexuosa, Sabatia brevifolia, Kalmia hirsute, Polygala lutea, Sorghastrum secundum, Quercus pumila, Seymeria cassioides, Helianthus heterophyllus, Juncus sp., Ilex glabra, Rhexia sp., Marshallia graminifolia, Pityopsis sp., and Carex sp.[7]
Phenology
In the southeastern and mid-Atlantic United States, flowering occurs from late July through September.[1] Another, study reports flowering starting in June.[4] It has been observed to flower from November to Janurary, March and April, and July through September, with peak inflorescence in September.[10]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by wind. [11]
Fire ecology
In Mississippi pine barrens, flowering increased significantly from one year after a burn into the second year following a burn.[12]
Pollination
It attracts bumblebees and butterflies which pollinates it.[13] Pollen grains are 40-45 µm in diameter.[4]
Herbivory and toxicology
Henslow's sparrows were observed to eat B. uniflora as a part of their diet.[14]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration=
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Weakley AS (2015) Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ Jump up to: 2.0 2.1 2.2 USDA NRCS (2016) The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 26 January 2018). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ Jump up to: 3.0 3.1 Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ Jump up to: 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Parker ES, Jones SB (1975) A systematic study of the genus Balduina (Compositae, Heliantheae). Brittonia 27(4):355-361.
- Jump up ↑ Brewer JS, Baker DJ, Nero AS, Patterson AL, Robers RS, Turner LM (2011) Carnivoory in plants as a beneficial trait in wetlands. Aquatic Botany 94:62-70.
- Jump up ↑ Sorrie, B. A. and A. S. Weakley 2001. Coastal Plain valcular plant endemics: Phytogeographic patterns. Castanea 66: 50-82.
- ↑ Jump up to: 7.0 7.1 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: March 2019. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, L. E. Arnold, Wendy Casper, A. F. Clewell, A. H. Curtiss, M. Darst, Donald Davidson, M. Davis, R. K. Godfrey, Floyd Griffith, Bruce Hansen, JoAnn Hansen, Ann F. Johnson, Lisa Keppner, R. Kral, R. A. Norris, Katelin D. Pearson, R. E. Perdue, Jr., Paul R. Redfearn, Jr., Bob Rice, E. L. Tyson, D. B. Ward, Rodie White, and Lovett E. Williams. States and Counties: Florida: Bay, Calhoun, Duval, Escambia, Franklin, Jackson, Leon, Nassau, Okaloosa, Santa Rosa, St Johns, Volusia, Wakulla, Walton, and Washington. Georgia: Grady, Thomas, and Worth.
- Jump up ↑ Moore, W.H., B.F. Swindel, and W.S. Terry. (1982). Vegetative Response to Clearcutting and Chopping in a North Florida Flatwoods Forest. Journal of Range Management 35(2):214-218.
- Jump up ↑ Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.
- Jump up ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 26 MAR 2019
- Jump up ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.
- Jump up ↑ Hinman SE, Brewer JS (2007) Responses of two frequently-burned wet pine savannas to an extended period without fire. Journal of the Torrey Botanical Society 134(4):512-526.
- Jump up ↑ Pitts-Singer TL, Hanula JL, Walker JL (2002) Insect pollinators of three rare plants in a Florida longleaf pine forest. Florida Entomologist 85(2):308-316.
- Jump up ↑ DiMiceli, J. K., et al. (2007). "Seed preferences of wintering Henslow's sparrows." Condor 109: 595-604.