Difference between revisions of "Crocanthemum corymbosum"
HaleighJoM (talk | contribs) (→Ecology) |
|||
| (21 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | Common | + | Common names: Pine barren frostweed; pinebarren sunrose |
| + | ==Taxonomic notes== | ||
| + | Synonym: ''Helianthemum corymbosum'' Michaux.<ref name="weakley">Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Varieties: none.<ref name="weakley">Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| − | ''C. corymbosum'' is a perennial species with alternate, simple leaves<ref name="southeastern''>[[http://www.southeasternflora.com/view_flora.asp?plantid=2091 Southeastern Flora]]Accessed: December 11, 2015</ref> | + | ''C. corymbosum'' is a perennial species with alternate, simple leaves.<ref name="southeastern''>[[http://www.southeasternflora.com/view_flora.asp?plantid=2091 Southeastern Flora]]Accessed: December 11, 2015</ref> It has tomentose stems.<ref name="alabama">[[http://alabamaplants.com/Yellowalt/Helianthemum_corymbosum_page.html]]Accessed: December 14, 2015</ref> |
| − | Generally, for the ''Crocanthemum'' genus, they are erect, heraceous or suffrutescent perennials with alternate, stellate-pubescent leaves. There are two types of flowers, chasmogamous and cleistogamous. Chasmogamous flowers are on the pedicels that elongate to usually more than 1 cm long with large showy, tallow petals; there are numerous stamens and large sepals. The cleistogamous flowers are on the pedicels are usually less than 3 mm long, where the petals are absent, the stamens are few and the sepals are smaller than those of the chasmogamous flowers. The sepals are in 2 whorls, the outer are narrower than the inner. The capsule is 3-locular | + | Generally, for the ''Crocanthemum'' genus, they are erect, heraceous or suffrutescent perennials with alternate, stellate-pubescent leaves. There are two types of flowers, chasmogamous and cleistogamous. Chasmogamous flowers are on the pedicels that elongate to usually more than 1 cm long with large showy, tallow petals; there are numerous stamens and large sepals. The cleistogamous flowers are on the pedicels are usually less than 3 mm long, where the petals are absent, the stamens are few and the sepals are smaller than those of the chasmogamous flowers. The sepals are in 2 whorls, the outer are narrower than the inner. The capsule is 3-locular. <ref name="Radford">Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 718-9.</ref> |
| − | Specifically, for ''Crocanthemum corymbosum'' species, the roots have tuberous thickenings, the stems grow 1.3-5 tall, stellate canescent. The basal leaves are absent; the stem leaves 10-20, elliptic to oblanceolate, growing 1.5-3 cm long, and 5-10 mm wide, stellate-canescent above, tomentose beneath. The petioles 1-3 mm long. The cleistogamous flowers in compact terminal cymes; pedicels usually less than 5 mm long; the sepals and capsules 3-4 mm long. The chasmogamous flowers on pedicels 1-2 cm, scattered in the compact, the cleistogamous infloresence, or arising from its base; petals ca. 1 cm long; sepals and ovoid capsule, 5-7 mm long, pilose. The seeds are reddish brown in color, 1-1.2 mm long | + | Specifically, for ''Crocanthemum corymbosum'' species, the roots have tuberous thickenings, the stems grow 1.3-5 tall, stellate canescent. The basal leaves are absent; the stem leaves 10-20, elliptic to oblanceolate, growing 1.5-3 cm long, and 5-10 mm wide, stellate-canescent above, tomentose beneath. The petioles 1-3 mm long. The cleistogamous flowers in compact terminal cymes; pedicels usually less than 5 mm long; the sepals and capsules 3-4 mm long. The chasmogamous flowers on pedicels 1-2 cm, scattered in the compact, the cleistogamous infloresence, or arising from its base; petals ca. 1 cm long; sepals and ovoid capsule, 5-7 mm long, pilose. The seeds are reddish brown in color, 1-1.2 mm long.<ref name="Radford"/> |
| + | |||
| + | ==Distribution== | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
| − | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | + | ===Habitat===<!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> |
| − | It can been found in upland, well-drained sandy habitats, such as scrubby flatwoods (Pearson 1954)<ref name="hawthorn">[[http://hawthornhillwildflowers.blogspot.com/2010/05/florida-scrub-frostweed-helianthemum.html]]Accessed: December 15, 2015</ref> | + | It can been found in upland, well-drained sandy habitats, such as scrubby flatwoods (Pearson 1954).<ref name="hawthorn">[[http://hawthornhillwildflowers.blogspot.com/2010/05/florida-scrub-frostweed-helianthemum.html]]Accessed: December 15, 2015</ref> It has been observed growing in drying sand (FSU Herbarium). |
| − | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | + | Associated species include ''[[Quercus virginiana]], [[Quercus myrtifolia]], Quercus pumila, [[Quercus chapmanii]], [[Serenoa repens]], Osmanthus americanus, [[Vaccinium myrsinites]], [[Aristida stricta]]'', and ''[[Trilisa odoratissima]]" (Pearson 1954). |
| − | The canary yellow flowers bloom March through June <ref name="hawthorne">[[http://hawthornhillwildflowers.blogspot.com/2010/05/florida-scrub-frostweed-helianthemum.html]]</ref> | + | |
| + | ===Phenology===<!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| + | The canary yellow flowers bloom March through June.<ref name="hawthorne">[[http://hawthornhillwildflowers.blogspot.com/2010/05/florida-scrub-frostweed-helianthemum.html Hawthorn Hill Flowers Blogspot]]</ref> | ||
<!--===Seed dispersal===--> | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> | ||
<!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
<!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | <!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| + | |||
===Pollination=== | ===Pollination=== | ||
| − | + | ''Crocanthemum corymbosum'' is visited by sweat bees such as ''Lasioglossum nymphalis'' (family Halictidae).<ref name= "Deyrup">Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.</ref> | |
| + | <!--===Herbivory and toxicology===--> | ||
| + | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Cultural use== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
| + | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: October 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson. States and Counties: Florida: Franklin. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy. | Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: October 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson. States and Counties: Florida: Franklin. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy. | ||
Pearson, Paul G.. “Mammals of Gulf Hammock, Levy County, Florida”. American Midland Naturalist 51.2 (1954): 468–480. | Pearson, Paul G.. “Mammals of Gulf Hammock, Levy County, Florida”. American Midland Naturalist 51.2 (1954): 468–480. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 13:22, 22 June 2022
| Crocanthemum corymbosum | |
|---|---|
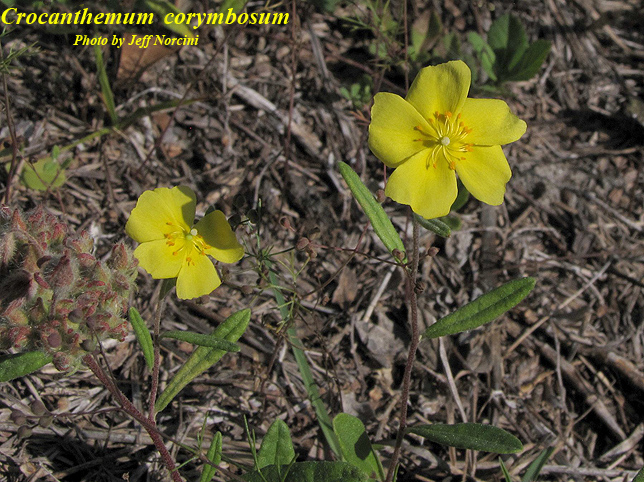

| |
| Photo by Jeff Norcini, Atlas of Florida Vascular Plants | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Violales |
| Family: | Cistaceae |
| Genus: | Crocanthemum |
| Species: | C. corymbosum |
| Binomial name | |
| Crocanthemum corymbosum Michx. | |
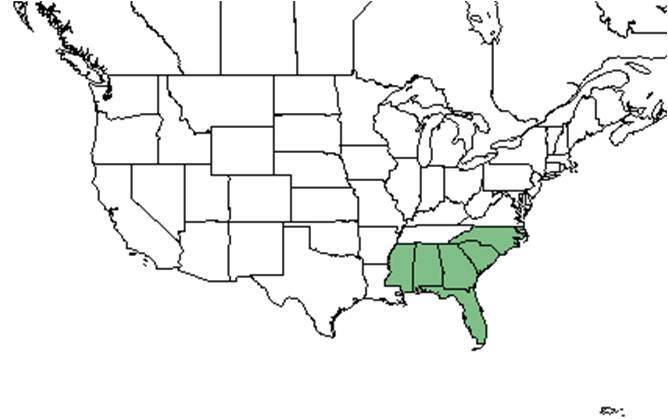
| |
| Natural range of Crocanthemum corymbosum from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Pine barren frostweed; pinebarren sunrose
Contents
[hide]Taxonomic notes
Synonym: Helianthemum corymbosum Michaux.[1]
Varieties: none.[1]
Description
C. corymbosum is a perennial species with alternate, simple leaves.[2] It has tomentose stems.[3]
Generally, for the Crocanthemum genus, they are erect, heraceous or suffrutescent perennials with alternate, stellate-pubescent leaves. There are two types of flowers, chasmogamous and cleistogamous. Chasmogamous flowers are on the pedicels that elongate to usually more than 1 cm long with large showy, tallow petals; there are numerous stamens and large sepals. The cleistogamous flowers are on the pedicels are usually less than 3 mm long, where the petals are absent, the stamens are few and the sepals are smaller than those of the chasmogamous flowers. The sepals are in 2 whorls, the outer are narrower than the inner. The capsule is 3-locular. [4]
Specifically, for Crocanthemum corymbosum species, the roots have tuberous thickenings, the stems grow 1.3-5 tall, stellate canescent. The basal leaves are absent; the stem leaves 10-20, elliptic to oblanceolate, growing 1.5-3 cm long, and 5-10 mm wide, stellate-canescent above, tomentose beneath. The petioles 1-3 mm long. The cleistogamous flowers in compact terminal cymes; pedicels usually less than 5 mm long; the sepals and capsules 3-4 mm long. The chasmogamous flowers on pedicels 1-2 cm, scattered in the compact, the cleistogamous infloresence, or arising from its base; petals ca. 1 cm long; sepals and ovoid capsule, 5-7 mm long, pilose. The seeds are reddish brown in color, 1-1.2 mm long.[4]
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
It can been found in upland, well-drained sandy habitats, such as scrubby flatwoods (Pearson 1954).[5] It has been observed growing in drying sand (FSU Herbarium).
Associated species include Quercus virginiana, Quercus myrtifolia, Quercus pumila, Quercus chapmanii, Serenoa repens, Osmanthus americanus, Vaccinium myrsinites, Aristida stricta, and Trilisa odoratissima" (Pearson 1954).
Phenology
The canary yellow flowers bloom March through June.[6]
Pollination
Crocanthemum corymbosum is visited by sweat bees such as Lasioglossum nymphalis (family Halictidae).[7]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: October 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson. States and Counties: Florida: Franklin. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
Pearson, Paul G.. “Mammals of Gulf Hammock, Levy County, Florida”. American Midland Naturalist 51.2 (1954): 468–480.
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- Jump up ↑ [Southeastern Flora]Accessed: December 11, 2015
- Jump up ↑ [[1]]Accessed: December 14, 2015
- ↑ Jump up to: 4.0 4.1 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 718-9.
- Jump up ↑ [[2]]Accessed: December 15, 2015
- Jump up ↑ [Hawthorn Hill Flowers Blogspot]
- Jump up ↑ Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.