Difference between revisions of "Aristida purpurascens"
(→Description) |
Adam.Vansant (talk | contribs) |
||
| (41 intermediate revisions by 10 users not shown) | |||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
| range_map_caption = Natural range of ''Aristida purpurascens'' from USDA NRCS [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=ARPUP4 Plants Database]. | | range_map_caption = Natural range of ''Aristida purpurascens'' from USDA NRCS [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=ARPUP4 Plants Database]. | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | Common Name(s): arrowfeather,<ref name= | + | Common Name(s): arrowfeather,<ref name=weakley>Weakley, A.S. 2020. Flora of the Southeastern United States. Edition of 20 October 2020. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> arrowfeather threeawn<ref name="USDA">USDA, NRCS. (2016). The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 14 December 2017). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.</ref> |
==Taxonomic Notes== | ==Taxonomic Notes== | ||
| − | Synonyms: ''A. purpurascens'' | + | Synonyms: ''A. purpurascens'' var. ''purpurascens'' <ref name=weakley/> |
| − | Varieties: | + | Varieties: ''A. purpurascens'' var. ''minor'' Vasey; ''A. purpurascens'' var. ''purpurascens''<ref name=weakley/> |
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| − | ''A. purpurascens'' is a monoecious cool-season perennial | + | ''A. purpurascens'' is a monoecious cool-season perennial grass<ref name="USDA"/> that reaches heights of 1.5 - 2.0 ft (0.46 - 0.61 m)<ref name="Magee 2012"/> and tolerates moderate shade.<ref name="Magee 2012"/> In sandhill pine communities, it can be found in a green or strongly glaucous-blue form.<ref name=weakley/> The leaves are flat narrow blades 4 - 12 in (10.2-30.5 m) long. The seedheads have a narrow panicle that is <sup>1</sup>/<sub>3</sub> to <sup>1</sup>/<sub>2</sub> the height of the plant.<ref name="Magee 2012"/> the awnes are <sup>1</sup>/<sub>2</sub> to <sup>3</sup>/<sub>4</sub> inches long<ref name="Magee 2012"/> and twice as thick at the base<ref name="Allred 1986">Allred K. W. (1986). Studies in the ''Aristida'' (Gramineae) of the southeastern United States. IV. Key and Conspectus. Rhodora 88(855):367-387.</ref>. The seeds contain barb-like hairs at the base.<ref name="Magee 2012"/> |
| + | ''Aristida purpurascens'' does not have specialized underground storage units apart from its fibrous roots.<ref name="Diaz"> Diaz-Toribio, M.H. and F. E. Putz 2021. Underground carbohydrate stores and storage organs in fire-maintained longleaf pine savannas in Florida, USA. American Journal of Botany 108: 432-442.</ref> Diaz-Toribio and Putz (2021) recorded this species to have a water content of 47.9% (ranking 91 out of 100 species studied).<ref name="Diaz"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | According to Diaz-Torbio and Putz (2021), ''Aristida purpurascens'' has fibrous roots with a below-ground to above-ground biomass ratio of 0.49 and nonstructural carbohydrate concentration of 69.5 mg g<sup>-1</sup>.<ref>Diaz-Torbio, M. H. and F. E. Putz. 2021. Underground carbohydrate stores and storage organs in fire-maintained longleaf pine savannas in Florida, USA. American Journal of Botany 108(3):432-442.</ref> | ||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
| − | ''Aristida purpurascens'' is found from Massachusetts west to Wisconsin and Kansas and southward to Florida and Texas.<ref name= | + | ''Aristida purpurascens'' is found from Massachusetts west to Wisconsin and Kansas and southward to Florida and Texas.<ref name=weakley/> <ref name="USDA"/> It may also be found in parts of Nebraska and Ontario, Canada.<ref name="USDA"/><ref name="Catling et al 1977">Catling P. M., Reznicek A. A., Riley J. L. (1977). Some new and interesting grass records from southern Ontario. Canadian Field-Naturalist 91(4):350-359.</ref> |
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | This species is found in dry habitats<ref name= | + | This species is found in dry habitats<ref name=weakley/> including pine savannas, fields, dunes, waste places, and other disturbed sites,<ref name= "Herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: March 2019. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Wilson Baker, L. Baltzell, Robert Blaisdell, Kathleen Craddock Burks, R. B. Channel, A. F. Clewell, M. Darst, A. Gholson, Jr., J. P. Gillespie, R. K. Godfrey, Floyd Griffith, Dianne Hall, J. M. Kane, Ed Keppner, Lisa Keppner, Gary R. Knight, R. Komarek, R. Kral, John M. Kunzer, Sidney McDaniel, Richard S. Mitchell, John Morrill, Robert A. Norris, R. E. Perdue, Jr., Cecil R. Slaughter, M. Stevenson, and A. Stiles. States and Counties: Florida: Alachua, Bay, Calhoun, Clay, Dixie, Duval, Escambia, Flagler, Franklin, Gadsden, Hamilton, Hillsborough, Jackson, Leon, Levy, Liberty, Madison, Manatee, Marion, Monroe, Nassau, Okaloosa, Osceola, Pinellas, Putnam, Sarasota, Wakulla, Walton, and Washington. Georgia: Atkinson, Baker, Coffee, Grady, Lanier, and Thomas. Louisiana: Vernon. Alabama: Baldwin. </ref><ref name="Allred 1986"/><ref name="Drewa et al 2002"/> especially those containing sandy or rocky soils.<ref name=weakley/> A study in Michigan old fields showed ''A. purpurascens'' had the second highest standing crop, which peaked in August at 270 g m<sup>-2</sup> dry weight.<ref name="Wiegert & Evans 1964">Wiegert R. G. and Evans F. C. (1964). Primary production and the disappearance of dead vegetation on an old field in southeastern Michigan. Ecology 45(1):49-63.</ref> In Maryland pine-cedar savannas, ''A. purpurascens'' was the second most important species (IV = 23.5%; Importance Value Index[IV] - calculated by summing the relative frequency and relative cover).<ref name="Tyndall & Farr 1989">Tyndall R. W. and Farr P. M. (1989). Vegetation structure and flora of a serpentine pin-cedar savanna in Maryland. Castanea 54(3):191-199.</ref> Lesser importance was found in Maryland serpentine barrens between 1989 and 1992 (IV = 1.4-6.5%).<ref name="Tyndall 1994">Tyndall R. W. (1994). Conifer clearing and prescribed burning effects to herbaceous layer vegetation on a Maryland serpentine "barren." Castanea 59(3):255-273.</ref> |
| + | |||
| + | Despite its importance in dryer systems, ''A. purpurascens'' is also observed in seepage bogs with similar, or slightly greater, coverage as pine savannas.<ref name="Drewa et al 2002">Drewa P. B., Platt W. J., and Moser B. (2002). Community structure along elevation gradients in headwater regions of longleaf pine savannas. Plant Ecology 160:61-78.</ref> In Louisiana sandstone outcrops where ''A. purpurascens'' also occurs, topsoil calcium were measured at 2267.5 ppm and magnesium at 586.5 ppm.<ref name="Kley 1999">Kley J. E. V. (1999). The vegetation of the Kisatchie Sandstone Hills, Louisiana. Castanea 64(1):64-80.</ref> Dead material of ''A. purpurascens'' disappears from 2.0-2.7 mg g<sup>-1</sup> in the fall (mid July-mid November) and 0.1-1.0 mg g<sup>-1</sup> the rest of the year in a Michigan old field.<ref name="Wiegert & Evans 1964"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''A. purpurascens'' has shown regrowth in reestablished longleaf pine woodlands that were disturbed by agricultural practices in South Carolina plant communities, making it a post-agriculture woodlands indicator species.<ref>Brudvig, L.A., E Grman, C.W. Habeck, and J.A. Ledvina. (2013). Strong legacy of agricultural land use on soils and understory plant communities in longleaf pine woodlands. Forest Ecology and Management 310: 944-955.</ref> However, it was found to reduce its coverage in response to roller chopping in South Florida. It has also shown resistance to regrowth in reestablished longleaf communities that were disturbed by roller chopping.<ref>Lewis, C.E. (1970). Responses to Chopping and Rock Phosphate on South Florida Ranges. Journal of Range Management 23(4):276-282.</ref> It does not respond to soil disturbance by clearcutting and chopping in North Florida flatwoods forests.<ref>Moore, W.H., B.F. Swindel, and W.S. Terry. (1982). Vegetative Response to Clearcutting and Chopping in a North Florida Flatwoods Forest. Journal of Range Management 35(2):214-218.</ref> Additionally, ''A. purpurascens'' has been found to be neutral in its short-term response to single mechanical soil disturbances as well as in its long-term response following cessation of repeated soil disturbance.<ref name=Dixon>Dixon, C. M., K. M. Robertson, A. M. Reid and M. T. Rother. 2024. Mechanical soil disturbance in a pine savanna has multiyear effects on plant species composition. Ecosphere 15(2):e4759.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Aristida purpurascens'' var. ''purpurascens'' is frequent and abundant in the Clayhill Longleaf Woodlands and Upper Panhandle Savannas community types as described in Carr et al. (2010).<ref>Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Aristida purpurascens'' var. ''tenuispica'' is an indicator species for the Central Florida Flatwoods/Prairies community type as described in Carr et al. (2010).<ref>Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Associated species include ''[[Andropogon virginicus]]'' var. ''virginicus'', ''[[Andropogon virginicus]]'' var. ''glaucus'', ''Andropogon'' sp., ''Schizochyrium stoloniferum'', ''Hedyotis uniflora'', ''[[Hypericum gentianoides]]'', ''[[Hypericum suffruticosum]]'', ''Hypericum'' sp., ''[[Paspalum setaceum]]'', ''[[Desmodium lineatum]]'', ''Desmodium'' sp., ''[[Panicum verrucosum]]'', ''Cenchrus'' sp., ''Setaria'' sp., ''Baccharis'' sp., ''[[Aristida stricta]]'', ''Sporobolus clandestinus'', ''Helianthus'' sp., and ''Lobelia'' sp.<ref name= "Herbarium"/> | ||
| − | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting | + | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> |
| − | Seeds production usually peaks in June.<ref name="Magee 2012"/> | + | ''A. purpurascens'' has been observed to flower from July to December with peak inflorescence in October. It has been observed fruiting from July to December as well as the month of February.<ref name= "Herbarium"/> Seeds production usually peaks in June.<ref name="Magee 2012"/> |
===Seed dispersal=== | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
| Line 43: | Line 56: | ||
===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| − | ''A. purpurascens'' | + | ''A. purpurascens'' has been known to withstand repeated annual burning.<ref name="Magee 2012"/><ref>Robertson, K.M. Unpublished data collected from Pebble Hill Fire Plots, Pebble Hill Plantation, Thomasville, Georgia.</ref><ref>Glitzenstein, J. S., D. R. Streng, R. E. Masters, K. M. Robertson and S. M. Hermann 2012. Fire-frequency effects on vegetation in north Florida pinelands: Another look at the long-term Stoddard Fire Research Plots at Tall Timbers Research Station. Forest Ecology and Management 264: 197-209.</ref> On Eglin Air Force Base, Florida, May and July burns increased the percentage of flowering culms on ''A. purpurascens''.<ref>Shepherd B. J., Miller D. L., and Thetford M. (2012). Fire season effects on flowering characteristics and germination of longleaf pine (''Pinus palustris'') savanna grasses. Restoration Ecology 20(2):268-276.</ref> As well, a study in north Florida found that ''A. purpurascens'' increases in frequency in response to fire, and time of year for burning did not seem to affect it.<ref name= "Kush">Kush, J. S., et al. (2000). Understory plant community response to season of burn in natural longleaf pine forests. Proceedings 21st Tall Timbers Fire Ecology Conference. Fire and forest ecology: innovative silviculture & vegetation management, Tallahassee, FL, Tall Timbers Research, Inc.</ref> In Maryland serpentine barrens, clearing and the combination of clearing and burning increased the importance value percentage to between 3.0-12.2% from between 1.4-6.5%<ref name="Tyndall 1994"/> However, one study about fire exclusion found that ''A. purpurascens'' had a higher frequency in quadrats sampled in the fire exclusion areas compared to normal burning regiments.<ref name= "Clewell">Clewell, A. F. (2014). "Forest development 44 years after fire exclusion in formerly annually burned oldfield pine woodland, Florida." Castanea 79: 147-167.</ref> |
| + | |||
<!--===Pollination===--> | <!--===Pollination===--> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Herbivory and toxicology===<!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> |
Seeds from this grass compose 2-5% of the diet of some terrestrial birds.<ref name="USDA"/> A study in Michigan showed the seeds of ''A. purpurascens'' was also abundant in the caches of prairie deer mice (''Peromyscus maniculatus bairdii'').<ref name="Howard & Evans 1961">Howard W. E. and Evans F. C. (1961). Seeds stored by prairie deer mice. Journal of Mammalogy 42(2):260-263.</ref> For a few weeks in the spring cattle can graze arrowfeather, but in the rest of the year it is considered a low quality forage.<ref name="Magee 2012">Magee P. (2012). Plant fact sheet: Arrowfeather threeawn ''Aristida purpurascens''. United States Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service, Baton Rouge, LA.</ref> | Seeds from this grass compose 2-5% of the diet of some terrestrial birds.<ref name="USDA"/> A study in Michigan showed the seeds of ''A. purpurascens'' was also abundant in the caches of prairie deer mice (''Peromyscus maniculatus bairdii'').<ref name="Howard & Evans 1961">Howard W. E. and Evans F. C. (1961). Seeds stored by prairie deer mice. Journal of Mammalogy 42(2):260-263.</ref> For a few weeks in the spring cattle can graze arrowfeather, but in the rest of the year it is considered a low quality forage.<ref name="Magee 2012">Magee P. (2012). Plant fact sheet: Arrowfeather threeawn ''Aristida purpurascens''. United States Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service, Baton Rouge, LA.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
<!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | <!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | ||
==Conservation and Management== | ==Conservation and Management== | ||
| − | To reduce the abundance of ''A. purpurascens'', grazing can be allowed for 2-3 weeks in the spring just before seedheads appear.<ref name="Magee 2012"/> | + | To reduce the abundance of ''A. purpurascens'', grazing can be allowed for 2-3 weeks in the spring just before seedheads appear.<ref name="Magee 2012"/> ''A. purpurascens'' is listed as a species of special concern in Connecticut, and listed as threatened in Massachusetts, Pennsylvania, and Rhode Island.<ref name= "USDA"/> |
==Cultivation and restoration== | ==Cultivation and restoration== | ||
Latest revision as of 19:50, 10 July 2024
| Aristida purpurascens | |
|---|---|
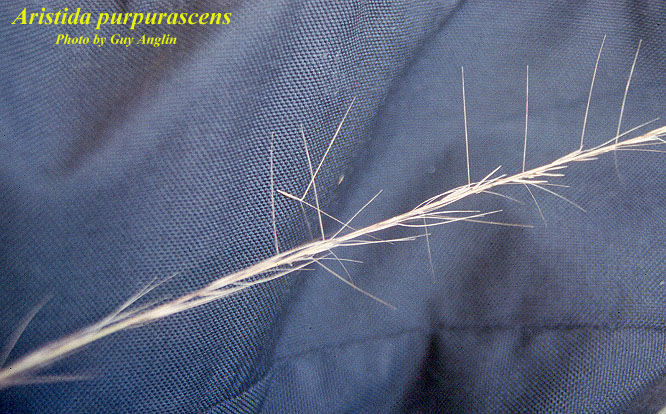

| |
| Photo by the Atlas of Florida Plants Database | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Cyperales |
| Family: | Poaceae |
| Genus: | Aristida |
| Species: | A. purpurascens |
| Binomial name | |
| Aristida purpurascens Poiret | |
| |
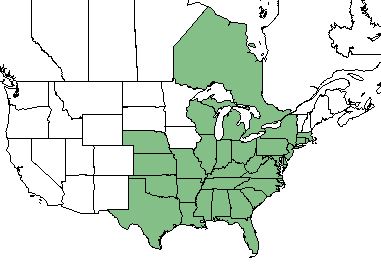
| Natural range of Aristida purpurascens from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common Name(s): arrowfeather,[1] arrowfeather threeawn[2]
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: A. purpurascens var. purpurascens [1]
Varieties: A. purpurascens var. minor Vasey; A. purpurascens var. purpurascens[1]
Description
A. purpurascens is a monoecious cool-season perennial grass[2] that reaches heights of 1.5 - 2.0 ft (0.46 - 0.61 m)[3] and tolerates moderate shade.[3] In sandhill pine communities, it can be found in a green or strongly glaucous-blue form.[1] The leaves are flat narrow blades 4 - 12 in (10.2-30.5 m) long. The seedheads have a narrow panicle that is 1/3 to 1/2 the height of the plant.[3] the awnes are 1/2 to 3/4 inches long[3] and twice as thick at the base[4]. The seeds contain barb-like hairs at the base.[3]
Aristida purpurascens does not have specialized underground storage units apart from its fibrous roots.[5] Diaz-Toribio and Putz (2021) recorded this species to have a water content of 47.9% (ranking 91 out of 100 species studied).[5]
According to Diaz-Torbio and Putz (2021), Aristida purpurascens has fibrous roots with a below-ground to above-ground biomass ratio of 0.49 and nonstructural carbohydrate concentration of 69.5 mg g-1.[6]
Distribution
Aristida purpurascens is found from Massachusetts west to Wisconsin and Kansas and southward to Florida and Texas.[1] [2] It may also be found in parts of Nebraska and Ontario, Canada.[2][7]
Ecology
Habitat
This species is found in dry habitats[1] including pine savannas, fields, dunes, waste places, and other disturbed sites,[8][4][9] especially those containing sandy or rocky soils.[1] A study in Michigan old fields showed A. purpurascens had the second highest standing crop, which peaked in August at 270 g m-2 dry weight.[10] In Maryland pine-cedar savannas, A. purpurascens was the second most important species (IV = 23.5%; Importance Value Index[IV] - calculated by summing the relative frequency and relative cover).[11] Lesser importance was found in Maryland serpentine barrens between 1989 and 1992 (IV = 1.4-6.5%).[12]
Despite its importance in dryer systems, A. purpurascens is also observed in seepage bogs with similar, or slightly greater, coverage as pine savannas.[9] In Louisiana sandstone outcrops where A. purpurascens also occurs, topsoil calcium were measured at 2267.5 ppm and magnesium at 586.5 ppm.[13] Dead material of A. purpurascens disappears from 2.0-2.7 mg g-1 in the fall (mid July-mid November) and 0.1-1.0 mg g-1 the rest of the year in a Michigan old field.[10]
A. purpurascens has shown regrowth in reestablished longleaf pine woodlands that were disturbed by agricultural practices in South Carolina plant communities, making it a post-agriculture woodlands indicator species.[14] However, it was found to reduce its coverage in response to roller chopping in South Florida. It has also shown resistance to regrowth in reestablished longleaf communities that were disturbed by roller chopping.[15] It does not respond to soil disturbance by clearcutting and chopping in North Florida flatwoods forests.[16] Additionally, A. purpurascens has been found to be neutral in its short-term response to single mechanical soil disturbances as well as in its long-term response following cessation of repeated soil disturbance.[17]
Aristida purpurascens var. purpurascens is frequent and abundant in the Clayhill Longleaf Woodlands and Upper Panhandle Savannas community types as described in Carr et al. (2010).[18]
Aristida purpurascens var. tenuispica is an indicator species for the Central Florida Flatwoods/Prairies community type as described in Carr et al. (2010).[19]
Associated species include Andropogon virginicus var. virginicus, Andropogon virginicus var. glaucus, Andropogon sp., Schizochyrium stoloniferum, Hedyotis uniflora, Hypericum gentianoides, Hypericum suffruticosum, Hypericum sp., Paspalum setaceum, Desmodium lineatum, Desmodium sp., Panicum verrucosum, Cenchrus sp., Setaria sp., Baccharis sp., Aristida stricta, Sporobolus clandestinus, Helianthus sp., and Lobelia sp.[8]
Phenology
A. purpurascens has been observed to flower from July to December with peak inflorescence in October. It has been observed fruiting from July to December as well as the month of February.[8] Seeds production usually peaks in June.[3]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by gravity. [20]
Fire ecology
A. purpurascens has been known to withstand repeated annual burning.[3][21][22] On Eglin Air Force Base, Florida, May and July burns increased the percentage of flowering culms on A. purpurascens.[23] As well, a study in north Florida found that A. purpurascens increases in frequency in response to fire, and time of year for burning did not seem to affect it.[24] In Maryland serpentine barrens, clearing and the combination of clearing and burning increased the importance value percentage to between 3.0-12.2% from between 1.4-6.5%[12] However, one study about fire exclusion found that A. purpurascens had a higher frequency in quadrats sampled in the fire exclusion areas compared to normal burning regiments.[25]
Herbivory and toxicology
Seeds from this grass compose 2-5% of the diet of some terrestrial birds.[2] A study in Michigan showed the seeds of A. purpurascens was also abundant in the caches of prairie deer mice (Peromyscus maniculatus bairdii).[26] For a few weeks in the spring cattle can graze arrowfeather, but in the rest of the year it is considered a low quality forage.[3]
Conservation and Management
To reduce the abundance of A. purpurascens, grazing can be allowed for 2-3 weeks in the spring just before seedheads appear.[3] A. purpurascens is listed as a species of special concern in Connecticut, and listed as threatened in Massachusetts, Pennsylvania, and Rhode Island.[2]
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Weakley, A.S. 2020. Flora of the Southeastern United States. Edition of 20 October 2020. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 USDA, NRCS. (2016). The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 14 December 2017). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 3.8 Magee P. (2012). Plant fact sheet: Arrowfeather threeawn Aristida purpurascens. United States Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service, Baton Rouge, LA.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Allred K. W. (1986). Studies in the Aristida (Gramineae) of the southeastern United States. IV. Key and Conspectus. Rhodora 88(855):367-387.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Diaz-Toribio, M.H. and F. E. Putz 2021. Underground carbohydrate stores and storage organs in fire-maintained longleaf pine savannas in Florida, USA. American Journal of Botany 108: 432-442.
- ↑ Diaz-Torbio, M. H. and F. E. Putz. 2021. Underground carbohydrate stores and storage organs in fire-maintained longleaf pine savannas in Florida, USA. American Journal of Botany 108(3):432-442.
- ↑ Catling P. M., Reznicek A. A., Riley J. L. (1977). Some new and interesting grass records from southern Ontario. Canadian Field-Naturalist 91(4):350-359.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: March 2019. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Wilson Baker, L. Baltzell, Robert Blaisdell, Kathleen Craddock Burks, R. B. Channel, A. F. Clewell, M. Darst, A. Gholson, Jr., J. P. Gillespie, R. K. Godfrey, Floyd Griffith, Dianne Hall, J. M. Kane, Ed Keppner, Lisa Keppner, Gary R. Knight, R. Komarek, R. Kral, John M. Kunzer, Sidney McDaniel, Richard S. Mitchell, John Morrill, Robert A. Norris, R. E. Perdue, Jr., Cecil R. Slaughter, M. Stevenson, and A. Stiles. States and Counties: Florida: Alachua, Bay, Calhoun, Clay, Dixie, Duval, Escambia, Flagler, Franklin, Gadsden, Hamilton, Hillsborough, Jackson, Leon, Levy, Liberty, Madison, Manatee, Marion, Monroe, Nassau, Okaloosa, Osceola, Pinellas, Putnam, Sarasota, Wakulla, Walton, and Washington. Georgia: Atkinson, Baker, Coffee, Grady, Lanier, and Thomas. Louisiana: Vernon. Alabama: Baldwin.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Drewa P. B., Platt W. J., and Moser B. (2002). Community structure along elevation gradients in headwater regions of longleaf pine savannas. Plant Ecology 160:61-78.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Wiegert R. G. and Evans F. C. (1964). Primary production and the disappearance of dead vegetation on an old field in southeastern Michigan. Ecology 45(1):49-63.
- ↑ Tyndall R. W. and Farr P. M. (1989). Vegetation structure and flora of a serpentine pin-cedar savanna in Maryland. Castanea 54(3):191-199.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Tyndall R. W. (1994). Conifer clearing and prescribed burning effects to herbaceous layer vegetation on a Maryland serpentine "barren." Castanea 59(3):255-273.
- ↑ Kley J. E. V. (1999). The vegetation of the Kisatchie Sandstone Hills, Louisiana. Castanea 64(1):64-80.
- ↑ Brudvig, L.A., E Grman, C.W. Habeck, and J.A. Ledvina. (2013). Strong legacy of agricultural land use on soils and understory plant communities in longleaf pine woodlands. Forest Ecology and Management 310: 944-955.
- ↑ Lewis, C.E. (1970). Responses to Chopping and Rock Phosphate on South Florida Ranges. Journal of Range Management 23(4):276-282.
- ↑ Moore, W.H., B.F. Swindel, and W.S. Terry. (1982). Vegetative Response to Clearcutting and Chopping in a North Florida Flatwoods Forest. Journal of Range Management 35(2):214-218.
- ↑ Dixon, C. M., K. M. Robertson, A. M. Reid and M. T. Rother. 2024. Mechanical soil disturbance in a pine savanna has multiyear effects on plant species composition. Ecosphere 15(2):e4759.
- ↑ Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.
- ↑ Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.
- ↑ Robertson, K.M. Unpublished data collected from Pebble Hill Fire Plots, Pebble Hill Plantation, Thomasville, Georgia.
- ↑ Glitzenstein, J. S., D. R. Streng, R. E. Masters, K. M. Robertson and S. M. Hermann 2012. Fire-frequency effects on vegetation in north Florida pinelands: Another look at the long-term Stoddard Fire Research Plots at Tall Timbers Research Station. Forest Ecology and Management 264: 197-209.
- ↑ Shepherd B. J., Miller D. L., and Thetford M. (2012). Fire season effects on flowering characteristics and germination of longleaf pine (Pinus palustris) savanna grasses. Restoration Ecology 20(2):268-276.
- ↑ Kush, J. S., et al. (2000). Understory plant community response to season of burn in natural longleaf pine forests. Proceedings 21st Tall Timbers Fire Ecology Conference. Fire and forest ecology: innovative silviculture & vegetation management, Tallahassee, FL, Tall Timbers Research, Inc.
- ↑ Clewell, A. F. (2014). "Forest development 44 years after fire exclusion in formerly annually burned oldfield pine woodland, Florida." Castanea 79: 147-167.
- ↑ Howard W. E. and Evans F. C. (1961). Seeds stored by prairie deer mice. Journal of Mammalogy 42(2):260-263.