Difference between revisions of "Carya floridana"
Emmazeitler (talk | contribs) (→Taxonomic notes) |
HaleighJoM (talk | contribs) (→Ecology) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat===<!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat===<!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | In the Coastal Plain in Florida, ''C. floridana'' has been found in sand pine woods with ''Lyonia ferruginea''; sand pine-oak scrubs; sand ridge scrubs; hardwood hammocks; scrub oak-wiregrass ridges; and scrub barrens.<ref name="FSU">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: October 2015. Collectors: L.J. Brass, D. Burch, Brevard, A.F. Clewell, R.F. Christensen, Angus Gholson, R.K. Godfrey, R. Kral, O. Lakela, Robert J. Lemaire, S.W. Leonard, Walter S. Judd, K.M. Meyer, John B. Nelson, R.W. Simons, A. Townesmith, D.B. Ward, R.H. Wnek. States and Counties: Florida: Brevard, Highlands, Indian River, Lake, Marion, Martin, Palm Beach. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy. | + | In the Coastal Plain in Florida, ''C. floridana'' has been found in sand pine woods with ''Lyonia ferruginea''; sand pine-oak scrubs; sand ridge scrubs; hardwood hammocks; scrub oak-wiregrass ridges; and scrub barrens.<ref name="FSU">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: October 2015. Collectors: L.J. Brass, D. Burch, Brevard, A.F. Clewell, R.F. Christensen, Angus Gholson, R.K. Godfrey, R. Kral, O. Lakela, Robert J. Lemaire, S.W. Leonard, Walter S. Judd, K.M. Meyer, John B. Nelson, R.W. Simons, A. Townesmith, D.B. Ward, R.H. Wnek. States and Counties: Florida: Brevard, Highlands, Indian River, Lake, Marion, Martin, Palm Beach. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.</ref> It is an aggressive invader of open xeric woodlands; however, nutrient availability and water limit seedling survival.<ref name="McCarthy"></ref><ref>Myers, R.L. 1990. Scrub and high pine, pp. 150-193. In R.L. Myers and J.J. Ewel, Ecosystems of Florida. Univ. of Central Florida Press, Orlando.</ref> Soil types include entisols, Astatula-Paola-Tavares of the series Quartzipsamments.<ref name="McCarthy"></ref> |
| − | </ref> It is an aggressive invader of open xeric woodlands; however, nutrient availability and water limit seedling survival.<ref name="McCarthy"></ref><ref>Myers, R.L. 1990. Scrub and high pine, pp. 150-193. In R.L. Myers and J.J. Ewel, Ecosystems of Florida. Univ. of Central Florida Press, Orlando.</ref> Soil types include entisols, Astatula-Paola-Tavares of the series Quartzipsamments.<ref name="McCarthy"></ref> Associated species include ''Persea, Quercus laevis, | + | |
| + | Associated species include ''Persea, [[Quercus laevis]], [[Quercus myrtifolia]], [[Quercus geminata]], [[Quercus chapmanii]], [[Sabal etonia]], [[Serenoa repens]], Polygonella, Ceranthera, Ilex cumulicola, [[Pinus elliottii]] var. densa'', and ''Garberia.''<ref name="FSU"></ref> | ||
===Phenology===<!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology===<!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| Line 51: | Line 52: | ||
===Pollination=== | ===Pollination=== | ||
| − | + | ''Carya floridana'' was observed at the Archbold Biological Station to host bees such as ''Apis mellifera'' (family Apidae).<ref>Deyrup, M.A. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.</ref> This species has been observed to host plant bugs such as ''Plagiognathus albatus'' (family Miridae).<ref>Discoverlife.org [https://www.discoverlife.org/20/q?search=Bidens+albaDiscoverlife.org|Discoverlife.org]</ref> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | === | + | ===Herbivory and toxicology=== |
Fruits are eaten by rodents, black bears, foxes and raccoons and provide a high concentration of energy, protein, fat, fiber, nitrogen, phosphorous, iron, copper, and zinc. They are important to squirrel diets during the autumn and spring months.<ref>Abrahamson, Warren G., and Christy R. Abrahamson. “Nutritional Quality of Animal Dispersed Fruits in Florida Sandridge Habitats”. Bulletin of the Torrey Botanical Club 116.3 (1989): 215–228. </ref>The leaves of scrub hickory are utilized by squirrels to construct outside leaf nests. Florida scrub jay, blue jay, red-bellied woodpecker, and red-headed woodpecker are recorded to feed on scrub hickory nuts. Curculionid beetle larvae are the only known invertebrate animals to feed on scrub hickory nuts. Scrub hickory sap also appears to be attractive to yellow-bellied sapsuckers during winter months. | Fruits are eaten by rodents, black bears, foxes and raccoons and provide a high concentration of energy, protein, fat, fiber, nitrogen, phosphorous, iron, copper, and zinc. They are important to squirrel diets during the autumn and spring months.<ref>Abrahamson, Warren G., and Christy R. Abrahamson. “Nutritional Quality of Animal Dispersed Fruits in Florida Sandridge Habitats”. Bulletin of the Torrey Botanical Club 116.3 (1989): 215–228. </ref>The leaves of scrub hickory are utilized by squirrels to construct outside leaf nests. Florida scrub jay, blue jay, red-bellied woodpecker, and red-headed woodpecker are recorded to feed on scrub hickory nuts. Curculionid beetle larvae are the only known invertebrate animals to feed on scrub hickory nuts. Scrub hickory sap also appears to be attractive to yellow-bellied sapsuckers during winter months. | ||
| Line 61: | Line 60: | ||
Mistletoe (''Phoradendron serotinum'') is a parasite that attacks ''Carya'' species.<ref name="Fresh">[[http://www.freshfromflorida.com/Divisions-Offices/Florida-Forest-Service/Our-Forests/Forest-Health/Forest-Health-Publications/Insects-and-Diseases/TABLE-X.-Some-Common-Types-of-High-Plants-Growing-In-or-On-Trees-in-Florida Fresh From Florida]]Accessed: December 4, 2015</ref> | Mistletoe (''Phoradendron serotinum'') is a parasite that attacks ''Carya'' species.<ref name="Fresh">[[http://www.freshfromflorida.com/Divisions-Offices/Florida-Forest-Service/Our-Forests/Forest-Health/Forest-Health-Publications/Insects-and-Diseases/TABLE-X.-Some-Common-Types-of-High-Plants-Growing-In-or-On-Trees-in-Florida Fresh From Florida]]Accessed: December 4, 2015</ref> | ||
| − | ==Conservation and | + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== |
In areas of fire suppression and well drained, nutrient poor soils along the Lake Wales Ridge, ''C. floridana'' will become the dominant overstory species.<ref name="McCarthy"></ref><ref name="Myers and White"></ref> | In areas of fire suppression and well drained, nutrient poor soils along the Lake Wales Ridge, ''C. floridana'' will become the dominant overstory species.<ref name="McCarthy"></ref><ref name="Myers and White"></ref> | ||
| − | == | + | ==Cultural use== |
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
<gallery widths=180px> | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
Latest revision as of 20:25, 15 June 2022
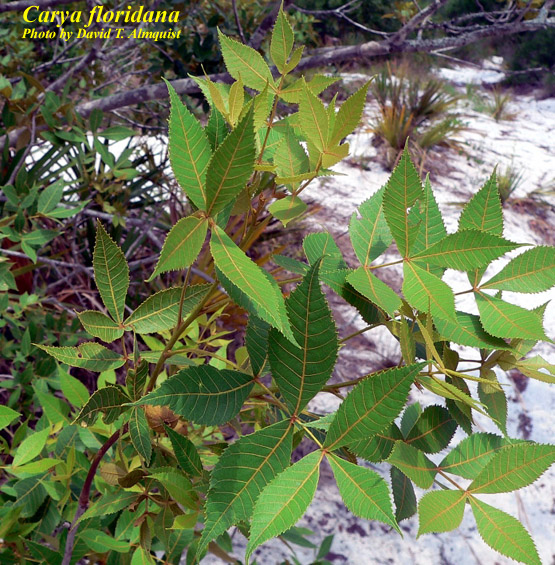
| Carya floridana | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by David T. Almquist, Atlas of Florida Vascular Plants | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Juglandales |
| Family: | Juglandaceae |
| Genus: | Carya |
| Species: | C. floridana |
| Binomial name | |
| Carya floridana Sarg. | |
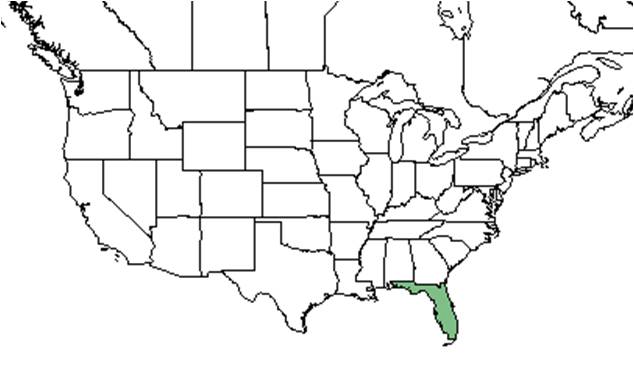
| |
| Natural range of Carya floridana from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Scrub hickory
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonym: Hicoria floridana (Sargent) Sudworth.[1]
Varieties: none.[1]
Description
A description of Carya floridana is provided in The Flora of North America.
C. floridana is a long-lived perennial woody species, that can grow up to 20 meters high.[2] [3] It can be identified from other Carya species by having rust-colored scales on the buds and lower leaf surfaces.[4]
Distribution
Carya floridana is endemic to central Florida and is the most abundant hardwood in the southern Lake Wales Ridge.[5][6] The range is influenced by edaphic and climatic conditions.[5]
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain in Florida, C. floridana has been found in sand pine woods with Lyonia ferruginea; sand pine-oak scrubs; sand ridge scrubs; hardwood hammocks; scrub oak-wiregrass ridges; and scrub barrens.[7] It is an aggressive invader of open xeric woodlands; however, nutrient availability and water limit seedling survival.[5][8] Soil types include entisols, Astatula-Paola-Tavares of the series Quartzipsamments.[5]
Associated species include Persea, Quercus laevis, Quercus myrtifolia, Quercus geminata, Quercus chapmanii, Sabal etonia, Serenoa repens, Polygonella, Ceranthera, Ilex cumulicola, Pinus elliottii var. densa, and Garberia.[7]
Phenology
Flowers are monecious, flowering January through April and fruiting June through October.[3][7]New leaves appear in late January or early February with considerable individual, site, and year-to-year variation in the timing of leaf development. Most nuts are shed from September to November.[9]
Seed dispersal
Seeds are dispersed by wind.[3]
Seed bank and germination
C. floridana does not have the seed dormancy trait that can be found in commercial hickories of the eastern deciduous forest.[5] Hickories have one of the longest taproots observed among the eastern hardwoods, this allows them to resprout repeatedly following heavy disturbances.[5] Adequate moisture is needed for seed germination.[5]
Fire ecology
C. floridana is an understory plant found in sandhills along the Lake Wales Ridge. In order to maintain an open southern ridge sandhill, frequent low intensity fires are needed. Long-term fire suppression in sandhill communities results in Quercus and Carya floridana dominated xeric hammocks.[10]Scrub hickory is well-adapted to fire and following a burn quickly regenerates through production of new ramets rather than through germination of nuts in the soil.
Pollination
Carya floridana was observed at the Archbold Biological Station to host bees such as Apis mellifera (family Apidae).[11] This species has been observed to host plant bugs such as Plagiognathus albatus (family Miridae).[12]
Herbivory and toxicology
Fruits are eaten by rodents, black bears, foxes and raccoons and provide a high concentration of energy, protein, fat, fiber, nitrogen, phosphorous, iron, copper, and zinc. They are important to squirrel diets during the autumn and spring months.[13]The leaves of scrub hickory are utilized by squirrels to construct outside leaf nests. Florida scrub jay, blue jay, red-bellied woodpecker, and red-headed woodpecker are recorded to feed on scrub hickory nuts. Curculionid beetle larvae are the only known invertebrate animals to feed on scrub hickory nuts. Scrub hickory sap also appears to be attractive to yellow-bellied sapsuckers during winter months.
Diseases and parasites
Mistletoe (Phoradendron serotinum) is a parasite that attacks Carya species.[14]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
In areas of fire suppression and well drained, nutrient poor soils along the Lake Wales Ridge, C. floridana will become the dominant overstory species.[5][6]
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ [Florida Native Plant Society]Accessed: December 4, 2015
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 [Plants for a Future] Accessed: December 4, 2015
- ↑ [[1]] Accessed: December 4, 2015
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 McCarthy, Brian C., and Donald R. Bailey. “Seed Germination and Seedling Establishment of Carya Floridana (sarg.) Small (juglandaceae)”. Bulletin of the Torrey Botanical Club 119.4 (1992): 384–391
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Myers, Ronald L., and Deborah L. White. “Landscape History and Changes in Sandhill Vegetation in North-central and South-central Florida”. Bulletin of the Torrey Botanical Club 114.1 (1987): 21–32.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: October 2015. Collectors: L.J. Brass, D. Burch, Brevard, A.F. Clewell, R.F. Christensen, Angus Gholson, R.K. Godfrey, R. Kral, O. Lakela, Robert J. Lemaire, S.W. Leonard, Walter S. Judd, K.M. Meyer, John B. Nelson, R.W. Simons, A. Townesmith, D.B. Ward, R.H. Wnek. States and Counties: Florida: Brevard, Highlands, Indian River, Lake, Marion, Martin, Palm Beach. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ Myers, R.L. 1990. Scrub and high pine, pp. 150-193. In R.L. Myers and J.J. Ewel, Ecosystems of Florida. Univ. of Central Florida Press, Orlando.
- ↑ Layne J. N., Abrahamson W. G. 2006. Scrub Hickory: A Florida Endemic. Palmetto 23(2):4-7, 13
- ↑ Menges, E. S. et al.. “Twenty Years of Vegetation Change in Five Long-unburned Florida Plant Communities”. Journal of Vegetation Science 4.3 (1993): 375–386.
- ↑ Deyrup, M.A. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
- ↑ Discoverlife.org [2]
- ↑ Abrahamson, Warren G., and Christy R. Abrahamson. “Nutritional Quality of Animal Dispersed Fruits in Florida Sandridge Habitats”. Bulletin of the Torrey Botanical Club 116.3 (1989): 215–228.
- ↑ [Fresh From Florida]Accessed: December 4, 2015