Difference between revisions of "Acalypha gracilens"
Krobertson (talk | contribs) |
Adam.Vansant (talk | contribs) |
||
| (29 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | Common names: | + | Common names: slender threeseed mercury; three-seeded mercury; shortstalk copperleaf |
==Taxonomic notes== | ==Taxonomic notes== | ||
| − | Synonyms: ''Acalypha virginica'' var. ''gracilens''<ref>Weakley, A.S. | + | Synonyms: ''Acalypha virginica'' var. ''gracilens''<ref name=Weakley>Weakley, A.S. 2020. Flora of the Southeastern United States. Edition of 20 October 2020. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> |
| + | |||
| + | Varieties: ''Acalypha gracilens'' var. ''fraseri''; ''Acalypha gracliens'' var. ''graclilens''<ref name=Weakley/> | ||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| − | + | ''Acalypha gracilens'' is an annual plant that grows up to 80cm tall with freely branched, densely pubescent stems growing from the taproots. The alternate, petiolate, pubescent-covered leaves are elliptic to elliptic-lanceolate in shape with a cuneate or rounded base and two lateral veins running parallel to the midrib from the base and exhibit crenate margins. <ref name="Radford">Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 664-665.</ref> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | The plant | + | The plant is monoecious (female and male flowers exist on the same plant). The female (pistillate) flowers do not have petals but do have 3-5 sepals and 3 locular ovaries, and there will be 3-5 pistillate flowers located near the base of the axillary spike of ''A. gracilens''. The male (staminate) flowers have 4 sepals and 8-16 stamens and interrupt and spike out from the female flowers. <ref name="Radford"/> |
| + | |||
| + | ''Acalypha gracilens'' begins flowering in June and will continue to flower late into the frost season. The seeds of this species are reddish to black in color, ovoid in shape, and very small at 1.2 – 1.8 mm long. <ref name="Radford"/> | ||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
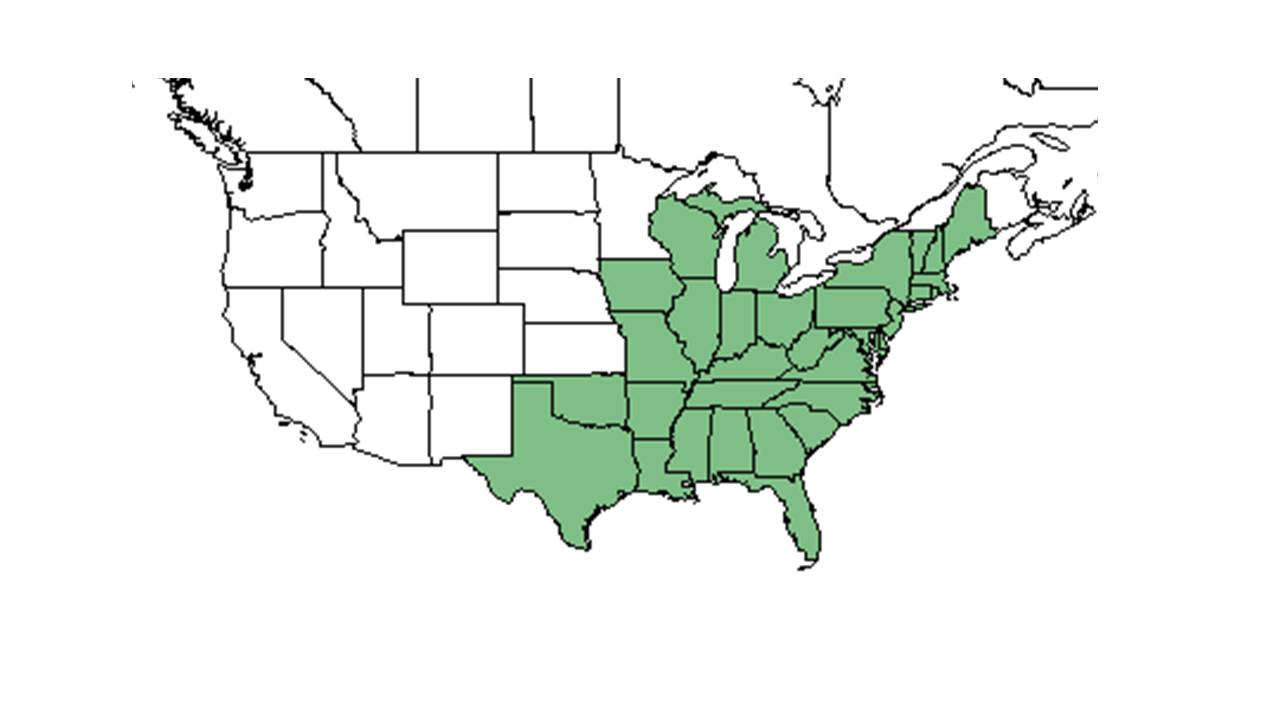
| − | + | ''A. gracilens'' is frequent in north, central, and west Florida, but can also found west to Texas and across much of the eastern half of the United States from the Great Lakes to Maine.<ref name="Radford"/> | |
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | In the | + | In the coastal plain of the southeast United States, ''A. gracilens'' thrives in frequently burned pine communities such as sandhills (Entisol soils), pine flatwoods (Spodosol soils), and upland pine communities (Ultisol soils), as well as floodplain forests (Alphasol soils).<ref>Heuberger, K. A. and F. E. Putz (2003) Fire in the suburbs: ecological impacts of prescribed fire in small remnants of longleaf pine (Pinus palustris) sandhill. Restoration Ecology 11: 72-81.</ref> The plant is also common throughout the Appalachian mountains.<ref name="Radford"/> |
| − | + | ''A. gracilens'' can also occur in areas with heavily disturbed soil, and is not picky about soil drainage types. ''Acalypha gracilens'' has been found to be an increaser in its short-term response to single mechanical soil disturbances as well as in its long-term response following cessation of repeated soil disturbance.<ref name=Dixon>Dixon, C. M., K. M. Robertson, A. M. Reid and M. T. Rother. 2024. Mechanical soil disturbance in a pine savanna has multiyear effects on plant species composition. Ecosphere 15(2):e4759.</ref> Its tolerance for light and shade is broad as it grows in open fully lit spaces to shaded field edges.<ref name="fsu">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Cecil R. Slaughter, R.A. Norris, R.F. Doren, and Robert K. Godfrey. States and Counties: Florida: Calhoun, Gadsden, Leon, Liberty, Wakulla, and St. Johns. Georgia: Thomas. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.</ref>. | |
| − | + | Additionally, it serves as indicator species for the Clayhill Longleaf Woodlands community type as described in Carr et al. (2010). <ref>Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.</ref> | |
| + | |||
| + | Associated species of ''A. gracilens'' include ''[[Liatris gracilis]]'', ''[[Liatris tenuifolia]]'', ''[[Polygonella gracilis]]'', ''Diodia teres'', ''Chrysopsis lanuginosa'', ''Rubus cuneifolis'', ''[[Hypericum gentianoides]]'', ''Trichostema dichostema'', ''Eupatorium compositifolium'', and others. <ref name="fsu"/>. | ||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| − | ''A. gracilens'' | + | ''A. gracilens'' flowers spring to fall through most of its range and all year in south Florida.<ref name="hall">Hall, David W. Illustrated Plants of Florida and the Coastal Plain: based on the collections of Leland and Lucy Baltzell. 1993. A Maupin House Book. Gainesville. 100. Print.</ref><ref>Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 27 FEB 2019</ref> On the Wade Tract in Thomas County of southern Georgia it has been observed to flower mostly in the late fall and early spring.<ref name=Platt>Platt, W.J. 2019. Personal observation.</ref> |
===Seed dispersal=== | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
| Line 47: | Line 53: | ||
===Seed bank and germination=== | ===Seed bank and germination=== | ||
| − | Observations | + | Observations ''A. graciliens'' on the Wade Tract (Thomas County, Georgia) longleaf pine savanna indicate that seeds germinate in the summer, post-fire in burned patches, and at similar times in unburned patches. Seeds mature and rapidly are dispersed in the early fall. Plants then become senescent and do not survive the winter. Areas of the Wade Tract with populations of ''A. graciliens'' do not always have plants present every year, suggesting that there is a seed bank with at least short-term dormancy.<ref name=Platt/> |
| − | < | + | |
| + | ===Fire ecology=== | ||
| + | Populations of ''Acalypha gracilens'' has been known to persist through repeated annual burns.<ref>Robertson, K.M. Unpublished data collected from Pebble Hill Fire Plots, Pebble Hill Plantation, Thomasville, Georgia.</ref><ref>Glitzenstein, J. S., D. R. Streng, R. E. Masters, K. M. Robertson and S. M. Hermann 2012. Fire-frequency effects on vegetation in north Florida pinelands: Another look at the long-term Stoddard Fire Research Plots at Tall Timbers Research Station. Forest Ecology and Management 264: 197-209.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
<!--===Pollination===--> | <!--===Pollination===--> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Herbivory and toxicology=== |
| − | ''A. gracilens'' is used by seed-eating songbirds and northern bobwhite quail, and in the | + | ''A. gracilens'' is used by seed-eating songbirds and northern bobwhite quail, and in the southeast is highly used by white-tailed deer as a forage plant due to their higher abundance in disturbed sites.<ref name= "Miller"> Miller, J. H. and K. V. Miller (1999). Forest Plants of the Southeast and Their Wildlife Uses, Southern Weed Science Society.</ref> This plant has been observed as a host for the plant bug ''Coridromius chenopoderis'' (family Miridae), an invasive insect originating from Australia.<ref>Discoverlife.org [https://www.discoverlife.org/20/q?search=Bidens+albaDiscoverlife.org|Discoverlife.org]</ref> |
| + | |||
<!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | ||
Latest revision as of 17:52, 10 July 2024
| Acalypha gracilens A. Gray | |
|---|---|
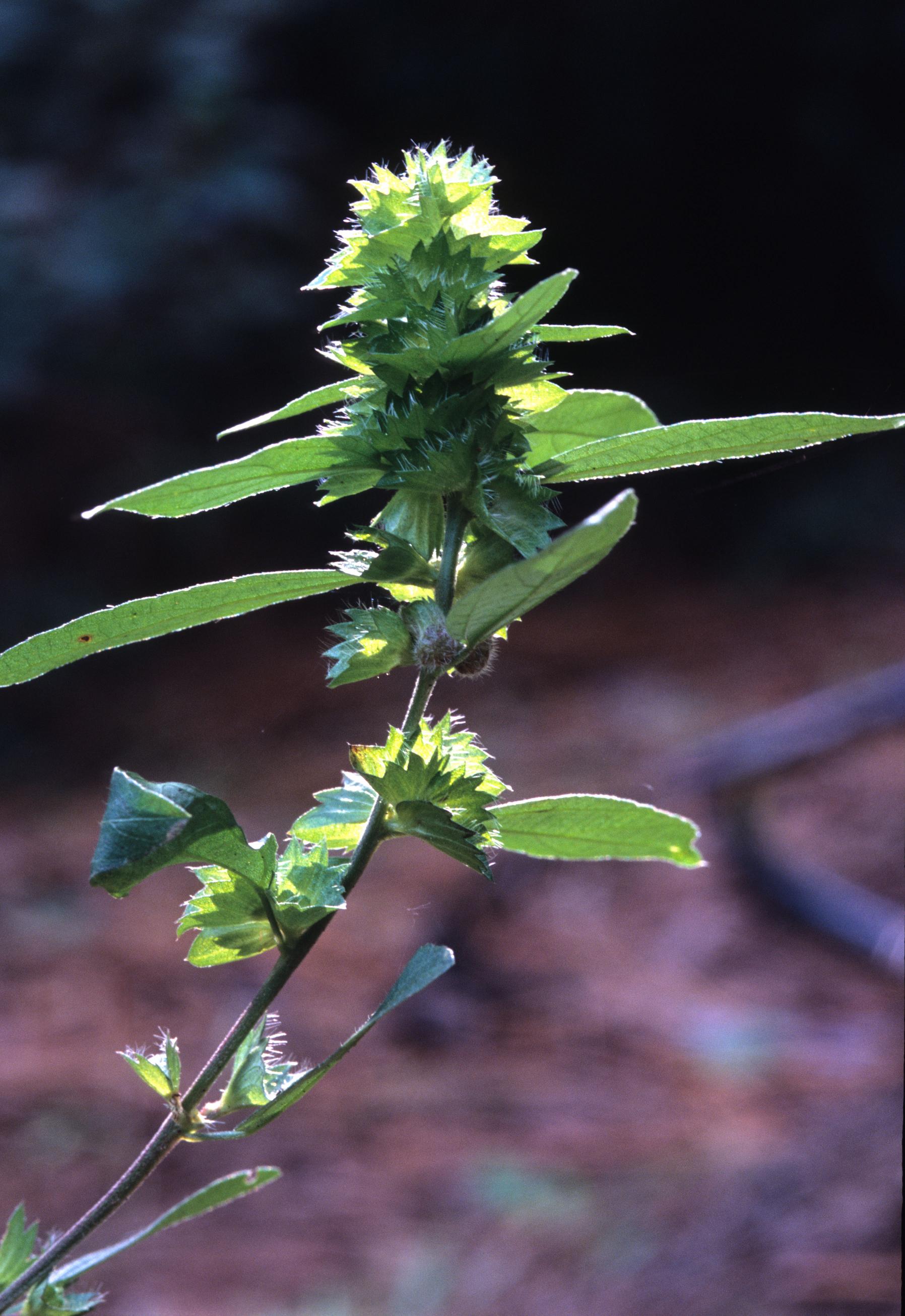

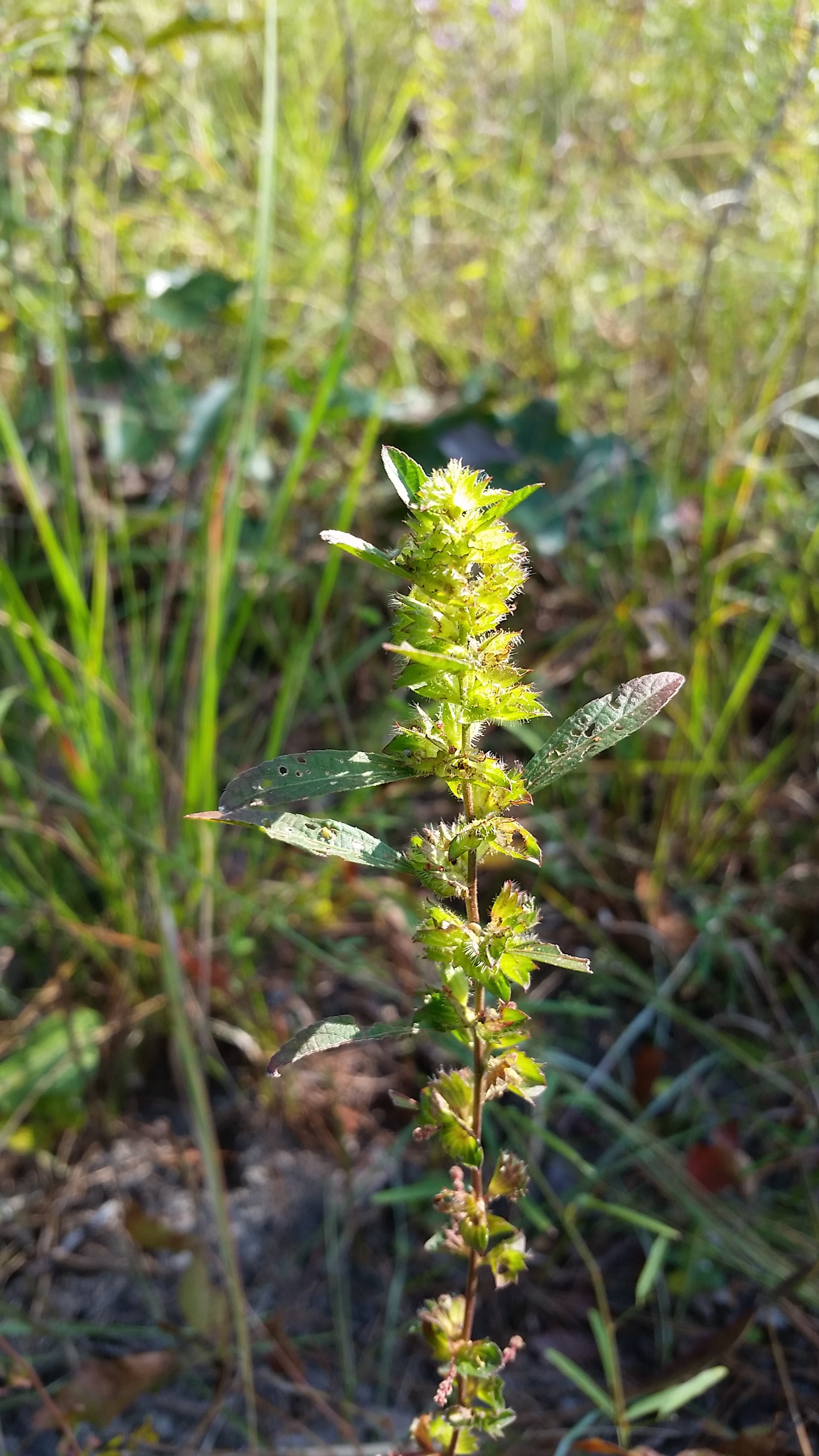
| |
| Photo was taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Euphorbiales |
| Family: | Euphorbiaceae |
| Genus: | Acalypha |
| Species: | A. gracilens |
| Binomial name | |
| Acalypha gracilens A. Gray | |
| |
| Natural range of Acalypha gracilens from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: slender threeseed mercury; three-seeded mercury; shortstalk copperleaf
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Acalypha virginica var. gracilens[1]
Varieties: Acalypha gracilens var. fraseri; Acalypha gracliens var. graclilens[1]
Description
Acalypha gracilens is an annual plant that grows up to 80cm tall with freely branched, densely pubescent stems growing from the taproots. The alternate, petiolate, pubescent-covered leaves are elliptic to elliptic-lanceolate in shape with a cuneate or rounded base and two lateral veins running parallel to the midrib from the base and exhibit crenate margins. [2]
The plant is monoecious (female and male flowers exist on the same plant). The female (pistillate) flowers do not have petals but do have 3-5 sepals and 3 locular ovaries, and there will be 3-5 pistillate flowers located near the base of the axillary spike of A. gracilens. The male (staminate) flowers have 4 sepals and 8-16 stamens and interrupt and spike out from the female flowers. [2]
Acalypha gracilens begins flowering in June and will continue to flower late into the frost season. The seeds of this species are reddish to black in color, ovoid in shape, and very small at 1.2 – 1.8 mm long. [2]
Distribution
A. gracilens is frequent in north, central, and west Florida, but can also found west to Texas and across much of the eastern half of the United States from the Great Lakes to Maine.[2]
Ecology
Habitat
In the coastal plain of the southeast United States, A. gracilens thrives in frequently burned pine communities such as sandhills (Entisol soils), pine flatwoods (Spodosol soils), and upland pine communities (Ultisol soils), as well as floodplain forests (Alphasol soils).[3] The plant is also common throughout the Appalachian mountains.[2]
A. gracilens can also occur in areas with heavily disturbed soil, and is not picky about soil drainage types. Acalypha gracilens has been found to be an increaser in its short-term response to single mechanical soil disturbances as well as in its long-term response following cessation of repeated soil disturbance.[4] Its tolerance for light and shade is broad as it grows in open fully lit spaces to shaded field edges.[5].
Additionally, it serves as indicator species for the Clayhill Longleaf Woodlands community type as described in Carr et al. (2010). [6]
Associated species of A. gracilens include Liatris gracilis, Liatris tenuifolia, Polygonella gracilis, Diodia teres, Chrysopsis lanuginosa, Rubus cuneifolis, Hypericum gentianoides, Trichostema dichostema, Eupatorium compositifolium, and others. [5].
Phenology
A. gracilens flowers spring to fall through most of its range and all year in south Florida.[7][8] On the Wade Tract in Thomas County of southern Georgia it has been observed to flower mostly in the late fall and early spring.[9]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by ants and/or explosive dehiscence.[10]
Seed bank and germination
Observations A. graciliens on the Wade Tract (Thomas County, Georgia) longleaf pine savanna indicate that seeds germinate in the summer, post-fire in burned patches, and at similar times in unburned patches. Seeds mature and rapidly are dispersed in the early fall. Plants then become senescent and do not survive the winter. Areas of the Wade Tract with populations of A. graciliens do not always have plants present every year, suggesting that there is a seed bank with at least short-term dormancy.[9]
Fire ecology
Populations of Acalypha gracilens has been known to persist through repeated annual burns.[11][12]
Herbivory and toxicology
A. gracilens is used by seed-eating songbirds and northern bobwhite quail, and in the southeast is highly used by white-tailed deer as a forage plant due to their higher abundance in disturbed sites.[13] This plant has been observed as a host for the plant bug Coridromius chenopoderis (family Miridae), an invasive insect originating from Australia.[14]
Conservation, cultivation and restoration
Cultural use
Photo gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Weakley, A.S. 2020. Flora of the Southeastern United States. Edition of 20 October 2020. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 664-665.
- ↑ Heuberger, K. A. and F. E. Putz (2003) Fire in the suburbs: ecological impacts of prescribed fire in small remnants of longleaf pine (Pinus palustris) sandhill. Restoration Ecology 11: 72-81.
- ↑ Dixon, C. M., K. M. Robertson, A. M. Reid and M. T. Rother. 2024. Mechanical soil disturbance in a pine savanna has multiyear effects on plant species composition. Ecosphere 15(2):e4759.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Cecil R. Slaughter, R.A. Norris, R.F. Doren, and Robert K. Godfrey. States and Counties: Florida: Calhoun, Gadsden, Leon, Liberty, Wakulla, and St. Johns. Georgia: Thomas. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.
- ↑ Hall, David W. Illustrated Plants of Florida and the Coastal Plain: based on the collections of Leland and Lucy Baltzell. 1993. A Maupin House Book. Gainesville. 100. Print.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 27 FEB 2019
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Platt, W.J. 2019. Personal observation.
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.
- ↑ Robertson, K.M. Unpublished data collected from Pebble Hill Fire Plots, Pebble Hill Plantation, Thomasville, Georgia.
- ↑ Glitzenstein, J. S., D. R. Streng, R. E. Masters, K. M. Robertson and S. M. Hermann 2012. Fire-frequency effects on vegetation in north Florida pinelands: Another look at the long-term Stoddard Fire Research Plots at Tall Timbers Research Station. Forest Ecology and Management 264: 197-209.
- ↑ Miller, J. H. and K. V. Miller (1999). Forest Plants of the Southeast and Their Wildlife Uses, Southern Weed Science Society.
- ↑ Discoverlife.org [1]
