Difference between revisions of "Quercus chapmanii"
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) |
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) (→References and notes) |
||
| Line 53: | Line 53: | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA. | Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: Collectors: States and Counties: Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy. | ||
Revision as of 16:41, 13 November 2015
| Quercus chapmanii | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Fagales |
| Family: | Fagaceae |
| Genus: | Quercus |
| Species: | Q. chapmanii |
| Binomial name | |
| Quercus chapmanii Sarg. | |
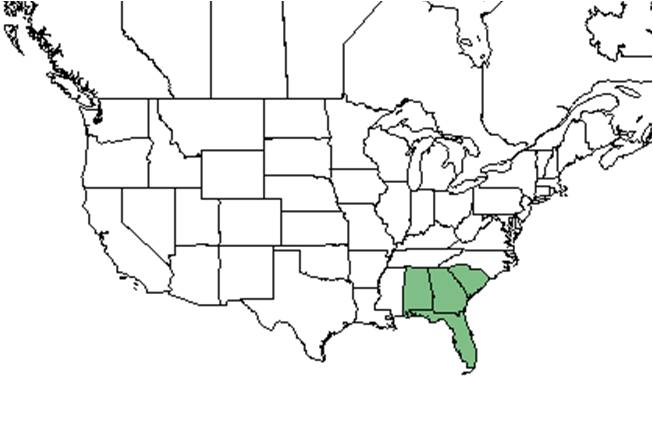
| |
| Natural range of Quercus chapmanii from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Chapman's oak
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Description
A description of Quercus chapmanii is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain in Florida, Q. chapmanii has occurred in a scrub thicket between dunes and a sound; sand pine scrubs; island sand ridges; sand barrens; high pine scrubs; ravines along creeks; scrub oak-wiregrass sand ridges; evergreen oak scrubs; live oak hammocks; sand pine/mixed oak scrub; coastal scrubs; dune scrubs; pine flatwoods; pine-scrub oak-palmetto communities; and oak-hickory-magnolia coastal hammocks. It has been observed in disturbed habitats such as along roadsides, a sandhill scrub next to powerlines, and a stand of cleared longleaf pine that is now a thick stand of mixed oaks (FSU Herbarium). Soil types include white sand, loamy sand and sandy loam (FSU Herbarium). Associated species include Quercus myrtifolia, Q. incana, Q. laevis, Q. geminata, Q. hemisphaerica, Q. laurifolia, Q. nigra, Q. minima, Ilex glabra, Serenoa repens, Sabal minor, Pinus clausa, Carya, and Vitis rotundifolia (FSU Herbarium).
Phenology
Q. chapmanii has been recorded flowering March through July and fruiting March through December (FSU Herbarium).
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
Pollination
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of Quercus chapmanii at Archbold Biological Station (Deyrup 2015):
Andrenidae: Andrena dimorpha
Apidae: Apis mellifera
Colletidae: Colletes brimleyi
Halictidae: Agapostemon splendens, Augochlora pura, Augochlorella aurata, Augochloropsis metallica, Lasioglossum miniatulus
Use by animals
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: Collectors: States and Counties: Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.