Difference between revisions of "Pluchea foetida"
(Created page with "{{italic title}} <!-- Get the taxonomy information from the NRCS Plants database --> {{taxobox | name = Pluchea foetida | image = Pluchea foetida_Gil.jpg | image_caption = Pho...") |
|||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
===Seed dispersal=== | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
===Seed bank and germination=== | ===Seed bank and germination=== | ||
| + | Several short-lived perennial forbs also have a seed bank persistent for at least several years (Platt et al 2006). | ||
===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
===Pollination=== | ===Pollination=== | ||
| Line 31: | Line 32: | ||
==Conservation and Management== | ==Conservation and Management== | ||
==Cultivation and restoration== | ==Cultivation and restoration== | ||
| + | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
| − | + | Platt, W. J., S. M. Carr, et al. (2006). "Pine savanna overstorey influences on ground-cover biodiversity." Applied Vegetation Science 9: 37-50. | |
Revision as of 15:55, 11 June 2015
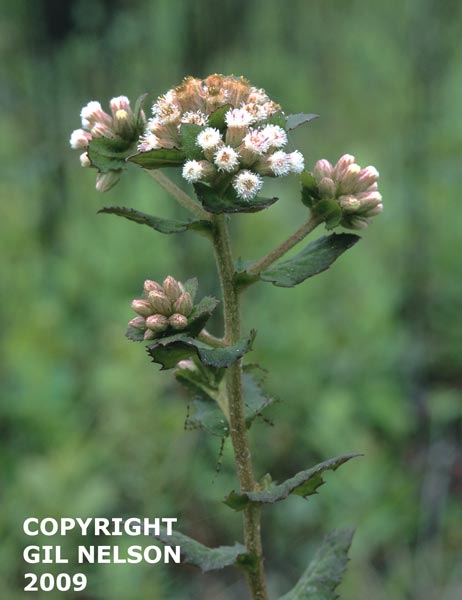
| Pluchea foetida | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae ⁄ Compositae |
| Genus: | Pluchea |
| Species: | P. foetida |
| Binomial name | |
| Pluchea foetida (L.) DC. | |
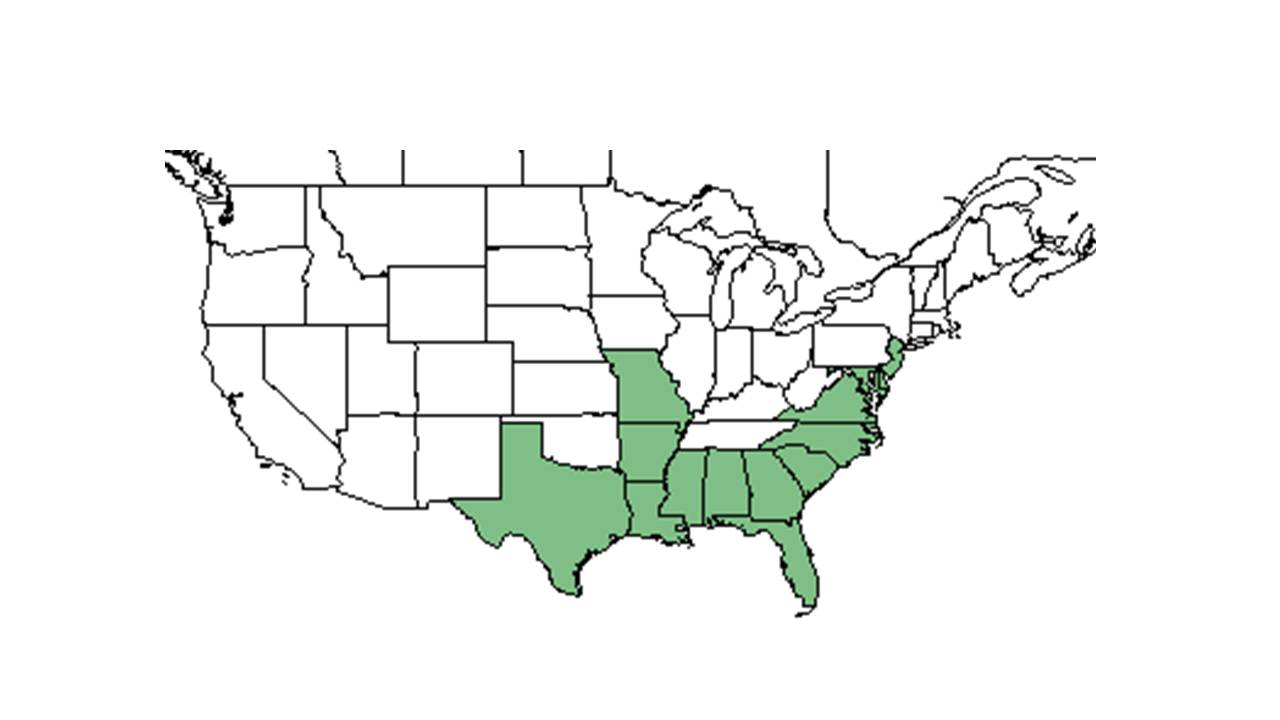
| |
| Natural range of Pluchea foetida from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Description
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
Phenology
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
Several short-lived perennial forbs also have a seed bank persistent for at least several years (Platt et al 2006).
Fire ecology
Pollination
Use by animals
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Platt, W. J., S. M. Carr, et al. (2006). "Pine savanna overstorey influences on ground-cover biodiversity." Applied Vegetation Science 9: 37-50.