Difference between revisions of "Nuttallanthus floridanus"
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) (→Description) |
HaleighJoM (talk | contribs) (→Ecology) |
||
| (30 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
{{taxobox | {{taxobox | ||
| name = Nuttallanthus floridanus | | name = Nuttallanthus floridanus | ||
| − | | image = | + | | image = Nutt_flor-Plant.jpg |
| − | | image_caption = | + | | image_caption = Photo by John R. Gwaltney, [http://www.southeasternflora.com/index.asp Southeastern Flora.com] |
| regnum = Plantae | | regnum = Plantae | ||
| divisio = Tracheophyta - Vascular plants | | divisio = Tracheophyta - Vascular plants | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | Common name: | + | Common names: Apalachicola toadflax; Florida toadflax<ref name="weakley">Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> |
| + | ==Taxonomic notes== | ||
| + | Synonym: ''Linaria floridana'' Chapman.<ref name="weakley">Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> | ||
| − | = | + | Varieties: none.<ref name="weakley">Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> |
| − | |||
| − | The genus ''Nuttallanthus'' was separated from ''Linaria'' in 1988 by Sutton due to the floral and seed characteristics | + | The genus ''Nuttallanthus'' was separated from ''Linaria'' in 1988 by Sutton due to the floral and seed characteristics. <ref name="Phillip and Elisens 2006">Phillip, T. C. and W. J. Elisens (2006). "Genetic Variation and Reproductive System among North American Species of Nuttallanthus (Plantaginaceae)." American Journal of Botany 93(4): 582-591.</ref> |
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
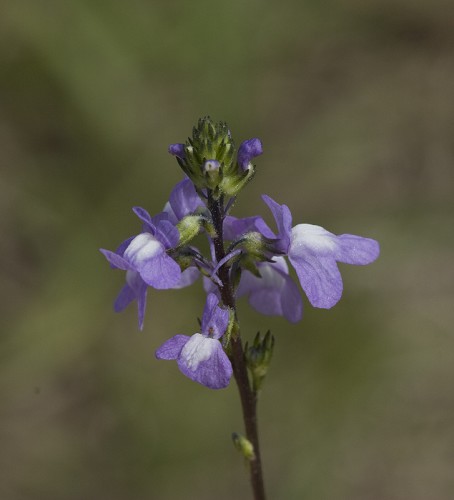
| − | This species is an annual herb that produces bluish, bilabiate, and spurred flowers that attract a variety of insects | + | This species is an annual herb that produces bluish, bilabiate, and spurred flowers that attract a variety of insects.<ref name="Phillip and Elisens 2006"/> |
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
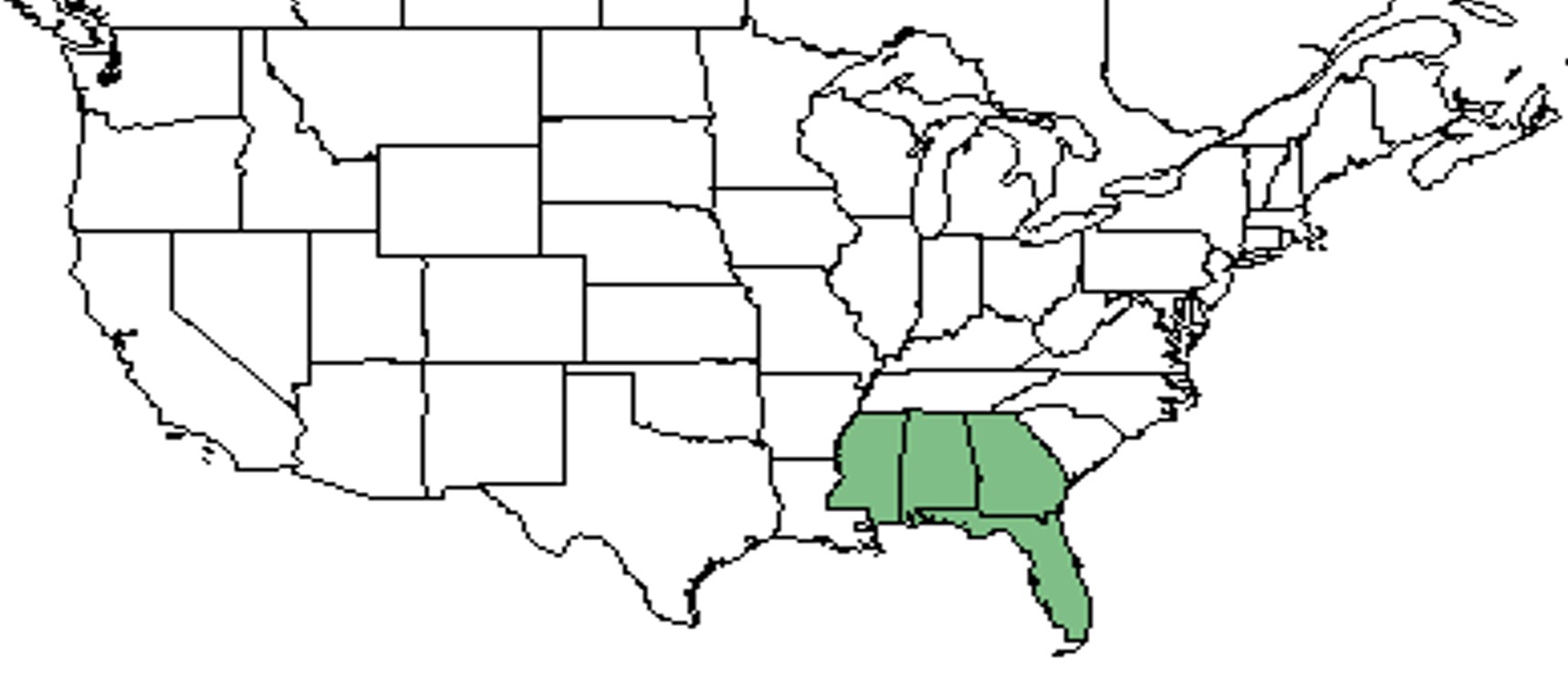
| + | ''N. floridanus'' is a narrowly distributed species occurring in the Atlantic and Gulf coastal plain in Alabama, Florida, Georgia, and Mississippi.<ref name="Phillip and Elisens 2006"/> | ||
| + | |||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| + | Habitats include sparsely vegetated white sands along lakes, scrubs, sand dunes, and dry sandhills.<ref name="wild">[[http://www.wildflphoto.com/species.php?k=p&id=210]]Accessed: January 20, 2016</ref> It has been observed growing in disturbed areas such as roadsides. Associated species include ''Krigia virginica'' and ''Crocanthemum''.<ref name="FSU Herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: February 2016. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Robert K. Godfrey, R. Kral, and Helen Roth. States and Counties: Florida: Franklin, Gadsden, Leon, Marion, and Wakulla.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| + | This species flowers and fruits in March.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | It is an autogamous species and produces both cleistogamous and chasmogamous flowers. The cleistogamous flowers are produced early and late in the life cycle and the chasmogamous flowers are self-pollinated before anthesis and attract insects after anthesis.<ref name="Phillip and Elisens 2006"/> | ||
| + | |||
===Seed dispersal=== | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
| + | The seeds are small and lack obvious dispersal mechanisms.<ref name="Carrington 1997">Carrington, M. E. (1997). "Soil Seed Bank Structure and Composition in Florida Sand Pine Scrub." American Midland Naturalist 137(1): 39-47.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
===Seed bank and germination=== | ===Seed bank and germination=== | ||
| − | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | + | Carrington (1997) found that germination depends on seeds accumulated in a persistent seed bank to maintain populations between disturbances. |
| + | <!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
===Pollination=== | ===Pollination=== | ||
| − | === | + | Pollen is required for fruit and seed development. It is completely cross-incompatible with other ''Nuttallanthus'' species due to the amount of genetic divergence between species and isolation.<ref name="Phillip and Elisens 2006"/> The following Hymenoptera species were observed visiting flowers of ''Linaria floridana'' at the Archbold Biological Station:<ref>Deyrup, M.A. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowering plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.</ref> |
| − | ===Diseases and parasites=== | + | |
| − | ==Conservation and | + | Sweat bees from the family Halictidae: ''Lasioglossum nymphalis'', ''Lasioglossum pectoralis'', ''Lasioglossum puteulanum'' |
| − | == | + | |
| + | Leafcutting bees from the family Megachilidae: ''Anthidiellum notatum rufomaculatum'', ''Megachile brevis pseudobrevis'', ''Megachile georgica'', ''Osmia sandhouse'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Thread-waisted wasps from the family Sphecidae: ''Tachysphex similis'' | ||
| + | <!--===Herbivory and toxicology===--> | ||
| + | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Cultural use== | ||
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
| + | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
| + | File: Nutt_flor.jpg | <center> ''Nuttallanthus floridanus'' flowers <p> Photo by John R. Gwaltney, [http://www.southeasternflora.com/index.asp Southeastern Flora.com] | ||
| + | File:Nutta_floridanus_J-Gwaltney-SEFlora-Flower8727.jpg | <center> ''Nuttallanthus floridanus'' flowers <p> Photo by John R. Gwaltney, [http://www.southeasternflora.com/index.asp Southeastern Flora.com] </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
Latest revision as of 15:54, 14 July 2022
| Nuttallanthus floridanus | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by John R. Gwaltney, Southeastern Flora.com | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Tracheophyta - Vascular plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Lamiales |
| Family: | Plantaginaceae |
| Genus: | Nuttallanthus |
| Species: | N. floridanus |
| Binomial name | |
| Nuttallanthus floridanus (Chapm.) D.A. Sutton | |
| |
| Natural range of Nuttallanthus floridanus from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Apalachicola toadflax; Florida toadflax[1]
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonym: Linaria floridana Chapman.[1]
Varieties: none.[1]
The genus Nuttallanthus was separated from Linaria in 1988 by Sutton due to the floral and seed characteristics. [2]
Description
This species is an annual herb that produces bluish, bilabiate, and spurred flowers that attract a variety of insects.[2]
Distribution
N. floridanus is a narrowly distributed species occurring in the Atlantic and Gulf coastal plain in Alabama, Florida, Georgia, and Mississippi.[2]
Ecology
Habitat
Habitats include sparsely vegetated white sands along lakes, scrubs, sand dunes, and dry sandhills.[3] It has been observed growing in disturbed areas such as roadsides. Associated species include Krigia virginica and Crocanthemum.[4]
Phenology
This species flowers and fruits in March.[4]
It is an autogamous species and produces both cleistogamous and chasmogamous flowers. The cleistogamous flowers are produced early and late in the life cycle and the chasmogamous flowers are self-pollinated before anthesis and attract insects after anthesis.[2]
Seed dispersal
The seeds are small and lack obvious dispersal mechanisms.[5]
Seed bank and germination
Carrington (1997) found that germination depends on seeds accumulated in a persistent seed bank to maintain populations between disturbances.
Pollination
Pollen is required for fruit and seed development. It is completely cross-incompatible with other Nuttallanthus species due to the amount of genetic divergence between species and isolation.[2] The following Hymenoptera species were observed visiting flowers of Linaria floridana at the Archbold Biological Station:[6]
Sweat bees from the family Halictidae: Lasioglossum nymphalis, Lasioglossum pectoralis, Lasioglossum puteulanum
Leafcutting bees from the family Megachilidae: Anthidiellum notatum rufomaculatum, Megachile brevis pseudobrevis, Megachile georgica, Osmia sandhouse
Thread-waisted wasps from the family Sphecidae: Tachysphex similis
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
Nuttallanthus floridanus flowers Photo by John R. Gwaltney, Southeastern Flora.com
Nuttallanthus floridanus flowers Photo by John R. Gwaltney, Southeastern Flora.com
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Phillip, T. C. and W. J. Elisens (2006). "Genetic Variation and Reproductive System among North American Species of Nuttallanthus (Plantaginaceae)." American Journal of Botany 93(4): 582-591.
- ↑ [[1]]Accessed: January 20, 2016
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: February 2016. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Robert K. Godfrey, R. Kral, and Helen Roth. States and Counties: Florida: Franklin, Gadsden, Leon, Marion, and Wakulla.
- ↑ Carrington, M. E. (1997). "Soil Seed Bank Structure and Composition in Florida Sand Pine Scrub." American Midland Naturalist 137(1): 39-47.
- ↑ Deyrup, M.A. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowering plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.

