Difference between revisions of "Liatris tenuifolia"
(→Ecology) |
|||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
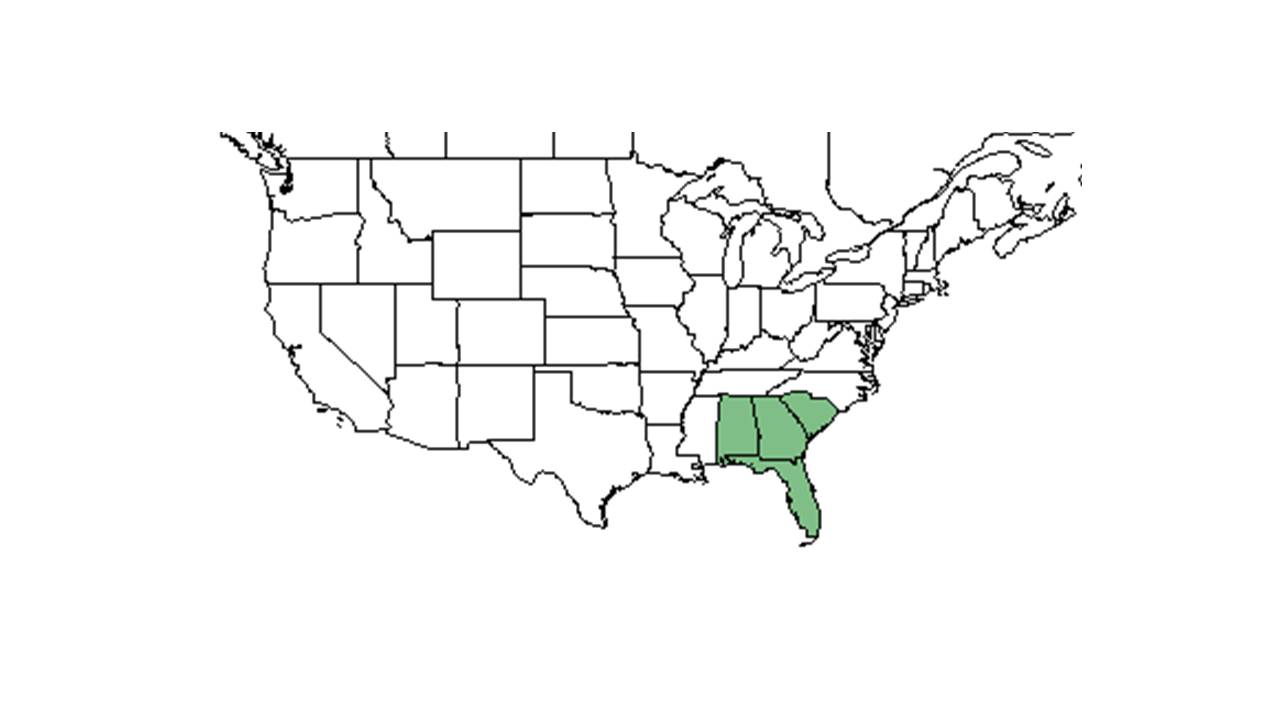
| range_map_caption = Natural range of ''Liatris tenuifolia'' from USDA NRCS [http://www.plants.usda.gov Plants Database]. | | range_map_caption = Natural range of ''Liatris tenuifolia'' from USDA NRCS [http://www.plants.usda.gov Plants Database]. | ||
}} | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Common name: shortleaf blazing star | ||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| − | |||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
| Line 34: | Line 35: | ||
===Pollination=== | ===Pollination=== | ||
| − | + | The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of ''Liatris tenuifolia'' at Archbold Biological Station (Deyrup 2015): | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Apidae: ''Apis mellifera, Bombus impatiens, B. pennsylvanicus'' | |
| − | + | Halictidae: ''Agapostemon splendens, Augochlorella aurata, Augochloropsis sumptuosa'' | |
| − | Megachilidae: Megachile petulans | + | Megachilidae: ''Coelioxys mexicana, C. sayi, Megachile albitarsis, M. brevis pseudobrevis, M. brimleyi, M. petulans, M. texana'' |
| − | + | Sphecidae: ''Ammophila procera'' | |
| − | |||
===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
| Line 73: | Line 55: | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
| + | Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA. | ||
Revision as of 10:35, 10 August 2015
| Liatris tenuifolia | |
|---|---|

| |
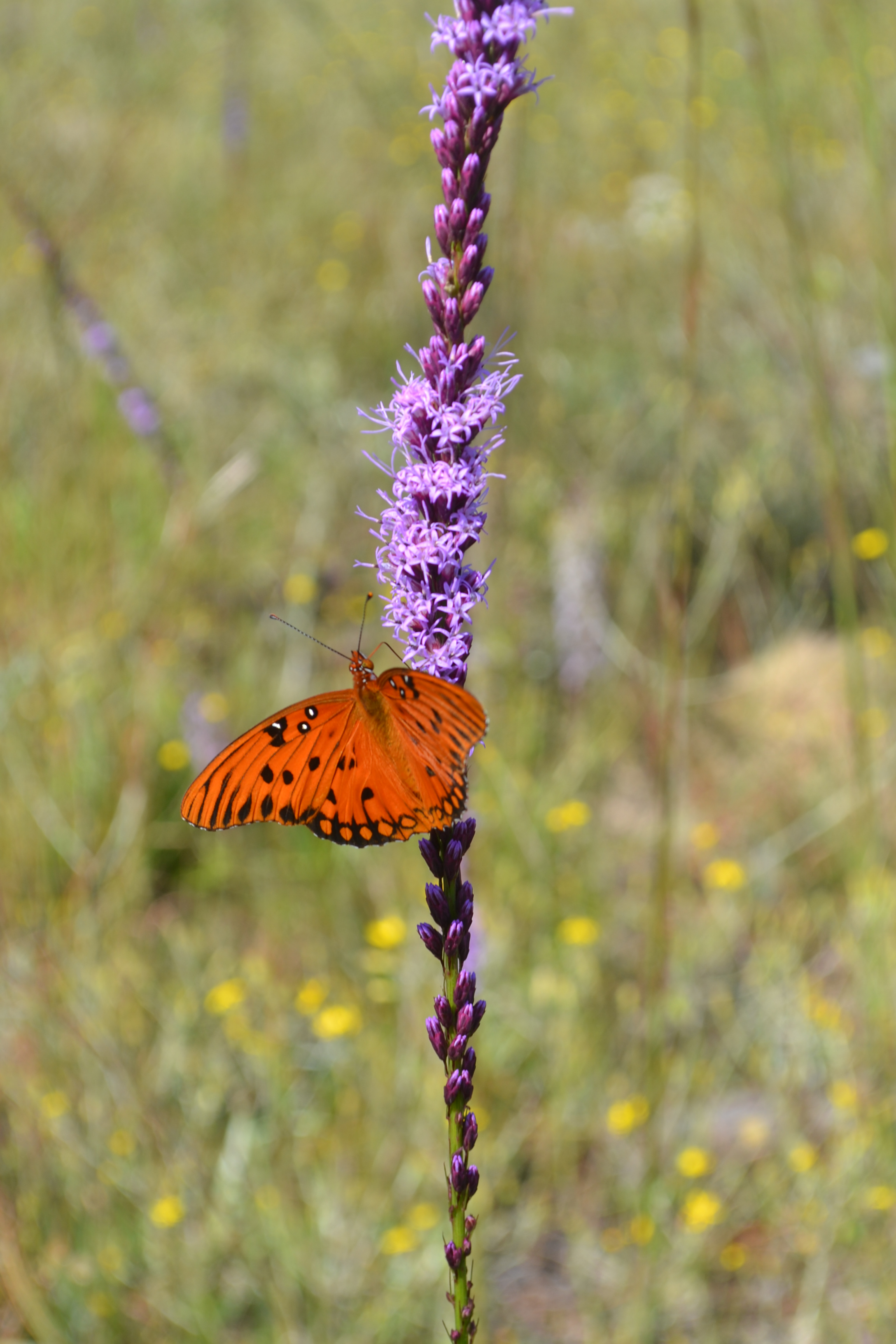
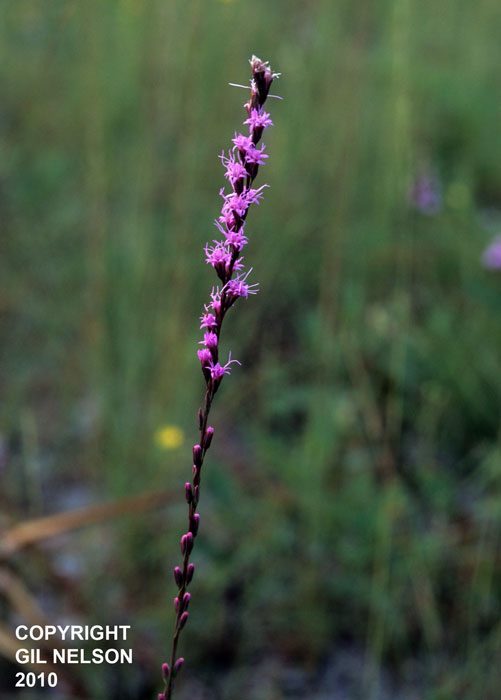
| Photo taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae ⁄ Compositae |
| Genus: | Liatris |
| Species: | L. tenuifolia |
| Binomial name | |
| Liatris tenuifolia Nutt. | |
| |
| Natural range of Liatris tenuifolia from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: shortleaf blazing star
Contents
Description
Distribution
Ecology
L. tenuifolia experienced increased growth and flowering in burned sandhill sites located in south-central Florida.[1] [2] Also found in burned and unburned patches of degraded longleaf pine sandhill.[3]
Habitat
Availability of all soil inorganic nutrients examined (Ca, K, Mg, and P) was low, as were total nitrogen, soil organic matter, and pH.[4]
Phenology
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
Fire improves seedling recruitment.[5]
Fire ecology
It responds positively to conditions following the burn by increased vegetative growth and flowering. It typically blooms within a year or so following fire.[4]
Pollination
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of Liatris tenuifolia at Archbold Biological Station (Deyrup 2015):
Apidae: Apis mellifera, Bombus impatiens, B. pennsylvanicus
Halictidae: Agapostemon splendens, Augochlorella aurata, Augochloropsis sumptuosa
Megachilidae: Coelioxys mexicana, C. sayi, Megachile albitarsis, M. brevis pseudobrevis, M. brimleyi, M. petulans, M. texana
Sphecidae: Ammophila procera
Use by animals
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
- ↑ Anderson, R. C. and E. S. Menges (1997). "Effects of fire on sandhill herbs: nutrients, mycorrhizae, and biomass allocation." American Journal of Botany 84: 938-948.
- ↑ Reinhart, K. O. and E. S. Menges (2004). "Effects of re-introducing fire to a central Florida sandhill community." Applied Vegetation Science 7: 141-150.
- ↑ Heuberger, K. A. and F. E. Putz (2003). "Fire in the suburbs: ecological impacts of prescribed fire in small remnants of longleaf pine (Pinus palustris) sandhill." Restoration Ecology 11: 72-81.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Anderson, R. C. and E. S. Menges (1997). "Effects of fire on sandhill herbs: nutrients, mycorrhizae, and biomass allocation." American Journal of Botany 84: 938-948.
- ↑ Whelan, W.A. 1970. Patterns of recruitment to plant populations after fire in western Australia and Florida. Proceedings of the Ecological Society of Australia 14:169-178.
