Difference between revisions of "Lespedeza violacea"
| (9 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{italic title}} | {{italic title}} | ||
| − | Common name: violet lespedeza <ref name= "USDA Plant Database"/>, wand lespedeza <ref name= | + | Common name: violet lespedeza<ref name= "USDA Plant Database"/>, wand lespedeza<ref name=weakley>Weakley, A.S. 2020. Flora of the Southeastern United States. Edition of 20 October 2020. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> |
<!-- Get the taxonomy information from the NRCS Plants database --> | <!-- Get the taxonomy information from the NRCS Plants database --> | ||
{{taxobox | {{taxobox | ||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
}} | }} | ||
==Taxonomic Notes== | ==Taxonomic Notes== | ||
| − | Synonyms: ''L. intermedia'' (S. Watson) Britton | + | Synonyms: ''L. intermedia'' (S. Watson) Britton<ref name=weakley/> |
| − | Varieties: | + | Varieties: none<ref name=weakley/> |
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| − | ''L. violacea'' is a perennial forb/herb of the ''Fabaceae'' family native to North America and Canada. <ref name= "USDA Plant Database"> USDA Plant Database [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=LEVI6 https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=LEVI6] </ref> | + | ''L. violacea'' is a perennial forb/herb of the ''Fabaceae'' family native to North America and Canada.<ref name= "USDA Plant Database"> USDA Plant Database [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=LEVI6 https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=LEVI6] </ref> |
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
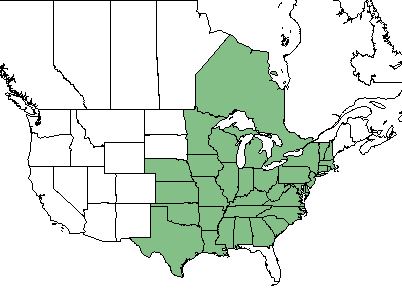
| − | ''L. violacea'' is found in the eastern half of the United States excluding Florida, as well as the Ontario region of Canada. <ref name= "USDA Plant Database"/> | + | ''L. violacea'' is found in the eastern half of the United States excluding Florida, as well as the Ontario region of Canada.<ref name= "USDA Plant Database"/> |
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | ''L. violacea'' proliferates in woodlands and woodland borders <ref name= | + | ''L. violacea'' proliferates in woodlands and woodland borders<ref name=weakley/>, and predominantly in lowland sites.<ref name "Towne 2008"> Towne, E. G. and K. E. Kemp (2008). "Long-term response patterns of tallgrass prairie to frequent summer burning." Rangeland Ecology & Management 61: 509-520. </ref> Specimens have been collected from limestone outcrop, second growth of black oak area, cedar bluff woods, sandy soil of upland oak-hickory forest, open oak woods, sandstone quarry, shaded roadside, river bank, old field scattered with trees, bluff above floodplain, burned over pine region with clay soil, and bottomland hardwood.<ref name = "FSU herbarium"> URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: R.K. Godfrey, R. komarek, Robert Thorne, G.W. Parmalee, Andre Clewell, Paul Redfearn, H. A. Wahl, Norlan Henderson, George Jones, Norlan Henderson, Sidney McDaniel, Dick Houk, V. Muehlenbach, Sidney McDaniel, Norman E. Hill. States and counties: Florida (Leon) Georgia (Grady) Virginia (Giles) Michigan (Jackson) Indiana (Brown, Monroe, Martin) Missouri (Johnson, Osage, Platte, Jackson, Barton, St. Clair) Mississippi (Chickasaw, Tallahatchie, Holmes, Madison) Alabama (Cleburne, Calhoun)</ref> |
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| − | ''L. violacea'' has been observed to flower | + | ''L. violacea'' has been observed to flower from July through September and fruit from August to November.<ref name=weakley/> |
<!--===Seed dispersal===--> | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> | ||
<!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
<!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | <!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
<!--===Pollination===--> | <!--===Pollination===--> | ||
| − | <!--=== | + | <!--===Herbivory and toxicology===--> |
| − | <!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | + | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> |
| − | ==Conservation and | + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== |
| − | ''L. violacea'' is listed as rare by the New York Department of Environmental Conservation Division of Land and Forests, and as threatened by the Vermont Department of Fish and Wildlife Nongame and Natural Heritage Program. <ref name= "USDA Plant Database"/> | + | ''L. violacea'' is listed as rare by the New York Department of Environmental Conservation Division of Land and Forests, and as threatened by the Vermont Department of Fish and Wildlife Nongame and Natural Heritage Program.<ref name= "USDA Plant Database"/> |
| − | + | ==Cultural use== | |
| − | == | ||
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
<gallery widths=180px> | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
Latest revision as of 11:08, 12 June 2023
Common name: violet lespedeza[1], wand lespedeza[2]
| Lespedeza violacea | |
|---|---|
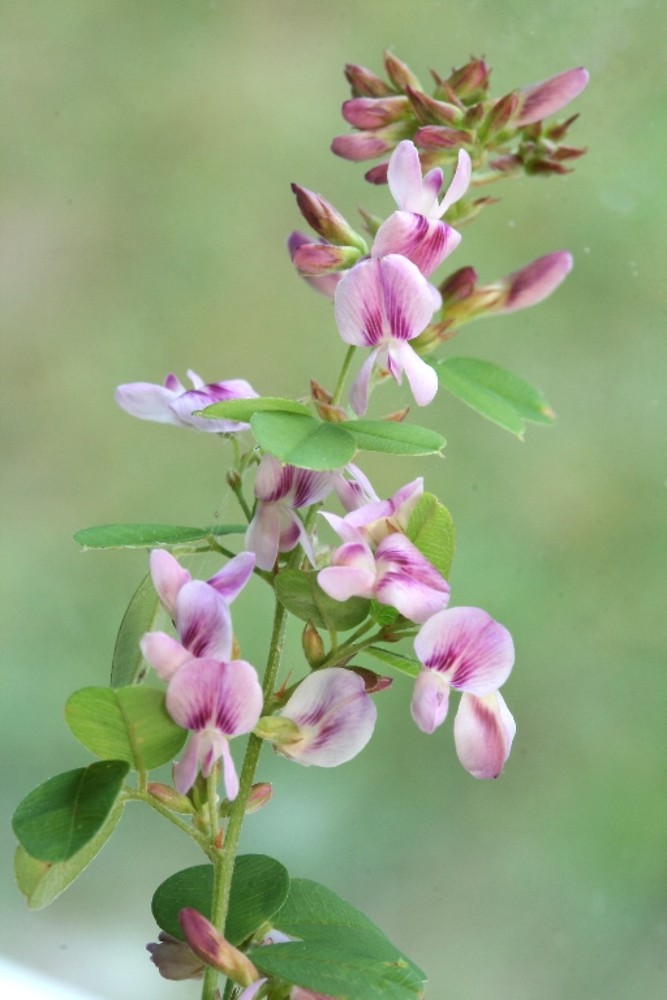

| |
| Photo by Arieh Tal of Botphoto.com | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae |
| Genus: | Lespedeza |
| Species: | L. violacea |
| Binomial name | |
| Lespedeza violacea L. | |
| |
| Natural range of Lespedeza violacea from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: L. intermedia (S. Watson) Britton[2]
Varieties: none[2]
Description
L. violacea is a perennial forb/herb of the Fabaceae family native to North America and Canada.[1]
Distribution
L. violacea is found in the eastern half of the United States excluding Florida, as well as the Ontario region of Canada.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
L. violacea proliferates in woodlands and woodland borders[2], and predominantly in lowland sites.[3] Specimens have been collected from limestone outcrop, second growth of black oak area, cedar bluff woods, sandy soil of upland oak-hickory forest, open oak woods, sandstone quarry, shaded roadside, river bank, old field scattered with trees, bluff above floodplain, burned over pine region with clay soil, and bottomland hardwood.[4]
Phenology
L. violacea has been observed to flower from July through September and fruit from August to November.[2]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
L. violacea is listed as rare by the New York Department of Environmental Conservation Division of Land and Forests, and as threatened by the Vermont Department of Fish and Wildlife Nongame and Natural Heritage Program.[1]
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 USDA Plant Database https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=LEVI6
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Weakley, A.S. 2020. Flora of the Southeastern United States. Edition of 20 October 2020. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ Towne, E. G. and K. E. Kemp (2008). "Long-term response patterns of tallgrass prairie to frequent summer burning." Rangeland Ecology & Management 61: 509-520.
- ↑ URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: R.K. Godfrey, R. komarek, Robert Thorne, G.W. Parmalee, Andre Clewell, Paul Redfearn, H. A. Wahl, Norlan Henderson, George Jones, Norlan Henderson, Sidney McDaniel, Dick Houk, V. Muehlenbach, Sidney McDaniel, Norman E. Hill. States and counties: Florida (Leon) Georgia (Grady) Virginia (Giles) Michigan (Jackson) Indiana (Brown, Monroe, Martin) Missouri (Johnson, Osage, Platte, Jackson, Barton, St. Clair) Mississippi (Chickasaw, Tallahatchie, Holmes, Madison) Alabama (Cleburne, Calhoun)