Hypericum hypericoides
| Hypericum hypericoides | |
|---|---|
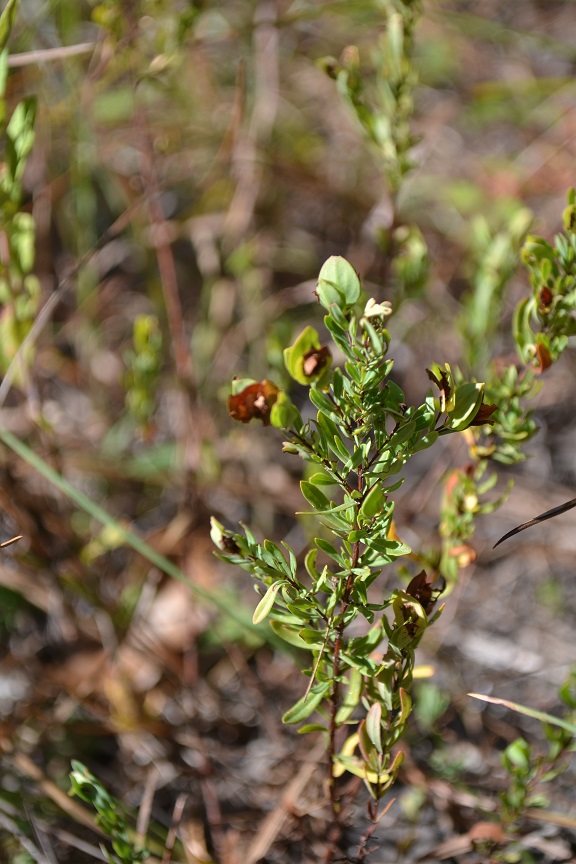

| |
| Photo taken by Kevin Robertson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Theales |
| Family: | Clusiaceae ⁄ Guttiferae |
| Genus: | Hypericum |
| Species: | H. hypericoides |
| Binomial name | |
| Hypericum hypericoides (L.) Crantz | |
| |
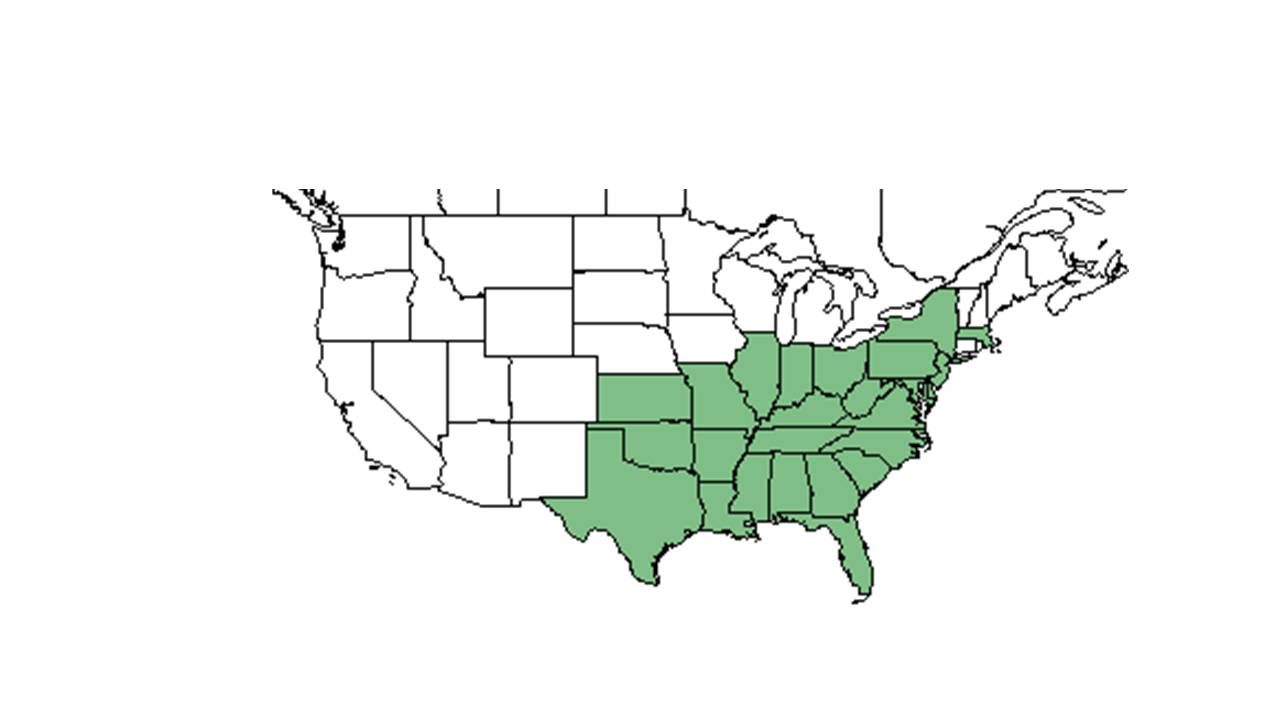
| Natural range of Hypericum hypericoides from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: St. Andrew's cross
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Ascyrum hypericoides Linnaeus; A. hypericoides Linnaeus var. hypericoides; A. hypericoides Linnaeus var. oblongifolium (Spach) Fernald; A. linifolium Spach; H. hypericoides Linnaeus ssp. hypericoides.[1]
Varieties: none.[1]
Description
Hypericum hypericoides is a perennial shrub species.
“Usually glabrous herbs or shrubs. Leaves usually punctate, simple, opposite, entire, usually sessile or subsessile, exstipulate. Inflorescence basically cymose; flowers perfect, regular, bracteates, subsessile or short-pedicellate, sepals 2, 4, or 5, persistent; petals 4 or 5, usually marcescent, yellow or pink; stamens 5-numerous, separate or connate basally forming 3-5 clusters or fascicles, filaments usually persistent; carpels 2-5, stigmas and styles separate or fused, ovary superior, 1-locular or partly or wholly 2-5 locular, placentation axile or parietal. Capsules basically ovoid, longitudinally dehiscent, styles usually persistent; seeds numerous, lustrous, areolate, cylindric, or oblong. In general, our species form a polymorphic complex with many intergrading taxa.” [2]
"Shrub 3-10 dm tall with erect or ascending, wing-angled. Leaves elliptic, linear, or oblanceolate, 8-26 mm long, 1-7 mm wide, acute or obtuse, base cuneate, notched. Flowers solitary, axillary, or ins mall cymules; bracts paired, at base of sepals; pedicels ascending, 1-5 mm long. Outer sepals 2, ovate, or widely elliptic, 5-12 mm long, 3.5-7 mm wide, acute, base frequently subcordate, inner sepals usually obsolete; petal 4, 6-10 mm long; styles 2, partly fuse, 0.5-1 mm long, ovary 1-locular. Capsules ovoid, 4-9 mm long, 2.5-4 mm long, 2.5-4 mm broad; seeds black, ca.1 mm long."[2]
Distribution
It is distributed from New Jersey, western Virginia, central Kentucky, southeastern Missouri, and central Oklahoma south to southern Florida and eastern Texas. It is also native to the West Indies, Mexico, and South America.[3]
Ecology
Habitat
Generally, H. hypericoides can be found in various woodlands and dry forests.[3] It occurs in wet or moist loamy soils and semi-shady to open light conditions. It can be found in annually burned longleaf pineland, wetland depressions, limestone glades, and by ponds. However, it also appears in disturbed areas including roadsides, open fields, and pine plantations.[4] It is associated with areas that are heavily logged, herbicided for woody plants, and burned several times, as compared to unlogged areas that are selectively herbicided for hardwoods and infrequently burned.[5] It is considered a possible native ground-cover indicator in upland longleaf pine communities in southern Georgia.[6] H. hypericoides responds positively to soil disturbance by heavy silviculture in North Carolina.[7]
Associated species include Pinus palutris and Pinus elliottii.[4]
Hypericum hypericoides is frequent and abundant in the North Florida Longleaf Woodlands and Calcareous Savannas community types as described in Carr et al. (2010).[8]
Phenology
H. hypericoides generally flowers from May until August.[3] It has been observed flowering in March, April, June, July, and September, while fruiting has been observed in September.[4][9]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by gravity.[10]
Seed bank and germination
It was found as a prevalent member of the seed bank at a loblolly pine plantation restoration site in southwest Georgia.[11] As well, it was found in the seed bank of early successional 2- and 5-year old field sites as well as a 112-year-old field site.[12]
Fire ecology
This species has been found in habitats that are burned annually, indicating some level of fire tolerance.[13] Seedlings were found in a survey at the Ocala National Forest in Florida after a fire disturbance.[14] It benefits most from a low fire return interval.[15] As well, it found found in higher frequency in burned-bluestem plots rather than burned-wiregrass plots in northwest Florida.[16]
Use by animals
It consists of approximately 2-5% of the diet of various large mammals and terrestrials birds.[17] It is known to be eaten by white-tailed deer mostly during the winter.[18][19]
Diseases and parasites
It is a host plant for false spider mites, including Brevipalpus californicus, B. obovatus, and B. phoenicis.[20]
Conservation and management
On the state level, Hypericum hypericoides is considered vulnerable in the state of Delaware.[21]
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 709-713. Print.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Ann F. Johnson, Wilson Baker, Loran C. Anderson, Leon Neel, R. Komarek, R.A. Norris, R.F. Doren, Robert K. Godfrey, Andre F. Clewell, Kevin Oakes, Chris Cooksey, and Sidney McDaniel. States and Counties: Florida: Franklin, Jackson, Jefferson, Lee, Leon, and Wakulla. Georgia: Baker and Thomas. Texas: Orange. Other Countries: Dominican Republic.
- ↑ Cipollini, M. L., J. Culberson, et al. (2012). "Herbaceous plants and grasses in a mountain longleaf pine forest undergoing restoration: a survey and comparative study." Southeastern Naturalist 11: 637-668.
- ↑ Ostertag, T. E. and K. M. Robertson (2007). A comparison of native versus old-field vegetation in upland pinelands managed with frequent fire, south Georgia, USA. Proceedings of the 23rd Tall Timbers Fire Ecology Conference: Fire in Grassland and Shrubland Ecosystems, Tallahassee, Tall Timbers Research Station.
- ↑ Cohen, S., R. Braham, and F. Sanchez. (2004). Seed Bank Viability in Disturbed Longleaf Pine Sites. Restoration Ecology 12(4):503-515.
- ↑ Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 12 DEC 2016
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.
- ↑ Andreu, M. G., et al. (2009). "Can managers bank on seed banks when restoring Pinus taeda L. plantations in Southwest Georgia?" Restoration Ecology 17: 586-596.
- ↑ Oosting, H. J. and M. E. Humphreys (1940). "Buried viable seeds in a successional series of old field and forest soils." Bulletin of the Torrey Botanical Club 67(4): 253-273.
- ↑ Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Ann F. Johnson, Wilson Baker, Loran C. Anderson, Leon Neel, R. Komarek, R.A. Norris, R.F. Doren, Robert K. Godfrey, Andre F. Clewell, Kevin Oakes, Chris Cooksey, and Sidney McDaniel. States and Counties: Florida: Franklin, Jackson, Jefferson, Lee, Leon, and Wakulla. Georgia: Baker and Thomas. Texas: Orange. Other Countries: Dominican Republic.
- ↑ Carrington, M. E. (1999). "Post-Fire Seedling Establishment in Florida Sand Pine Scrub." Journal of Vegetation Science 10(3): 403-412.
- ↑ Mehlman, D. W. (1992). "Effects of fire on plant community composition of North Florida second growth pineland." Bulletin of the Torrey Botanical Club 119(4): 376-383.
- ↑ Rodgers, H. L. and L. Provencher (1999). "Analysis of Longleaf Pine Sandhill Vegetation in Northwest Florida." Castanea 64(2): 138-162.
- ↑ Miller, J.H., and K.V. Miller. 1999. Forest plants of the southeast and their wildlife uses. Southern Weed Science Society.
- ↑ Atwood, E. L. (1941). "White-tailed deer foods of the United States." The Journal of Wildlife Management 5(3): 314-332.
- ↑ Gee, K. L., et al. (1994). White-tailed deer: their foods and management in the cross timbers. Ardmore, OK, Samuel Roberts Noble Foundation.
- ↑ Childers, C. C., et al. (2003). "Host plants of Brevipalpus californicus, B. obovatus, and B. phoenicis (Acari: Tenuipalpidae) and their potential involvement in the spread of viral diseases vectored by these mites." Experimental & Applied Acarology 30: 29-105.
- ↑ [[1]] NatureServe Explorer. Accessed: May 24, 2019