Difference between revisions of "Gymnopogon ambiguus"
(→Distribution) |
|||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
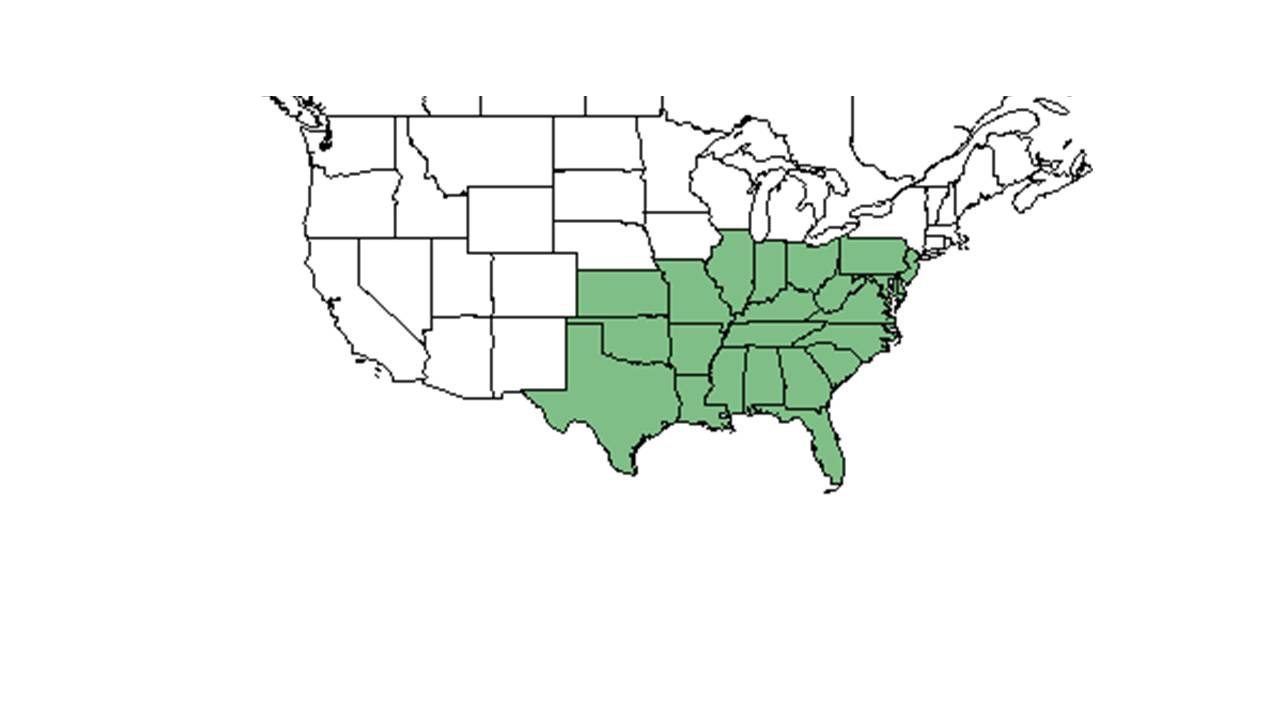
| − | ''Gymnopogon ambiguus'' is | + | ''Gymnopogon ambiguus'' is generally found in the eastern United States, from Pennsylvania, Ohio, Indiana, and Iowa south to Florida, Kansas, Missouri, and Texas.<ref name= "USDA">USDA, NRCS. (2016). The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 17 May 2019). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.</ref> More specifically, ''G. ambiguus'' is found from southern New Jersey west to Kentucky, Ohio, and Missouri, south to southern Florida and Texas.<ref name= "Weakley">Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.</ref> |
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
Revision as of 14:48, 17 May 2019
| Gymnopohon ambiguus | |
|---|---|
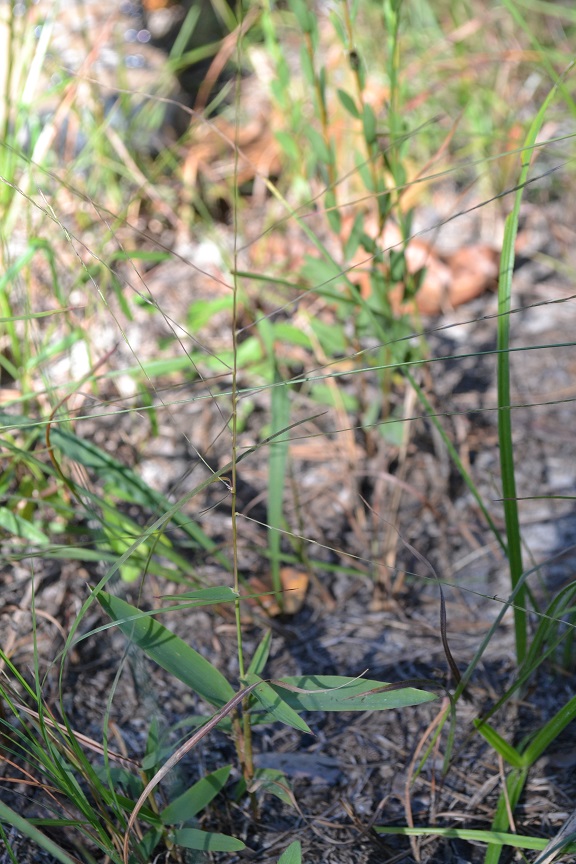

| |
| Photo taken by Kevin Robertson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida – Monocotyledons |
| Order: | Poales |
| Family: | Poaceae ⁄ Gramineae |
| Genus: | Gymnopogon |
| Species: | G. ambiguus |
| Binomial name | |
| Gymnopogon ambiguus (Michx.) Britton, Sterns & Poggenb. | |
| |
| Natural range of Gymnopogon ambiguus from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: bearded skeletongrass; Eastern skeleton grass; Eastern beard grass
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Description
"Tufted, rhizomatous, perennial; culms branching, nodes and internodes glabrous. Leaves cauline; blades glabrous on both surfaces, margins scaberulous, bases cordate; sheaths conspicuously overlapping, glabrous, usually pilose apically; ligules membranous, ciliolate, less than 0.4 mm long; collars usually pilose. Spikes racemose; branches spreading, flexuous, angled, scaberulous. Spikelets in two rows on one side of rachis, 1-flowered, occasionally a rudiment present in G. amibguus, appressed; pedicels angled, scaberulous, absent or to 1.5 mm long. Glumes 1-nerved, margins usually scarious; paleas 2-nerved, margins usually scarious, acute; callus usually bearded; rachilla prolonged or capped by sterile floret. Grain reddish, linear-ellipsoid." [1]
"Culms 3-7 dm tall. Blades to 6 cm long, 2-8 mm wide; ligules occasionally ciliate, 2.5 mm long. Spikelets beyond middle of spike only, 2.5-4.5 mm long. Glumes 2.5-4.5 mm long; lemmas pubescent apically, body 2-2.3 mm long, dorsal awns 1-3.5 mm long; paleas 2.2-3 mm long. Grain 1.8-2 mm long."[1]
Distribution
Gymnopogon ambiguus is generally found in the eastern United States, from Pennsylvania, Ohio, Indiana, and Iowa south to Florida, Kansas, Missouri, and Texas.[2] More specifically, G. ambiguus is found from southern New Jersey west to Kentucky, Ohio, and Missouri, south to southern Florida and Texas.[3]
Ecology
Habitat
General habitats of G. ambiguus includes glades, prairies, dry pinelands and woodlands, dry fields, and barrens.[3] This species has been observed to grow in open pine woods along the edges of depression ponds, longleaf pine-oak-wiregrass sandhill communities, sparsely wooded ecotone borders of limestone glades, longleaf pine-turkey oak flats and sand ridges, xeric sand pine scrub, upland pine oak woodlands, and clearings within mixed woodland forests. This plant has been seen growing in open and partial shaded environments in dry, loamy, and loose sands and well as moist sandy clay loam. Also growing in disturbed areas, G. ambiguus has been observed in powerline corridors, along trails, on pine plantations, and on open fields. [4]
Associated species includes Pinus palustris, Quercus falcata, Baptista hirsuta, Quercus nigra, Pterocaulon, stillingia, Heterotheca, Liquidambar styraciflua, Aristida stricta,Solidago, Andropogon, Sorghastrum, Pinus taeda, and Bluestem.[4]
Phenology
This species commonly flowers between August and October.[3] Flowers and fruits have been observed on this species from September to November.[4]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by gravity. [5]
Fire ecology
It occurs on annually burned pine plantations.[4]
Use by animals
Comprised deer diets more in the summer than in the winter.[6]
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 118. Print.
- ↑ USDA, NRCS. (2016). The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 17 May 2019). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 .Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Wilson Baker, Robert K. Godfrey, James R. Burkhalter, Angus Gholson, Richard D. Houk, Robert Kral, Andre F. Clewell, D. L. Martin, S. T. Cooper, Sidney McDaniel, R.A. Norris, D. C. Hunt, R. Komarek, and J.M. Kane. States and Counties: Florida: Gadsden, Jackson, Jefferson, Lafayette, Leon, Madison, Marion, Nassau, Putnam, Santa Rosa, and Wakulla. Georgia: Grady and Thomas.
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.
- ↑ Thill, R. E. (1983). Deer and cattle forage selection on Louisiana pine-hardwood sites. New Orleans, LA, USDA Forest Service.