Difference between revisions of "Gamochaeta purpurea"
(→Distribution) |
|||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
| − | ''G. purpurea'' ranges from northeast California through the southeastern and eastern United States and southeastern Canada <ref name="USDA"/> | + | ''G. purpurea'' ranges from northeast California through the southeastern and eastern United States and southeastern Canada. It has also been introduced in Hawaii and the Pacific Basin.<ref name="USDA"/> As well, it is adventive in the western United States as well as Mexico, South America, and elsewhere.<ref name= "Weakley"/> |
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
Revision as of 12:58, 15 May 2019
Common names: purple everlasting; spoonleaf purple everlasting; purple cudweed
| Gamochaeta purpurea | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by the Atlas of Florida Plants Database | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae |
| Genus: | Gamochaeta |
| Species: | G. purpurea |
| Binomial name | |
| Gamochaeta purpurea L. | |
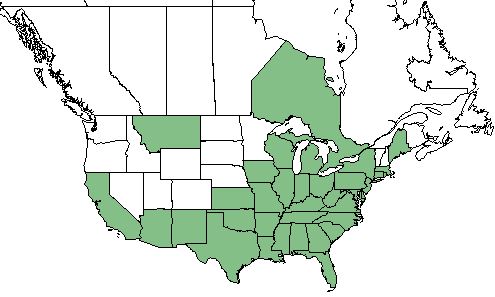
| |
| Natural range of Gamochaeta purpurea from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: Gnaphalium purpureum Linnaeus var. purpureum, Gnaphalium purpureum Linnaeus, Gamochaeta purpurea (Linnaeus) Cabrera
Varieties: none
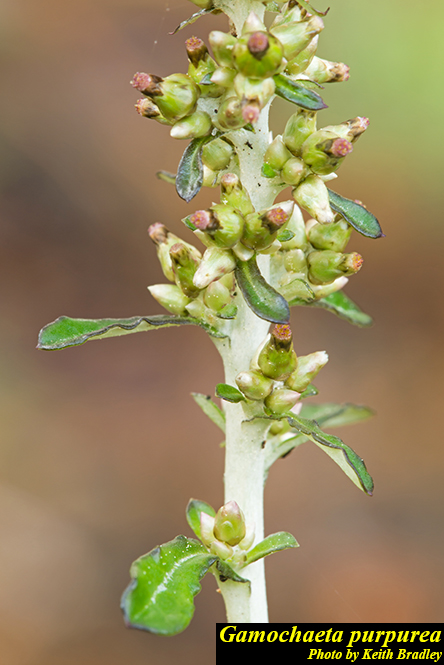
Description
G. purpurea is a weedy forb in the Asteraceae family native to North America. It that can be either annual or biennial [1]. It can reach a height of 1.25 feet, and forms a basal rosette with leaves alternate and spatulate. [2]
Distribution
G. purpurea ranges from northeast California through the southeastern and eastern United States and southeastern Canada. It has also been introduced in Hawaii and the Pacific Basin.[1] As well, it is adventive in the western United States as well as Mexico, South America, and elsewhere.[3]
Ecology
Habitat
G. purpurea can be found in disturbed areas such as roadsides, fields, and pastures [3].
Phenology
Generally, G. purpurea flowers from late March until September.[3] It has been observed to flower from March to May.[4] However, it has been observed to be flowering during November and January.[5]
Seed dispersal
Seeds are wind-dispered [6].
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 USDA Plants Database URL:https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=Gapu3
- ↑ Gee, K. L., et al. (1994). White-tailed deer: their foods and management in the cross timbers. Ardmore, OK, Samuel Roberts Noble Foundation.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 22 MAY 2018
- ↑ Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: May 2018. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson and R. Kral. States and Counties: Florida: Martin and Putnam.