Difference between revisions of "Euthamia caroliniana"
(→Description) |
|||
| (44 intermediate revisions by 10 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
{{taxobox | {{taxobox | ||
| name = Euthamia caroliniana | | name = Euthamia caroliniana | ||
| − | | image = | + | | image = FL 8021.jpg |
| − | | image_caption = | + | | image_caption = Photo taken by Gil Nelson |
| regnum = Plantae | | regnum = Plantae | ||
| divisio = Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants | | divisio = Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
| binomial_authority = (L.) Greene ex Porter & Britton | | binomial_authority = (L.) Greene ex Porter & Britton | ||
| range_map = euth_caro_dist.jpg | | range_map = euth_caro_dist.jpg | ||
| − | | range_map_caption = Natural range of ''Euthamia caroliniana'' from USDA NRCS [http://www.plants.usda.gov Plants Database]. | + | | range_map_caption = Natural range of ''Euthamia caroliniana'' from USDA NRCS [http://www.plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=EUPU7 Plants Database]. |
}} | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Common names: Carolina goldentop; slender goldentop; slender flattop goldenrod; coastal plain goldentop | ||
| + | ==Taxonomic notes== | ||
| + | Synonyms: ''Euthamia minor'' (Michaux) Greene; ''E. tenuifolia''; ''E. tenuifolia'' (Pursh) Nuttall var. ''microcephala'' Nuttall; ''Solidago microcephala'' (Nuttall) Bush<ref name=weakley>Weakley, A.S. 2020. Flora of the Southeastern United States. Edition of 20 October 2020. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Varieties: ''Euthamia minor'' (Michaux) Greene; ''Solidago microcephala'' (Nuttall) Bush <ref name=weakley/> | ||
| + | |||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| − | + | A description of ''Euthamia caroliniana'' is provided in [http://www.efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=1&taxon_id=250066764 The Flora of North America]. Overall, it has grass-like leaves that contain tiny resin dots as well as only one vein or rib.<ref name= "lady bird">[[https://www.wildflower.org/plants/search.php?search_field=&newsearch=true]] Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center. Accessed: May 13, 2019</ref> It grows up to a meter tall from a branched and creeping rhizome. Inflorescence contains 10 to 20 flowers.<ref>[[http://explorer.natureserve.org]] NatureServe Explorer. Accessed: May 13, 2019</ref> | |
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
| + | ''E. caroliniana'' is distributed from southern Maine south to southern Florida and west to southeastern Louisiana, and mainly along the southeast coastal plain. However, its distribution does extend into the Piedmont in some areas.<ref name=weakley/> It is also native to the Nova Scotia province in Canada.<ref name ="USDA">USDA, NRCS. (2016). The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 13 May 2019). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
| + | |||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | = | + | Generally, ''E. caroliniana'' is found in moist forests, pine savannas, pastures, ditches, and other disturbed areas.<ref name=weakley/> It has been observed in a range of habitats including roadsides, pine flatwoods, barren sandhills, poorly drained areas, boggy margins, exposed sand in sparse woods, and other disturbed areas like roadside ditches. Soils observed are dry sand and various sandy loam.<ref name= "herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: May 2019. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Wilson Baker, - Boothes, Andre F. Clewell, Angus Gholson, Robert K. Godfrey, Faith Jackson, R. Komarek, T. MacClendon, Leon Neel, and R. A. Norris. States and Counties: Florida: Calhoun, Franklin, Gadsden, Gulf, Jackson, Lafayette, Leon, Liberty, Nassau, Wakulla, and Washington. Georgia: Baker, Grady, and Thomas. South Carolina: Richland.</ref> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Associated species include ''Liatris laevigata'', ''Liatris gracilis'', ''Polygonella polygama'', ''Polygonella gracilis'', ''Diodia teres'', ''Diodia virginiana'', ''Croptilion'' sp., ''Sisyrinchium'' sp., ''Dalea'' sp., ''Solidago'' sp., ''Acalypha gracilens'', ''Chrysopsis lanuginosa'', ''Rubus cuneifolius'', ''Hypericum gentianoides'', ''Trichostema dichotomum'', ''Eupatorium compositifolium'', and others.<ref name= "herbarium"/> | |
| − | + | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | |
| + | It generally flowers from September to December as well as sometimes in August.<ref name=weakley/> ''E. caroliniana'' has been observed to flower in September and October.<ref>Nelson, G. [http://www.gilnelson.com/ PanFlora]: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 9 DEC 2016</ref> | ||
| − | + | ===Seed dispersal=== | |
| + | This species is thought to be dispersed by wind. <ref>Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.</ref> | ||
| − | + | ===Seed bank and germination=== | |
| + | Forms a persistent soil seed bank.<ref> Navarra, J. J., N. Kohfeldt, et al. (2011). "Seed bank changes with time since fire in Florida rosemary scrub." Fire Ecology 7(2). </ref> One study also found the seeds of ''E. caroliniana'' to persist in the seed bank after a fire disturbance.<ref name= "Kalmbacher">Kalmbacher, R., et al. (2005). "Seeds obtained by vacuuming the soil surface after fire compared with soil seedbank in a flatwoods plant community." Native Plants Journal 6: 233-241.</ref> | ||
| − | + | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | |
| + | It has been observed to commonly grow in habitats that are frequently burned and annually burned.<ref name= "herbarium"/> The seeds of this plant were also seen to persist in the seed bank even after a fire disturbance.<ref name= "Kalmbacher"/> | ||
| − | Colletidae | + | ===Pollination=== |
| − | + | ''Euthamia caroliniana'' has been observed at the Archbold Biological Station to host ground-nesting bees such as ''Andrena fulvipennis'' (family Andrenidae), bees from the family Apidae such as ''Apis mellifera, Bombus impatiens,'' and ''Epeolus carolinus'', sweat bees from the family Colletidae such as ''Colletes mandibularis, C. simulans, C. thysanellae,'' and ''Hylaeus confluens'', sweat bees from the family Halictidae such as ''Agapostemon splendens, Augochlorella aurata, Halictus poeyi, Lasioglossum nymphalis, L. placidensis, L. puteulanum,'' and ''Sphecodes heraclei'', wasps from the family Leucospidae such as ''Leucospis affinis, L. affinis, L. robertsoni,'' and ''L. slossonae'', leafcutting bees from the family Megachilidae such as ''Anthidiellum perplexum, Coelioxys dolichos, C. octodentata, C. sayi, Megachile albitarsis,'' and ''M. mendica'', spider wasps from the family Pompilidae such as ''Anoplius atrox, A. marginalis,'' and ''Paracyphonyx funereus'', thread-waisted wasps from the family Sphecidae such as ''Ammophila pictipennis, Anacrabro ocellatus, Bembix sayi, Cerceris blakei, Ectemnius rufipes ais, Epinysson mellipes, Isodontia exornata, Liris beata, Microbembex monodonta, Palmodes dimidiatus, Philanthus politus, P. ventilabris, Prionyx thomae, Tachysphex similis,'' and ''Tachytes validus'', as well as wasps from the family Vespidae such as ''Euodynerus boscii boharti, E. hidalgo, Pachodynerus erynnis, Parancistrocerus salcularis rufulus, Polistes bellicosus, P. carolina, P. dorsalis hunteri, P. fuscatus, P. perplexus, Zethus slossonae,'' and ''Z. spinipes''.<ref name=dey> Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.</ref> Other members of the Hymenoptera order observed to pollinate ''E. caroliniana'' include ''Dialictus nymphalis'', ''D. placidensis'', ''D. tegulairs'', ''Halictus ligatus'', ''Tripeolus georgicus'', and ''Xylocopa micans''.<ref>Deyrup, M. J. E., and Beth Norden (2002). "The diversity and floral hosts of bees at the Archbold Biological Station, Florida (Hymenoptera: Apoidea)." Insecta mundi 16(1-3).</ref><ref>Hall, H. G. a. J. S. A. (2010). "Surveys of bees (Hymenoptera: Apoidea: Anthophila) in natural areas of Alachua County in north-central Florida." The Florida Entomologist 93(4): 609-629.</ref> Additionally, this species has been observed to host ground-nesting bees from the family Andrenidae such as ''Andrena braccata'' and ''A. hirticincta'', bees from the family Apidae such as ''Bombus griseocollis'' and ''Melissodes druriella'', plasterer bees from the family Colletidae such as ''Colletes americanus'' and ''Colletes speculiferus'', and sweat bees from the family Halictidae such as ''Halictus rubicundus'' and ''Lasioglossum zephyrum''.<ref>Discoverlife.org [https://www.discoverlife.org/20/q?search=Bidens+albaDiscoverlife.org|Discoverlife.org]</ref> Overall, this species is recognized by pollination ecologists to be of special value for native bees since it attracts large numbers of native bees for pollination.<ref name= "lady bird"/> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Halictidae | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Leucospidae | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Megachilidae | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Pompilidae | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Sphecidae | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Vespidae | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ===Herbivory and toxicology=== | |
| + | ''E. caroliniana'' consists of approximately 2-5% of the diet for large mammals, small mammals, and various terrestrial birds.<ref>Miller, J.H., and K.V. Miller. 1999. Forest plants of the southeast and their wildlife uses. Southern Weed Science Society.</ref> | ||
| + | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | ||
| − | + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== | |
| + | This species is listed as threatened by the Maine Department of Conservation, Natural Areas Program, and by the Pennsylvania Department of Conservation and Natural Resources.<ref name= "USDA"/> | ||
| − | == | + | ==Cultural use== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
| + | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
Latest revision as of 12:01, 26 May 2023
| Euthamia caroliniana | |
|---|---|
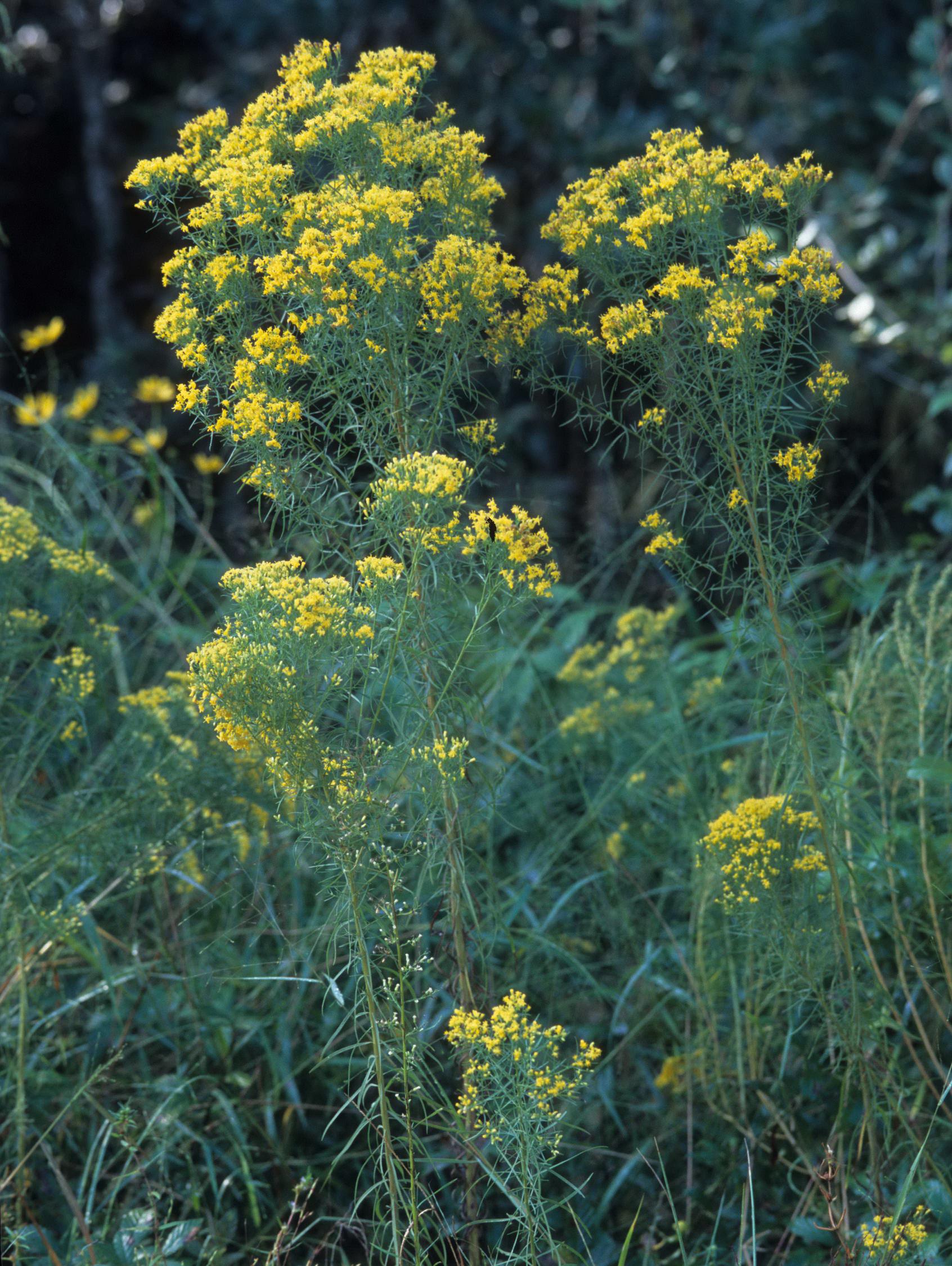

| |
| Photo taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae ⁄ Compositae |
| Genus: | Euthamia |
| Species: | E. caroliniana |
| Binomial name | |
| Euthamia caroliniana (L.) Greene ex Porter & Britton | |
| |
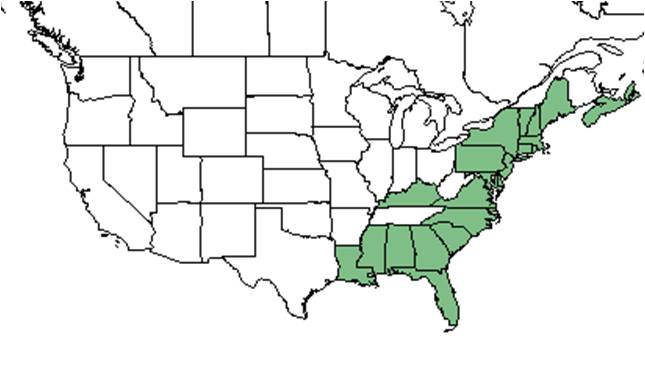
| Natural range of Euthamia caroliniana from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Carolina goldentop; slender goldentop; slender flattop goldenrod; coastal plain goldentop
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Euthamia minor (Michaux) Greene; E. tenuifolia; E. tenuifolia (Pursh) Nuttall var. microcephala Nuttall; Solidago microcephala (Nuttall) Bush[1]
Varieties: Euthamia minor (Michaux) Greene; Solidago microcephala (Nuttall) Bush [1]
Description
A description of Euthamia caroliniana is provided in The Flora of North America. Overall, it has grass-like leaves that contain tiny resin dots as well as only one vein or rib.[2] It grows up to a meter tall from a branched and creeping rhizome. Inflorescence contains 10 to 20 flowers.[3]
Distribution
E. caroliniana is distributed from southern Maine south to southern Florida and west to southeastern Louisiana, and mainly along the southeast coastal plain. However, its distribution does extend into the Piedmont in some areas.[1] It is also native to the Nova Scotia province in Canada.[4]
Ecology
Habitat
Generally, E. caroliniana is found in moist forests, pine savannas, pastures, ditches, and other disturbed areas.[1] It has been observed in a range of habitats including roadsides, pine flatwoods, barren sandhills, poorly drained areas, boggy margins, exposed sand in sparse woods, and other disturbed areas like roadside ditches. Soils observed are dry sand and various sandy loam.[5]
Associated species include Liatris laevigata, Liatris gracilis, Polygonella polygama, Polygonella gracilis, Diodia teres, Diodia virginiana, Croptilion sp., Sisyrinchium sp., Dalea sp., Solidago sp., Acalypha gracilens, Chrysopsis lanuginosa, Rubus cuneifolius, Hypericum gentianoides, Trichostema dichotomum, Eupatorium compositifolium, and others.[5]
Phenology
It generally flowers from September to December as well as sometimes in August.[1] E. caroliniana has been observed to flower in September and October.[6]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by wind. [7]
Seed bank and germination
Forms a persistent soil seed bank.[8] One study also found the seeds of E. caroliniana to persist in the seed bank after a fire disturbance.[9]
Fire ecology
It has been observed to commonly grow in habitats that are frequently burned and annually burned.[5] The seeds of this plant were also seen to persist in the seed bank even after a fire disturbance.[9]
Pollination
Euthamia caroliniana has been observed at the Archbold Biological Station to host ground-nesting bees such as Andrena fulvipennis (family Andrenidae), bees from the family Apidae such as Apis mellifera, Bombus impatiens, and Epeolus carolinus, sweat bees from the family Colletidae such as Colletes mandibularis, C. simulans, C. thysanellae, and Hylaeus confluens, sweat bees from the family Halictidae such as Agapostemon splendens, Augochlorella aurata, Halictus poeyi, Lasioglossum nymphalis, L. placidensis, L. puteulanum, and Sphecodes heraclei, wasps from the family Leucospidae such as Leucospis affinis, L. affinis, L. robertsoni, and L. slossonae, leafcutting bees from the family Megachilidae such as Anthidiellum perplexum, Coelioxys dolichos, C. octodentata, C. sayi, Megachile albitarsis, and M. mendica, spider wasps from the family Pompilidae such as Anoplius atrox, A. marginalis, and Paracyphonyx funereus, thread-waisted wasps from the family Sphecidae such as Ammophila pictipennis, Anacrabro ocellatus, Bembix sayi, Cerceris blakei, Ectemnius rufipes ais, Epinysson mellipes, Isodontia exornata, Liris beata, Microbembex monodonta, Palmodes dimidiatus, Philanthus politus, P. ventilabris, Prionyx thomae, Tachysphex similis, and Tachytes validus, as well as wasps from the family Vespidae such as Euodynerus boscii boharti, E. hidalgo, Pachodynerus erynnis, Parancistrocerus salcularis rufulus, Polistes bellicosus, P. carolina, P. dorsalis hunteri, P. fuscatus, P. perplexus, Zethus slossonae, and Z. spinipes.[10] Other members of the Hymenoptera order observed to pollinate E. caroliniana include Dialictus nymphalis, D. placidensis, D. tegulairs, Halictus ligatus, Tripeolus georgicus, and Xylocopa micans.[11][12] Additionally, this species has been observed to host ground-nesting bees from the family Andrenidae such as Andrena braccata and A. hirticincta, bees from the family Apidae such as Bombus griseocollis and Melissodes druriella, plasterer bees from the family Colletidae such as Colletes americanus and Colletes speculiferus, and sweat bees from the family Halictidae such as Halictus rubicundus and Lasioglossum zephyrum.[13] Overall, this species is recognized by pollination ecologists to be of special value for native bees since it attracts large numbers of native bees for pollination.[2]
Herbivory and toxicology
E. caroliniana consists of approximately 2-5% of the diet for large mammals, small mammals, and various terrestrial birds.[14]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
This species is listed as threatened by the Maine Department of Conservation, Natural Areas Program, and by the Pennsylvania Department of Conservation and Natural Resources.[4]
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Weakley, A.S. 2020. Flora of the Southeastern United States. Edition of 20 October 2020. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 [[1]] Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center. Accessed: May 13, 2019
- ↑ [[2]] NatureServe Explorer. Accessed: May 13, 2019
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 USDA, NRCS. (2016). The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 13 May 2019). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: May 2019. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Wilson Baker, - Boothes, Andre F. Clewell, Angus Gholson, Robert K. Godfrey, Faith Jackson, R. Komarek, T. MacClendon, Leon Neel, and R. A. Norris. States and Counties: Florida: Calhoun, Franklin, Gadsden, Gulf, Jackson, Lafayette, Leon, Liberty, Nassau, Wakulla, and Washington. Georgia: Baker, Grady, and Thomas. South Carolina: Richland.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 9 DEC 2016
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.
- ↑ Navarra, J. J., N. Kohfeldt, et al. (2011). "Seed bank changes with time since fire in Florida rosemary scrub." Fire Ecology 7(2).
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Kalmbacher, R., et al. (2005). "Seeds obtained by vacuuming the soil surface after fire compared with soil seedbank in a flatwoods plant community." Native Plants Journal 6: 233-241.
- ↑ Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
- ↑ Deyrup, M. J. E., and Beth Norden (2002). "The diversity and floral hosts of bees at the Archbold Biological Station, Florida (Hymenoptera: Apoidea)." Insecta mundi 16(1-3).
- ↑ Hall, H. G. a. J. S. A. (2010). "Surveys of bees (Hymenoptera: Apoidea: Anthophila) in natural areas of Alachua County in north-central Florida." The Florida Entomologist 93(4): 609-629.
- ↑ Discoverlife.org [3]
- ↑ Miller, J.H., and K.V. Miller. 1999. Forest plants of the southeast and their wildlife uses. Southern Weed Science Society.