Difference between revisions of "Euphorbia discoidalis"
(→Ecology) |
(→Distribution) |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
| + | ''Euphorbia discoidalis'' is distributed from eastern and central Georgia south and west to the Florida panhandle and eastern Texas.<ref name= "Weakley">Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
Revision as of 16:14, 10 May 2019
| Euphorbia discoidalis | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo taken by Kevin Robertson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Euphorbiales |
| Family: | Euphorbiaceae |
| Genus: | Euphorbia |
| Species: | E. discoidalis |
| Binomial name | |
| Euphorbia discoidalis Chapm. | |
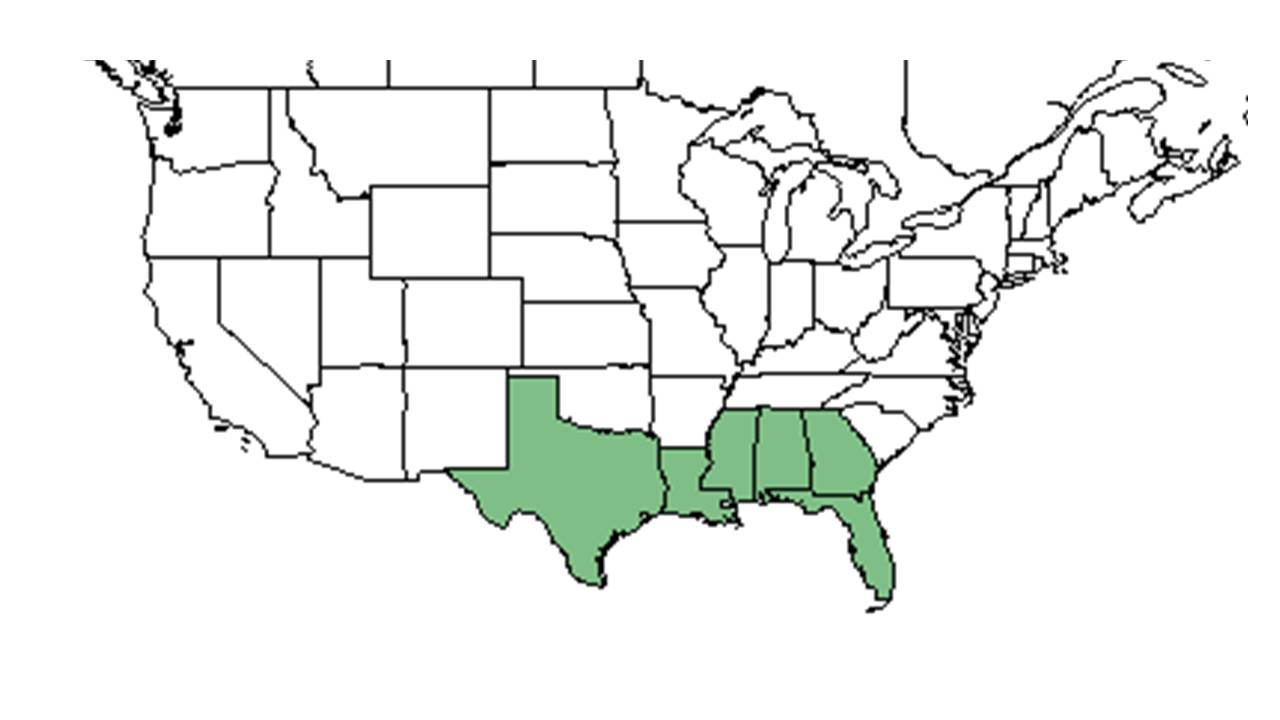
| |
| Natural range of Euphorbia discoidalis from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
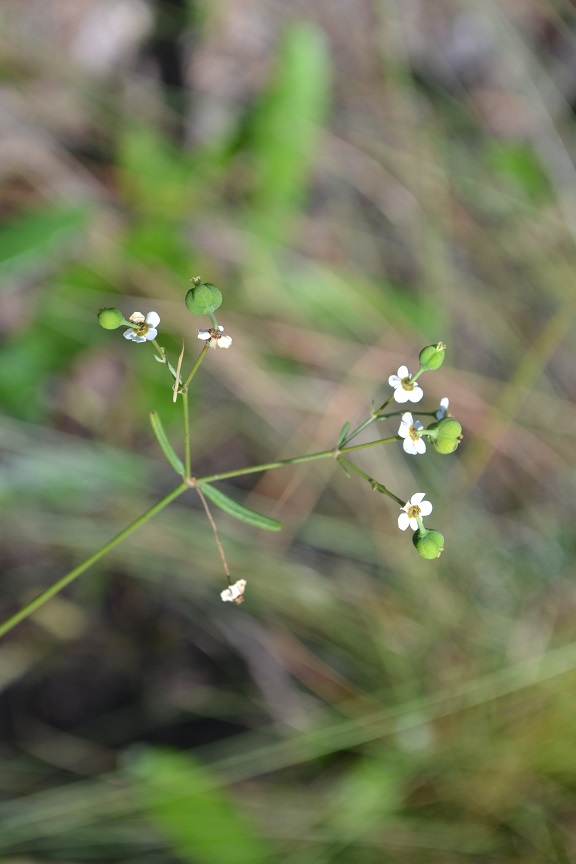
Common name: Summer spurge
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Tithymalopsis discoidalis (Chapman) Small; E. corollata var. corollata
Description
Distribution
Euphorbia discoidalis is distributed from eastern and central Georgia south and west to the Florida panhandle and eastern Texas.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
Habitats of E. discoidalis include pine dominated habitats such as longleaf pine scrubs, sandhills, upland pine, and drained uplands. It prefers areas that have high light level/ open canopies. It also occurs in disturbed habitats such as fallow fields, clearings, and in annually burned pinelands. It likes sandy soil types.[2] Euphorbia discoidalis is restricted to native groundcover with a statistical affinity in upland pinelands of South Georgia.[3] Populations appear to increase due to disturbance.[4]
Associated species include longleaf pine, slash pine, shortleaf pine, oaks, red oak, mockernut hickory, magnolia.[2]
Phenology
It flowers from late August to frost.[4] This species has been observed flowering in August and September.[2]
Fire ecology
This species is found in areas that are burned annually such as longleaf pine-wiregrass savannas and sandhills.[2] It responds positively to fire. Kral (1983) writes "In naturally stocked uplands it increases as a result of woods fires which reduce competing woody vegetation." [4]
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: R. A. Norris, R. Komarek, Andre F. Clewell, Robert K. Godfrey, Jefferson, R. Komarek, Loran C. Anderson, Travis MacClendon, Karen McClendon, G. Wilder, Ann F. Johnson, Wilson Baker, and G. Wilder. States and Counties: Florida: Calhoun, Jackson, Leon. Georgia: Thomas.
- ↑ Ostertag, T.E., and K.M. Robertson. 2007. A comparison of native versus old-field vegetation in upland pinelands managed with frequent fire, South Georgia, USA. Pages 109–120 in R.E. Masters and K.E.M. Galley (eds.). Proceedings of the 23rd Tall Timbers Fire Ecology Conference: Fire in Grassland and Shrubland Ecosystems.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Kral, R. (1983). Euphorbia discoidalis Chapman. A report on some rare, threatened or endangered forest-related vascular plants of the South. R. Kral. Atlanta, USDA Forest Service, Paper 228: 701-705.