Difference between revisions of "Eupatorium rotundifolium"
(Created page with "{{italic title}} <!-- Get the taxonomy information from the NRCS Plants database --> {{taxobox | name = Eupatorium rotundifolium | image = Eupatorium rotundifolium 2014-07-17...") |
|||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
| + | It has well-documented anticancer activities against various human cancer cell lines.<ref>Kintzios, S. E. (2007). "Terrestrial plant-derived anticancer agents and plant species used in anticancer research." Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences 25: 79-113.</ref> | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| + | It can be found in areas regularly burned every 1 to 2 years in the winter. It can be found in longleaf pine savanna communities.<ref name="Brewer and Cralle 2003"/> | ||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
===Seed dispersal=== | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
===Seed bank and germination=== | ===Seed bank and germination=== | ||
===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| + | It is fire-tolerant.<ref name="Brewer and Cralle 2003">Brewer, J. S. and S. P. Cralle (2003). "Phosphorus addition reduces invasion of a longleaf pine savanna (southeastern USA) by a non-indigenous grass (Imperata cylindrica)." Plant Ecology 167: 237-245.</ref> | ||
===Pollination=== | ===Pollination=== | ||
===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
Revision as of 08:39, 11 June 2015
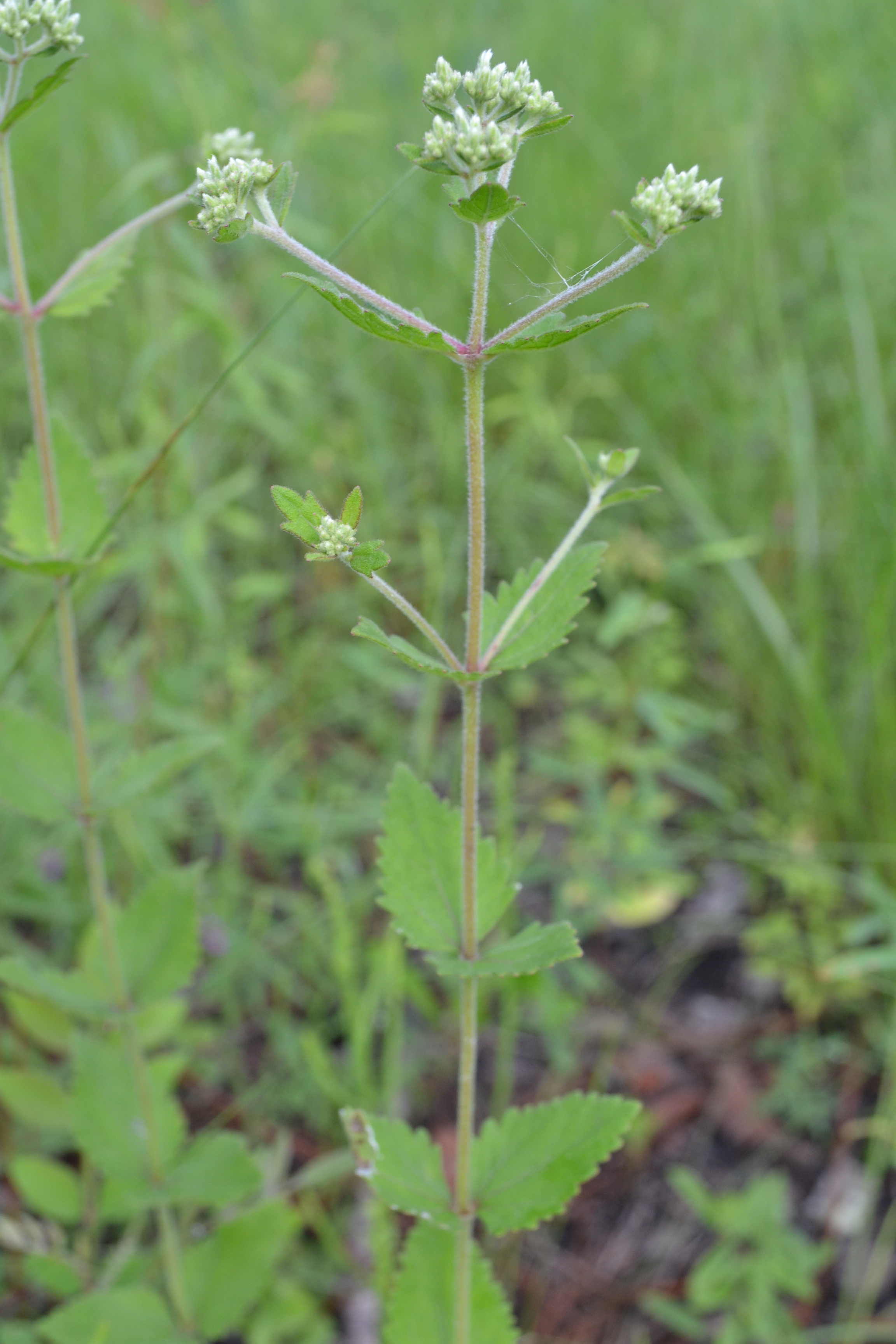
| Eupatorium rotundifolium | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae ⁄ Compositae |
| Genus: | Eupatorium |
| Species: | E. rotundifolium |
| Binomial name | |
| Eupatorium rotundifolium L. | |
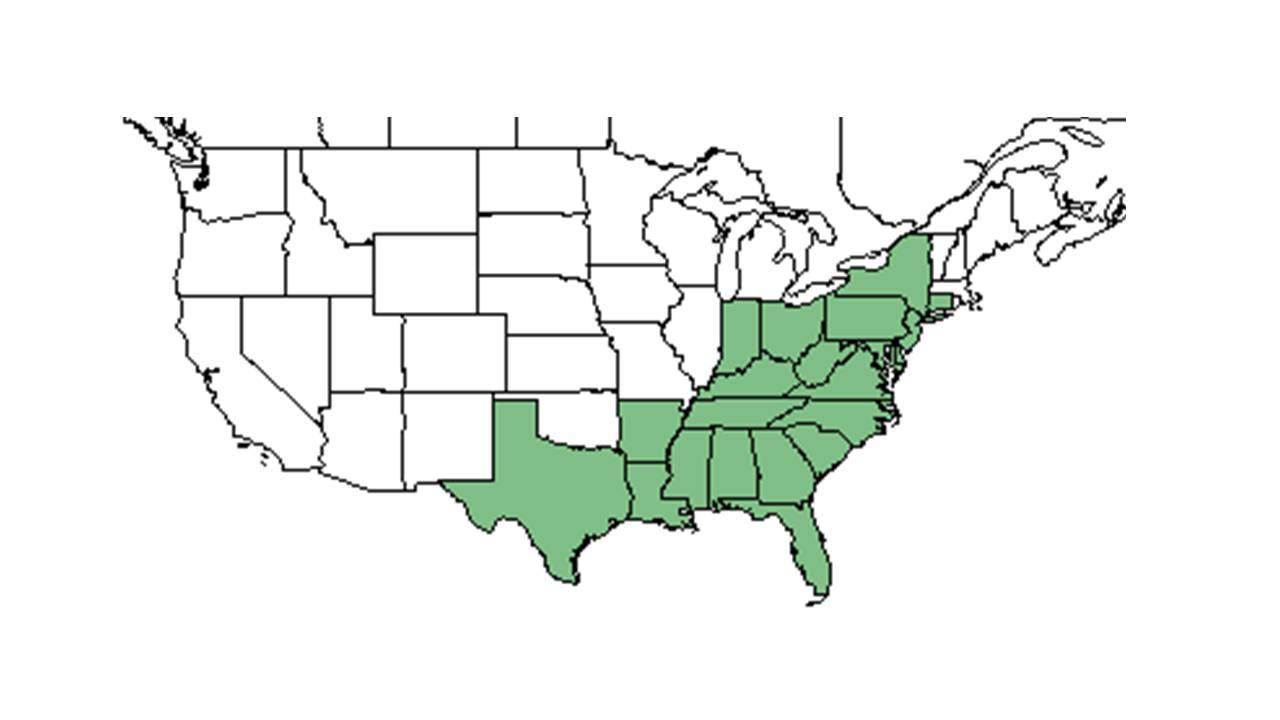
| |
| Natural range of Eupatorium rotundifolium from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Description
Distribution
Ecology
It has well-documented anticancer activities against various human cancer cell lines.[1]
Habitat
It can be found in areas regularly burned every 1 to 2 years in the winter. It can be found in longleaf pine savanna communities.[2]
Phenology
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
It is fire-tolerant.[2]
Pollination
Use by animals
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
References and notes
Photo Gallery
- ↑ Kintzios, S. E. (2007). "Terrestrial plant-derived anticancer agents and plant species used in anticancer research." Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences 25: 79-113.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Brewer, J. S. and S. P. Cralle (2003). "Phosphorus addition reduces invasion of a longleaf pine savanna (southeastern USA) by a non-indigenous grass (Imperata cylindrica)." Plant Ecology 167: 237-245.