Difference between revisions of "Eleocharis tricostata"
(→Distribution) |
|||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
| − | This sedge ranges from Massachusetts to Florida with sporadic occurrences inland in Michigan<ref name="Ward & Leigh 1975"/> and Louisiana.<ref name="USDA"/> | + | This sedge ranges from Massachusetts to Florida with sporadic occurrences inland in Michigan<ref name="Ward & Leigh 1975"/> and Louisiana.<ref name="USDA"/> It is a mostly coastal plain endemic that is disjunct to the Great Lakes region.<ref>Sorrie, B. A. and A. S. Weakley (2001). "Coastal plain vascular plant endemics: Phytogeographic Patterns." Castanea 66(1/2): 50-82.</ref> |
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
Revision as of 16:02, 3 May 2019
| Eleocharis tricostata | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by © Arthur Haines, New England Wild Flower Society | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Poales |
| Family: | Cyperaceae |
| Genus: | Eleocharis |
| Species: | E. tricostata |
| Binomial name | |
| Eleocharis tricostata Torr. | |
| |
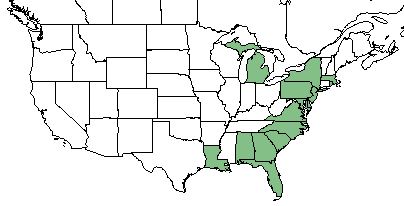
| Natural range of Eleocharis tricostata from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: three-angle spikerush[1][2]
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: Scirpus tricostatus (Torrey) Kuntze, Trichophyllum ticostatum (Torrey) House[3]
Description
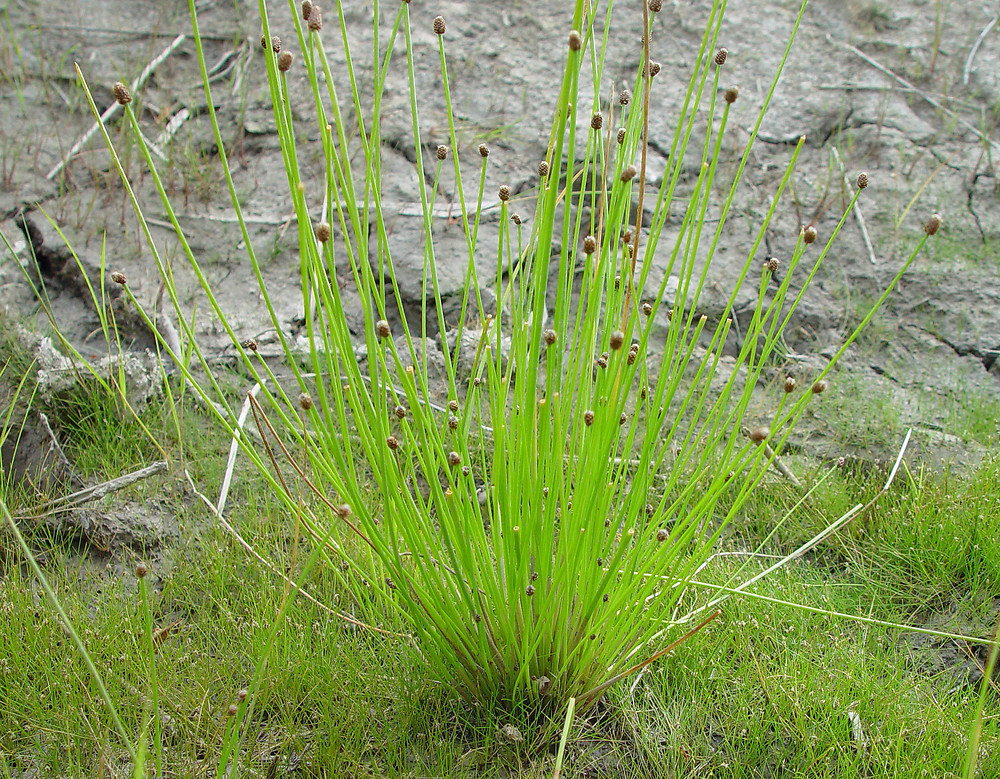
Eleocharis tricostata is a perennial, monoecious, graminoid sedge.[2]
Distribution
This sedge ranges from Massachusetts to Florida with sporadic occurrences inland in Michigan[4] and Louisiana.[2] It is a mostly coastal plain endemic that is disjunct to the Great Lakes region.[5]
Ecology
Habitat
E. tricostata is an obligate wetland species[2] found in wet pine savannas, bogs,[1] cypress gum swamps, marshes, swales, flatwoods,[6] wet soil of pond margins, and infrequently in saline marshes.[4] Occurrences in such areas show the plants preference for sandy, peaty, and mucky soils.[6] This species has also been observed in a dried up pond, cypress-gum depression, in muck on a swamp border, wet margins, boggy swales, and in sand.[7]
Associated species: Taxodium sp., Serenoa repens, Typha sp., Eleocharis sp., Echinodorous sp., Nyssa sp., Rhexia mariana, Dichanthelium wrightianum, and others.[7]
Phenology
It flowers and fruits between July and September.[1] E. tricostata has been observed to flower April through July and September, and fruit from the same time period.[7]
Conservation and Management
This species is listed as endangered by the Massachusetts Division of Fisheries and Wildlife, Natural Heritage and Endangered Species Program, by the New York Department of Environmental Conservation, Division of Land and Forests, and by the Rhode Island Department of Environmental Management. It is also listed as endangered and extirpated by the Maryland Department of Natural Resources, Natural Heritage Program, as threatened by the Michigan Department of Natural Resources, Natural Features Inventory, and as extirpated by the Pennsylvania Department of Conservation and Natural Resources.[2] It has a global status of G4 since it is considered rare and is most likely threatened by alteration of habitat.[6]
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Weakley A. S.(2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 USDA, NRCS. (2016). The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 5 December 2017). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ Wunderlin R. P., Hansen B. F., Franck A. R. and Essig. F. B. (2017). Atlas of Florida Plants (http://florida.plantatlas.usf.edu/).[S. M. Landry and K. N. Campbell (application development), USF Water Institute.] Institute for Systematic Botany, University of South Florida, Tampa.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Ward D. B. and Leigh E. M. (1975). Contributions to the Flora of Florida: 8, Eleocharis (Cyperaceae). Castanea 40(1):16-36.
- ↑ Sorrie, B. A. and A. S. Weakley (2001). "Coastal plain vascular plant endemics: Phytogeographic Patterns." Castanea 66(1/2): 50-82.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 NatureServe. (2017). NatureServe Explorer: An online encyclopedia of life [web application]. Version 7.1. NatureServe, Arlington, Virginia. Available http://explorer.natureserve.org. (Accessed: December 6, 2017 ). Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "NatureServe" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: May 2019. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, George R. Cooley, A. H. Curtiss, R. A. Davidson, R. K. Godfrey, R. S. Mitchell, Gwynn W. Ramsey, Annie Schmidt, R. F. Thorne, and Carroll E. Wood, Jr. States and Counties: Florida: Calhoun, Clay, Duval, Gadsden, Hernando, Jackson, Liberty, Madison, and Wakulla.