Diospyros virginiana
Common Names: Common Persimmon [1]
| Diospyros virginiana | |
|---|---|
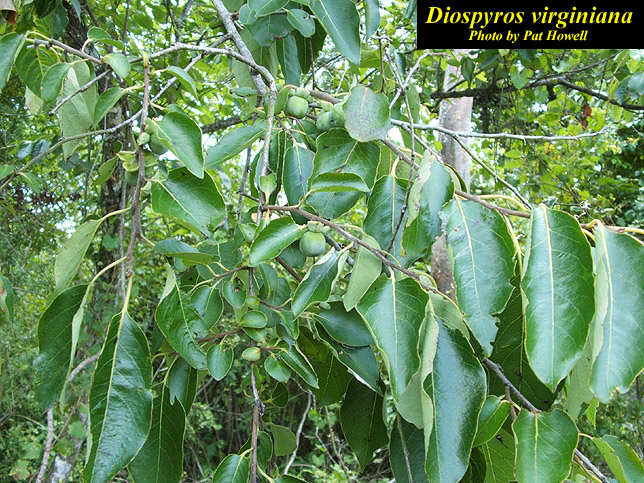

| |
| Photo by the Atlas of Florida Plants Database | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Ebenales |
| Family: | Ebenaceae |
| Genus: | Diospyros |
| Species: | D. virginiana |
| Binomial name | |
| Diospyros virginiana L. | |
| |
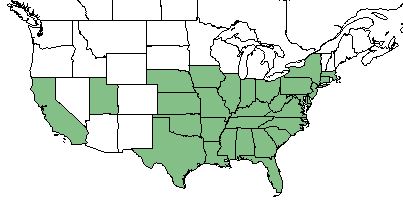
| Natural range of Diospyros virginiana from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonym: D. virginiana var. pubescens (Pursh), D. virginiana var. platycarpa (Sargent), D. mosieri (Small)
Variety:none
Description
D. virginiana is a perennial tree of the Ebenaceae family native to North America. [1]
Distribution
D. virginiana is found throughout the east coast and southeastern United States as well as California and Nevada. [1]
Ecology
Habitat
D. virginiana is easily adaptable to a variety of habitats. It is found in rocky hillsides, sandy woodlands, and even river bottoms. It prefers, terraces of streams and river bottoms that have clay in the soil. It prefers full sun but can tolerate shade. [1]
D. virginiana is considered one of the most common mid-story vegetation in the Upper Panhandle Savanna. [2]
A variety of habitats have been visited for samples of D. virginiana including mixed woodlands, pine wiregrass community, lowland woodlands, old field, dry sandy soils, edge of branch swamp, and sandy ridge near swamp. [3]
Phenology
D. virginiana has been observed flowering in April and May. [4]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by consumption by vertebrates. [5]
Fire ecology
Prescribed burns can be used to control the species, but fire exclusion can decrease its likelihood of surviving. [1]
Use by animals
Bess use the nectar from the flowers for honey. White-tailed deer eat the twigs and leaves. The fruit of the tree is eaten by squirrel, fox, skunk, deer, bear, coyote, racoon, opossum, quail, wild turkey, catbird, cedar waxwing and other various birds. [1]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 USDA Plant Database
- ↑ Carr, S. C., et al. (2010). "A Vegetation Classification of Fire-Dependent Pinelands of Florida." Castanea 75(2): 153-189.
- ↑ URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: R.K. Godfrey, Cecil Slaughter, Loran Anderson, T.Lott, B. Lund, Tom Barnes, Richard Mitchel, Gary Knight, Patricia Elliot, Bruce Hansen, Anne Perkins, Gwynn Ramsey, Karen MacClendon, M. Boothe, Leon Neel, Richard Gaskalla, R. Komarek, A. Johnson, M, Jenkins, Richard Carter. States and counties: Florida (Marion, Massau, Liberty, Franklin, Leon, Alachua, Wakulla, Highlands, Hernando, Jackson, Taylor, Collier, Lee, Sarasota, Gadsden, Suwannee, Calhoun, Washington, Holmes, Gulf) Georgia (Thomas, Grady, Lee)
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 21 MAY 2018
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.