Castanea pumila
Common name: Chinquapin [1], Common Chinquapin [2]
| Castanea pumila | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by the Atlas of Florida Plants Database | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Fagales |
| Family: | Fagaceae |
| Genus: | Castanea |
| Species: | C. pumila |
| Binomial name | |
| Castanea pumila (L) Mill. | |
| |
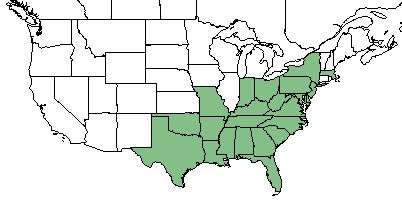
| Natural range of Castanea pumila from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: Castanea pumila (Linnaeus) P. Miller var. pumila, Castanea pumila (Linnaeus) P. Miller var. ashei Sudworth; Castanea alnifolia Nuttall var. alnifolia; Castanea alnifolia Nuttall var. floridana Sargent; Castanea ashei (Sudworth) Sudworth; Castanea floridana (Sargent) W.W. Ashe; Castanea alnifolia Nuttall
Varieties: none
Description
C. pumila is a perennial shrub/tree of the Fagaceae family native to North America.[1] Tree is single or multi-trunked with horizontal lower branches, which are ascending in the upper crown.[3] Twigs tomentose when young, and become shiny brown with densely hairy and reddish buds. Leaves alternate, simple, prominently veined, short-stemmed, tomentose on underside, and oblong shape with fine pointed teeth. Male flowers located in leaf axils, clustered, elongated, yellow or white in color, and have a strong odor. Female flowers more round. Fruit houses a single nut in a spiny bur.[4]
Distribution
C. pumila can be found along the southeastern coast of the United States, from Texas to Massachusetts.[1] However, it is rare in its natural range.[4]
Ecology
Habitat
C. pumila is found in xeric forests and woodlands. [2] It is also found along sand ridges. [5] Additionally, C. pumila is found in deciduous woods, old field areas, and sandy soil areas. [6]
Phenology
C. pumila has been observed to flower between March and June. [7]
Seed bank and germination
For propagation purposes, seeds must be sown in the fall or stratified for germination with the husks removed. For best results, the seeds should be stratified between 30 and 60 days at 41 degrees.[3]
Fire ecology
C. pumila is found mostly in fire-maintained habitats. [2] It is not fire resistant, but has a high fire tolerance. [1]
Use by animals
C. pumila is highly palatable to browsing animals and is edible by humans, but is not very palatable to grazing animals.[1] The nuts are eaten by squirrels, white-tailed deer, bobwhite quail, grouse, wild turkey, chipmunks, opossums, blue jays, woodpeckers, and other various birds. White-tailed deer also browse the foliage.[4][8] The nuts were a favorite of Native Americans.[3] Historically, the Cherokee Native American tribe used the dried leaves as washes to alleviate fevers, chills, headaches, fever blisters, and cold sweats. As well, the Koasati tribe utilized the roots to treat stomachaches. Today, chinkapin nuts as well as the wood are sold commercially.[4] It is also a larval host for the Orange-tipped oakworm moth (Anisota senatoria).[3]
Diseases and parasites
C. pumila is relatively resistant to chestnut blight. [2]
Conservation and Management
It is listed as threatened by the Kentucky State Nature Preserves Commission, and listed as endangered by the New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection and Energy.[1] C. pumila has also mostly been extirpated by chestnut blight in Alabama.[4]
Cultivation and restoration
The known cultivar of C. pumila is 'Golden' in Georgia, released in cooperation by the USDA-NRCS Plant Materials Center in Quicksand, Kentucky, the Kentucky Agricultural Experiment Station, and the Kentucky Department of Fish & Wildlife.[8]
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 USDA Plant Database https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CAPU9
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 [[1]] Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center. Accessed: April 2, 2019
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Wennerberg, S. (2006). Plant Guide: Chinkapin Castanea pumila. N.R.C.S. United States Department of Agriculture. Baton Rouge, LA.
- ↑ Johnson, A. S. and J. L. Landers (1978). "Fruit production in slash pine plantations in Georgia." The Journal of Wildlife Management 42(3): 606-613.
- ↑ URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Robert K. Godfrey, Wayne R. Faircloth, A. F. Clewell, C. Jackson, H. Kurz, W. D. Reese, Wilson Baker, R. Kral, Robert W Simons, Richard S. Mitchell, Erdman West, Angus Gholson, George P. Johnson, Lucy B. Abbe, Ernst C. Abbe, Robert F. Martin, R. F. Thorne, R. A. Davidson, D.B. Ward, R.B. Smith, John K. Small, Ed Keppner, Lisa Keppner, Rodie White, R. Komarek, Andre F. Clewell, D. Demaree, Kathleen Craddock Burks, Travis MacClendon. States and counties: Leon County Florida, Calhoun County Florida, Santa Rosa County Florida, Wakulla County Florida, Suwannee County Florida, Hamilton County Florida, Walton County Florida, Okaloosa County Florida, Columbia County Florida, Jackson County Florida, Alachua County Florida, Duval County Florida, Escambia County Florida, Madison County Florida, Gilchrist County Florida, Bay County Florida, Liberty County Florida, Washington County Florida, Gadsden County Florida, Grady County Georgia, Thomas County Georgia, Decatur County Georgia, Carroll County Arkansas, Franklin County Florida, Autauga County Alabama.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 18 MAY 2018
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 USDA NRCS Plant Materials Program. (2006). Plant Fact Sheet: Allegheny Chinkapin Castanea pumila. N.R.C.S. United States Department of Agriculture.