Balduina angustifolia
| Balduina angustifolia | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae ⁄ Compositae |
| Genus: | Balduina |
| Species: | B. angustifolia |
| Binomial name | |
| Balduina angustifolia (Pursh) B.L. Rob. | |
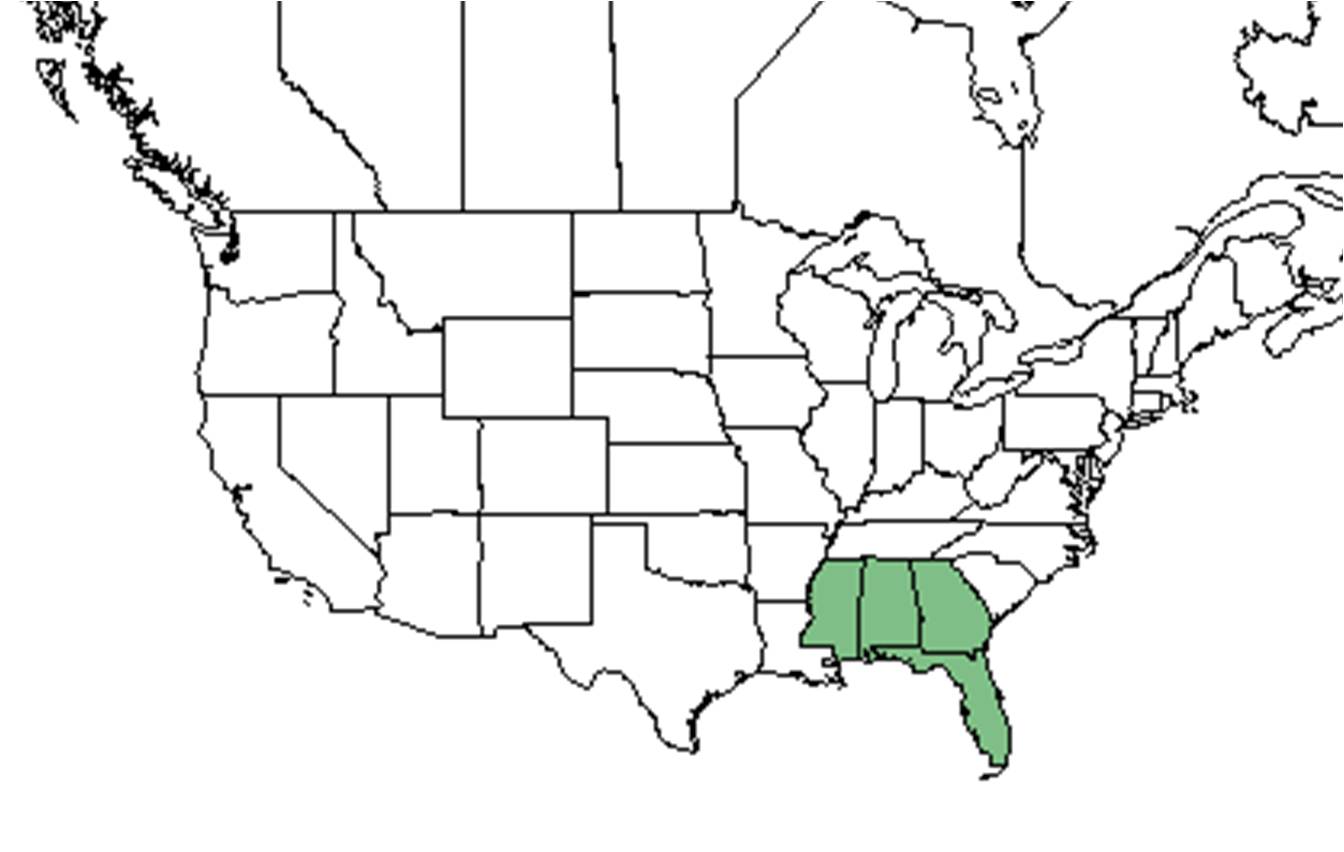
| |
| Natural range of Balduina angustifolia from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Coastal plain honeycombhead
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Balduina multiflora
Description
A description of Balduina angustifolia is provided in The Flora of North America.
The genus Balduina is characterized by receptacular bractlets connected in a honeycomb like structure surrounding the achene (Small 1933). It is a biennial species that forms a basal rosette the first year and a leafy flowering stem the second year (Anderson and Menges 1997). It can grow up to 4-5 feet in height, with many side branches near the top [1].
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain in Florida, B. angustifolia has been found in sand dunes; turkey oak sand ridges; pine scrubs; rosemary-oak scrub sandridge; scrub oak-longleaf pine ridges; wiregrass/longleaf pine sandhills; pine flatwoods; bordering sidestreams; open woodlands; and xeric oak/saw palmetto scrubs (FSU Herbarium).There are greater populations of B. angustifolia in bare, open sands than in sites with shrubs or litter, making it a gap specialist (Stephens et al. 2013). It is early successional species and has been found to have a greater population growth in degraded scrubs compared to intact scrubs (Stephens et al. 2013). It has been found in disturbed areas such as roadsides, highways, powerline corridors, bulldozed scrub oak ridges and clobbered slash pine forest (FSU Herbarium). Soil types include deep sand and loamy sand (FSU Herbarium). Associated species include Gaillardia, Pityopsis, Polygonella, Chrysoma, Ceratiola ericoides, Liatris, Leptoloma cognatum, Pinus clausa, and Quercus virginiana (FSU Herbarium).
Sandhill and scrub habitats have a low availability of inorganic nutrients such as phosphorous causing B. angustifolia to depend on mycorrhizal fungi colonization on the taproot system (Anderson and Menges 1997).
Phenology
Both the disc and ray flowers are yellow, with the ripe disc flowers forming a grey honeycomb shape seed [1]. The ripe seed can remain attached to the stem for months, allowing for favorable germination conditions in late winter and early spring[1]. It has been observed flowering August through November and fruiting September and October (FSU Herbarium).
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
Following a fire, the first year rosettes were unable to survive or resprout, making it a fire-sensitive biennial (Anderson and Menges 1997). However, populations have been found to later re-establish on a burn site from seed (Anderson and Menges 1997).
Pollination
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of Balduina angustifoliaat Archbold Biological Station (Deyrup 2015):
Andrenidae: Andrena fulvipennis
Apidae: Apis mellifera, Bombus impatiens, B. pennsylvanicus, Nomada fervida, Svastra aegis, Triepiolus concavus
Halictidae: Agapostemon splendens, Augochlora pura, Augochlorella aurata, Augochloropsis metallica, A. sumptuosa, Dieunomia heteropoda, Halictus poeyi, Lasioglossum coreopsis, L. miniatulus, L. nymphalis. L. pectoralis, L. puteulanum
Megachilidae: Anthidiellum perplexum, Coelioxys dolichos, C. germana, C. mexicana, C. modesta, C. sayi, C. texana, Dolichostelis louisae, Megachile albitarsis, M. brevis pseudobrevis, M. georgica, M. inimica, M. mendica, M. petulans, M. policaris, M. pruina, M. texana, M. xylocopoides, Trachusa fontemvitae
Sphecidae: Bembix sayi, Bicyrtes capnoptera, Ectemnius rufipes ais' Philanthus ventilabris
Vespidae: Mischocyttarus cubensis, Pachodynerus erynnis, Zethus slossonae
Use by animals
It is common in areas of soil disturbance produced by gopher tortoises (Anderson and Menges 1997).
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Global conservation status: G5[2].
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Deyrup, M.A. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowering plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: October 2015. Collectors: William P. Adams, Jame Amoroso, Loran C. Anderson, Robert Blaisdell, K.E. Blum, A.F. Clewell, George R. Cooley, Richard J. Eaton, R.K. Godfrey, H.E. Grelen, Bruce Hansen, JoAnn Hansen, Richard D. Houk, R. Kral, Bob Lazor, S.W. Leonard, Sidney McDaniel, Thomas E. Miller, J.B. Morrill, Putnam, James D. Ray Jr., Siri von Reis, Paul L. Redfearn Jr., Paul O. Schallert, Victoria I. Sullivan, Bian Tan, E.L. Tyson, Jean Wooten. States and Counties: Florida: Bay, Broward, Calhoun, Collier, Columbia, Clay, Columbia, Dixie, Escambia, Franklin, Hernando, Highlands, Jackson, Lafayette, Lee, Levy, Liberty, Madison, Manatee, Martin, Okaloosa, Osceola, Pinellas, Polk, Putnam, Santa Rosa, Sarasota, Seminole, Suwannee, Taylor, Walton, Wakulla. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 [Native Florida Wildflowers] Accessed December 1, 2015
- ↑ [NatureServe] Accessed: December 1, 2015