Angelica dentata
| Angelica dentata | |
|---|---|

| |
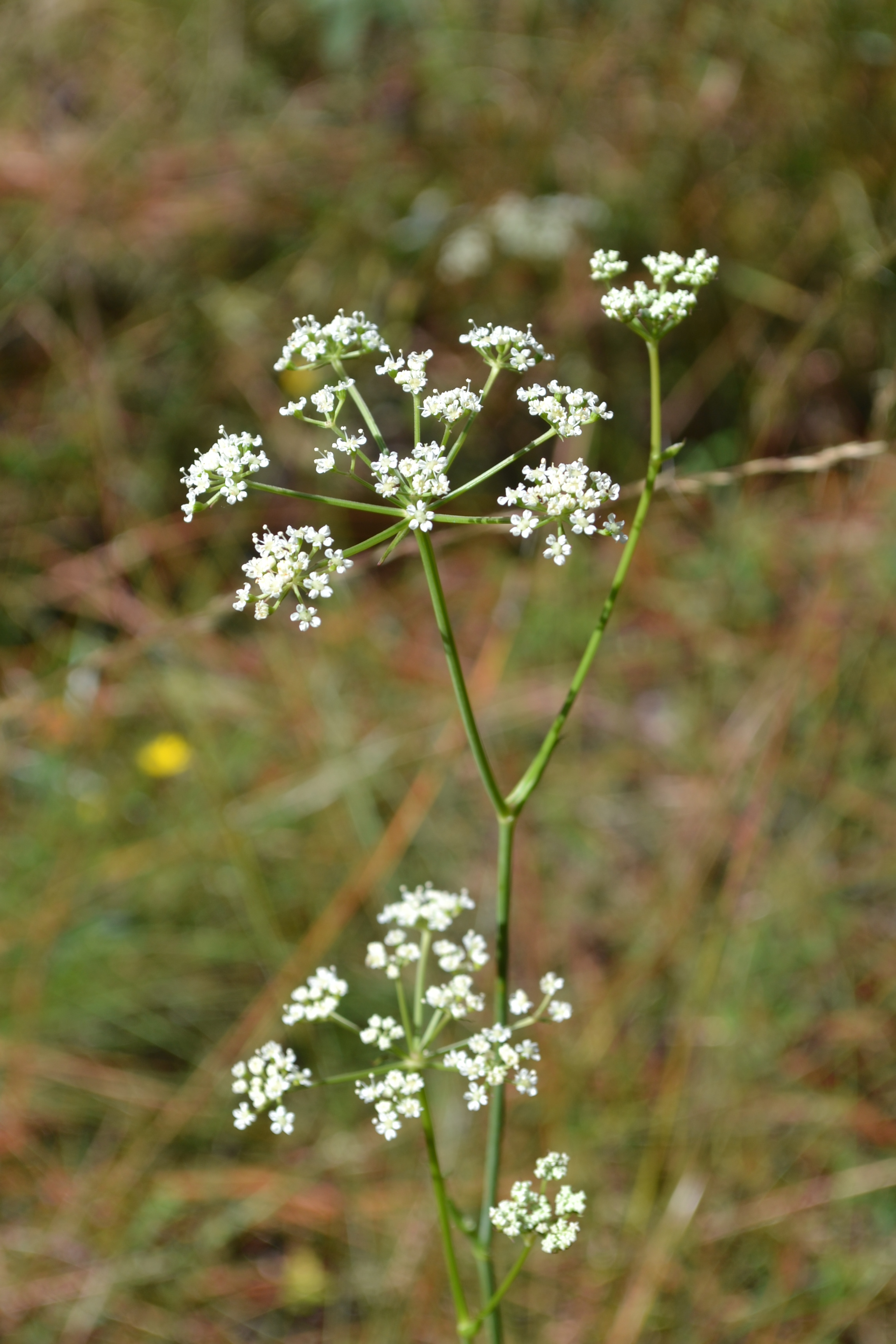
| Photo taken by Kevin Robertson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Apiales |
| Family: | Apiaceae ⁄ Umbelliferae |
| Genus: | Angelica |
| Species: | A. dentata |
| Binomial name | |
| Angelica dentata (Chapm.) J.M. Coult. & Rose | |
| |
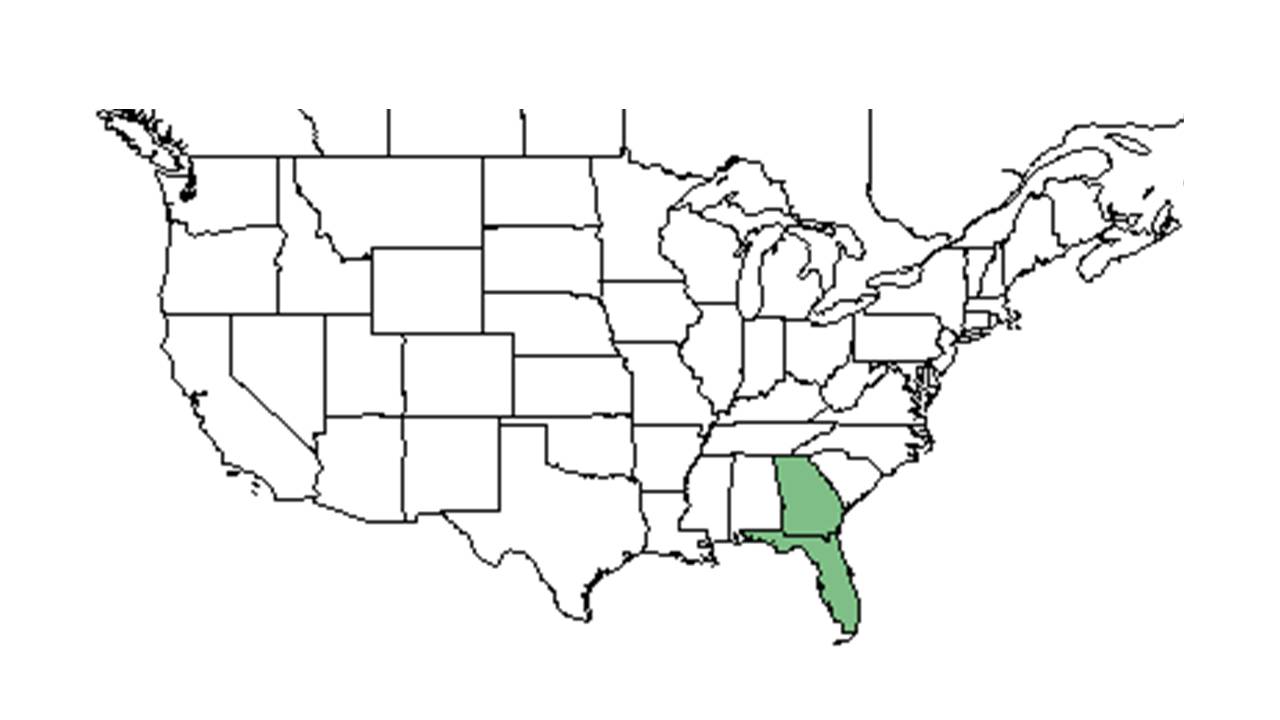
| Natural range of Angelica dentata from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Coastal Plain angelica; Sandhill angelica
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: none.[1]
Varieties: none.[1]
Description
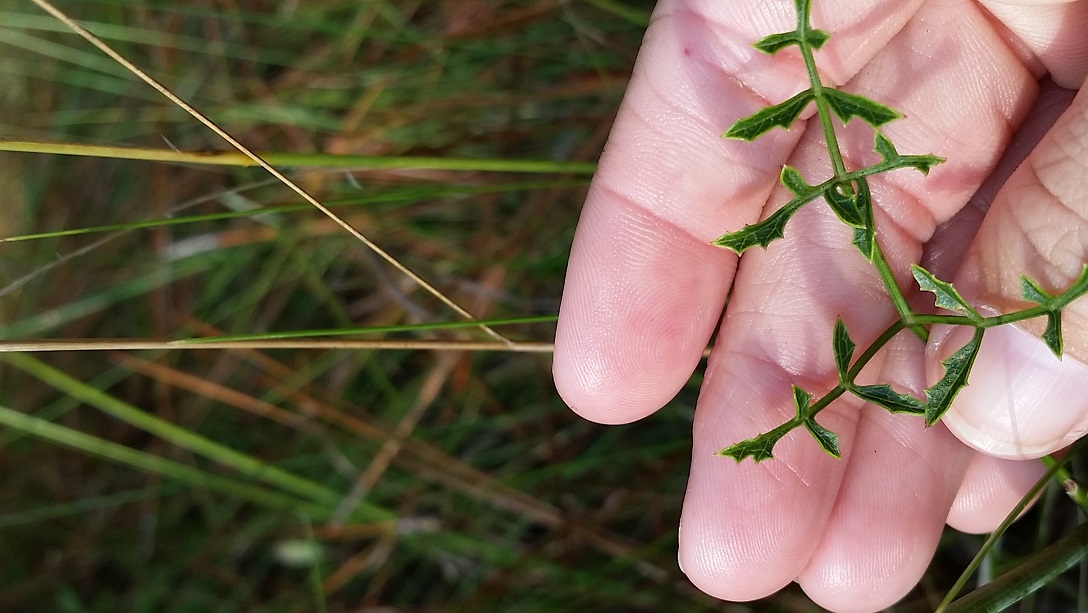
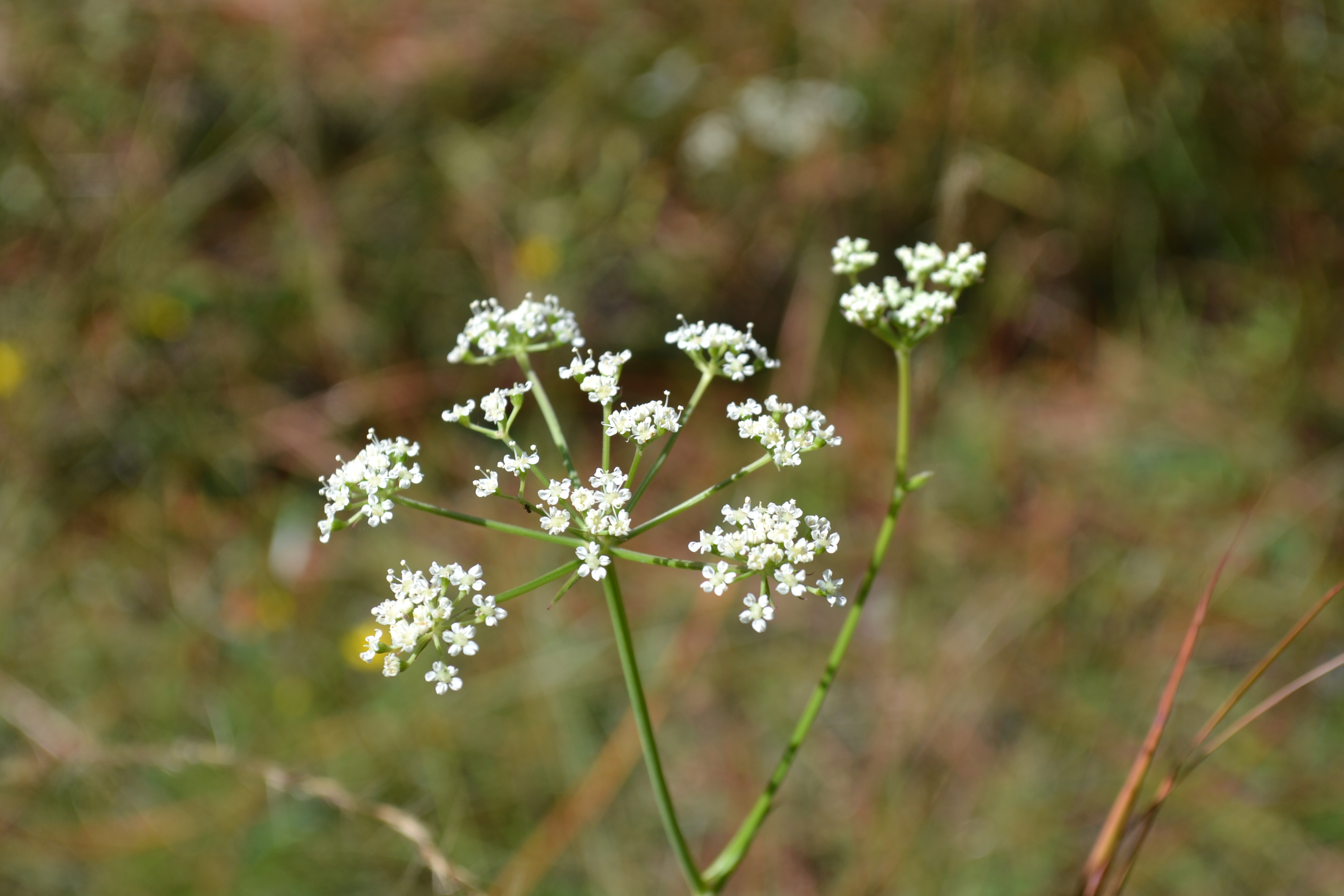
Angelica dentata is a perennial herb with erect, hairless stems growing 20 - 40 inches (50 - 100 cm) tall. The leaves grow on long leaf stalks, each leaf divided into several, leathery, lance-shaped, coarsely toothed leaflets. The flowers grow in flat-topped clusters, composed of 5 - 12 smaller clusters of tiny, white flowers. The flower stalks are hairless, and flowers themselves have 5 white, spreading petals. The fruits are about 1/4 inch (5 - 6 mm) long, hairless, oval, flattened, ribbed, and winged.[2] Flowers are arranged in umbels and are compound and bisexual.[3]
Distribution
It is found in southwest and south-central Georgia and in the eastern part of the panhandle of Florida.[1] However, one study found the presence of A. dentata in south Alabama.[4]
Ecology
Habitat
A. dentata is restricted to native groundcover and is commonly associated with upland pinelands of South Georgia. It was found to decrease in coverage in response to agricultural disturbance in southwest Georgia. Additionally, it has shown resistance to regrowth in reestablished native pine communities that had been disturbed by agricultural practices.[5] Habitats include sandhills, longleaf pine-wiregrass savannas, longleaf-scrub oaks, boggy areas, and pine flatwoods. It occurs in disturbed areas such as roadsides and logged fields. Thrives in areas that are open or semi-shaded. Soils include dry sand, gravelly soil, loamy sand and dry and moist loamy soil.[6][1]
Angelica dentata is an indicator species for the Panhandle Silty Longleaf Woodlands community type as described in Carr et al. (2010).[7]
Associated species: Croton sp., Pinus palustris, Quercus laevis, Quercus margaretta, Rhynchosia sp., Symphyotrichum dumosum, Carphephorus odoratissiumus, Carphephorus paniculatus, Chrysopsis sp., and Symphiotrichum dumosum.[6]
Phenology
Angelica dentata has been observed to flower June through January.[6][8]
Seed dispersal
Seeds are dispersed by gravity and small animals.[2]
Fire ecology
It can be found in frequently burned areas such as longleaf pine savannas.[6]
Pollination and use by animals
Angelica dentata is pollinated by wasps, flies, beetles and bees.[2] In Franklin County, FL, wasp pollinators include those from the family Vespidae.[9]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Threats include conversion of habitat to pine plantations, agriculture, pastures, development and fire suppression.[2][[1]]</ref>
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 [[2]]Georgia Wildlife. Accessed: March 29, 2016
- ↑ [[3]]Accessed: March 29, 2016
- ↑ Carter, R. E., et al. (2004). "Species composition of fire disturbed ecological land units in the Southern Loam Hills of south Alabama." Southeastern Naturalist 3: 297-308.
- ↑ Ostertag, T.E., and K.M. Robertson. 2007. A comparison of native versus old-field vegetation in upland pinelands managed with frequent fire, South Georgia, USA. Pages 109–120 in R.E. Masters and K.E.M. Galley (eds.). Proceedings of the 23rd Tall Timbers Fire Ecology Conference: Fire in Grassland and Shrubland Ecosystems.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: L. C. Anderson, W. Baker, B. Boothe, M. Boothe, A. F. Clewell, V. Craig, M. A. Garland, R. K. Godfrey, R. Kral, E. Keppner, L. Keppner, R. Komarek, T. MacClendon, K. MacClendon, R. A. Pursell, H. Roth, and R. White. States and Counties: Florida: Bay, Calhoun, Franklin, Gadsden, Jackson, Leon, Liberty, and Wakulla. Georgia: Decatur, Grady, and Thomas.
- ↑ Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 7 DEC 2016
- ↑ Observation by Floyd Griffith in Franklin County, FL, November 14, 2015, posted to Florida Flora and Ecosystematics Facebook group November 16, 2015.

