Rivina humilis
| Rivina humilis | |
|---|---|
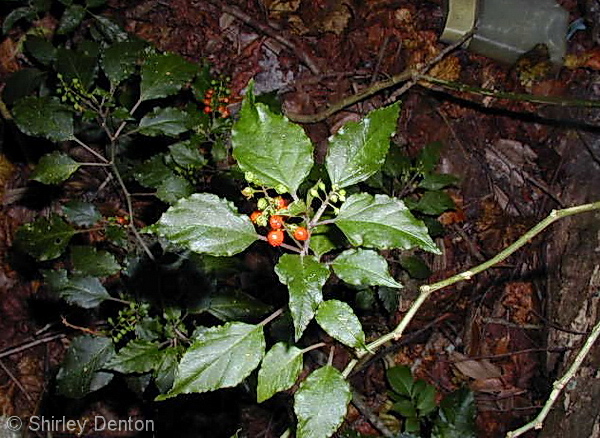

| |
| Photo by Shirley Denton (Copyrighted, use by photographer’s permission only), Nature Photography by Shirley Denton | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Caryophyllales |
| Family: | Phytolaccaceae |
| Genus: | Rivina |
| Species: | R. humilis |
| Binomial name | |
| Rivina humilis L. | |
| |
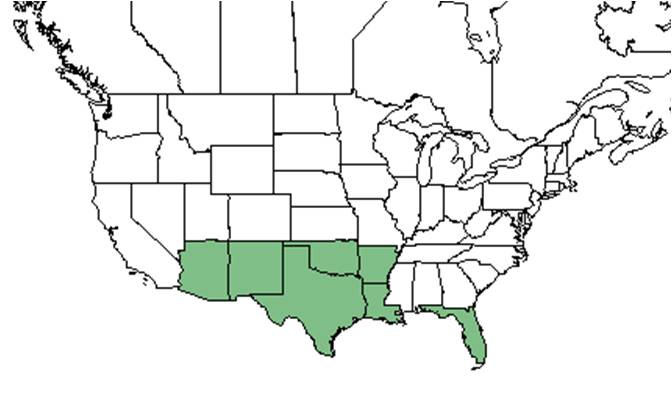
| Natural range of Rivina humilis from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Bloodberry rougeplant, Rougeplant, Pigeonberry, Baby-pepper
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: none
Varieties: none
Description
A description of Rivina humilis is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
It is found in southern North America from Florida to Arizona, north to Oklahoma and Arkansas, south through central America and the Caribbean to tropical South America.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
R. humilis has been found in sandy coastal hammocks, [2]
Habitats of include damp shady sites, riparian vegetationCite error: Closing </ref> missing for <ref> tag It is usually found on moist to well drained soils in both light shade and partial sun.[3]
Phenology
Blooms March through October.[1]
Pollination
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of Rivina humilis at Archbold Biological Station:[4]
Halictidae: Lasioglossum pectoralis
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Used in the southwest as red dye.[3] This species is poisonous.[5]
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 [[1]]Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center. Accessed: March 10, 2016
- ↑ Florida State University Herbarium Database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: May 2021. Collectors: R. Kral. States and counties: St. Lucie.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 [[2]]Accessed: March 10, 2016
- ↑ Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
- ↑ [[3]] Accessed: March 10, 2016