Oenothera biennis
Common name: common evening primrose[1]
| Oenothera biennis | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by John Hilty at IllinoisWildflowers.info | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Myrtales |
| Family: | Onagraceae |
| Genus: | Oenothera |
| Species: | O. biennis |
| Binomial name | |
| Oenothera biennis L. | |
| |
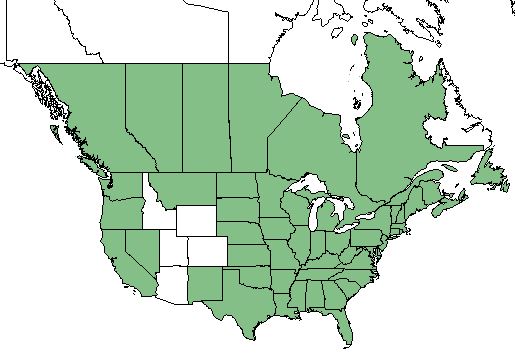
| Natural range of Oenothera biennis from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: none.[2]
Varieties: none.[2]
Description
O. biennis is a biennial forb/herb of the Onagraceae family native to North America and Canada.[1] Its leaves are green to pale green and the stems, ovary, floral tube, and sepals sparsely appressed-pubescent. Its fruit is terete, thickest near the base, and tapering to the apex. The capsules are colored gray-green or dull green while the seeds are borne horizontally in the locules, angled-prismatic, and not regularly pitted. There should be 50 to many seeds per capsule, all 0.3-2 mm long. The inflorescence is erect at the apex and the flower is yellow. The petals are 0.7-2.5 cm long, the stigma is surrounded by or below the anthers, the stamens are all equal in length, and the sepals are erect in the bud.[2]
Distribution
O. biennis is found in all of the United States and Canada excluding Idaho, Wyoming, Utah, Colorado, and Arizona.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
O. biennis proliferates in fields, pastures, roadsides, and disturbed areas.[3] Specimens have been collected from dry loamy sands, moist loamy sands, disturbed roadsides, trail clearings, the edges of old field habitat, road embankments, wet pinewood borders, the open bank of marshes, old fields, along the roads in hardwood forests, and parking area edges.[4]
Phenology
O. biennis flowers from June through October.[2]
Fire ecology
O. biennis is not fire resistant and has low fire tolerance.[1]
Conservation and Management
O. biennis is listed as a weedy or invasive plant by the University Press of Kentucky, the Nebraska Department of Agriculture Bureau of Plant Industry, and the Southern Weed Science Society.[1]
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 USDA Plant Database https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=OEBI
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, K. Craddock Burks, Gary Knight, R.K. Godfrey, Wilson Baker, Lisa Keppner, Ed Keppner, R.Komarek, Robert Lazor, Andre Clewell, Miguel Altieri, J.M. Kane. States and counties: Florida (Franklin, Nassau, Leon, Jefferson, Jackson, Madison, Wakulla, Liberty, Bay, Lee, Washington, Gulf.) Georgia (Grady, Thomas, Decatur)