Malus angustifolia
Common names: southern crab apple [1], crabapple, flowering crabapple [2]
| Malus angustifolia | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by the Southeastern Flora Database | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Rosales |
| Family: | Rosaceae |
| Genus: | Malus |
| Species: | M. angustifolia |
| Binomial name | |
| Malus angustifolia Michx. | |
| |
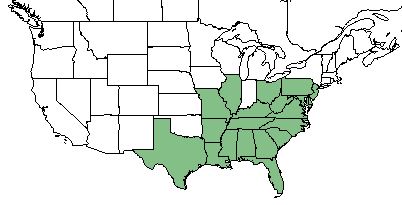
| Natural range of Malus angustifolia from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonym: Pyrus angustifolia (Aiton), Pyrus angustifolia var. spinosa (Rehder) L.H. Bailey
Variety: none
Description
M. angustifolia is a perennial shrub/tree of the Rosaceae family that is native to North America.[1]
Distribution
M. angustifolia is found throughout the southeastern United States; specifically in Florida, Georgia, Alabama, South Carolina, North Carolina, Virginia, Maryland, Pennsylvania, New Jersey, Deleware, West Virginia, Ohio, Kentucky, Tennessee, Arkansas, Mississippi, Louisiana, and Texas.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
Ideal habitats for the M. angustifolia is in well drained but moist soils in valleys and other slopes, stream beds, borders of woodlands, old fields in the southeast, and even fence rows. It requires full sun for successful fruit and flowers. [1]
Dry hammocks and occasionally bottomlands are habitats for M. angustifolia. [3] Specimens have been collected from loamy sand in xeric flatwoods, mesic woodland, pine flatwoods, pine woods, fence row, floodplain, upland mixed woodland, decidious woods, cultivated field, mesic hammock, sandy loam, wood bottoms and thickets. [4]
Phenology
Typical flowering season for M. angustifolia is a in the early spring; February through April with March normally producing the majority of the blooms.[5]
Pollination
M. angustifolia is mainly pollinated by bees, butterflies occasionally. .[6]
Use by animals
Whitetail deer will eat the fruit of the tree, as well as, bobwhites, grouse, pheasants, rabbits, squirrels, opposums, raccoons, skunks, foxes, and other small birds. [1]
Diseases and parasites
M angustifolia is prone to fireblight, cedar apple rust, apple scab, canker, scale, borers, and aphids. [1]
Conservation and Management
Florida has classified M. angustifolia as threatened; it is endangered in Illinois, and of special concern in Kentucky. [1]
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 USDA Plant Database
- ↑ Coile, N. C. (2000). Notes on Florida �s Regulated Plant Index (Rule 5B-40), Botany Contribution No. 38, 3nd edition. Gainesville, Florida, Florida Deaprtment of Agriculture and Consumer Services, Division of Plant Industry.
- ↑ Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, R.K. Godfrey, Patricia Elliot, John C. Ogden, R L Lazor, L R Fox, K Craddock Burks, Gary R Knight, R A Norris, M R Darst, R Komarek, H Roth, M Jenkins, Elmar C Prichard. States and counties: Florida (Wakulla, Leon, Gadsden, Jefferson, Liberty, Washington), Georgia (Thomas, Grady), North Carolina (Cumberland)
- ↑ Pan Flora
- ↑ Shared by Lisa Roberts; original post by Florida Wildflower Foundation; March 17, 2017, post shared to Florida Flora and Ecosystematics Facebook Group march 17, 2017.