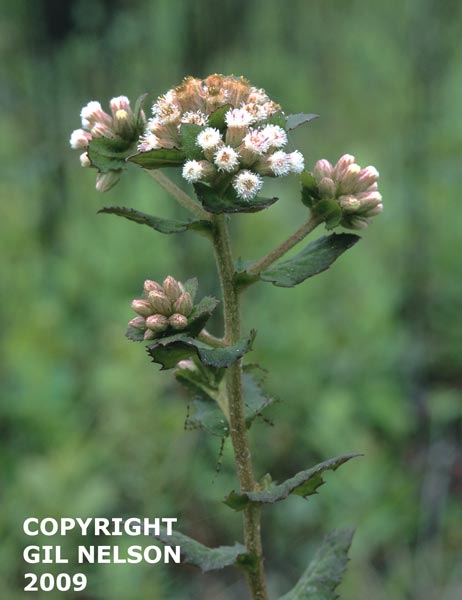
Pluchea foetida
| Pluchea foetida | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae ⁄ Compositae |
| Genus: | Pluchea |
| Species: | P. foetida |
| Binomial name | |
| Pluchea foetida (L.) DC. | |
| |
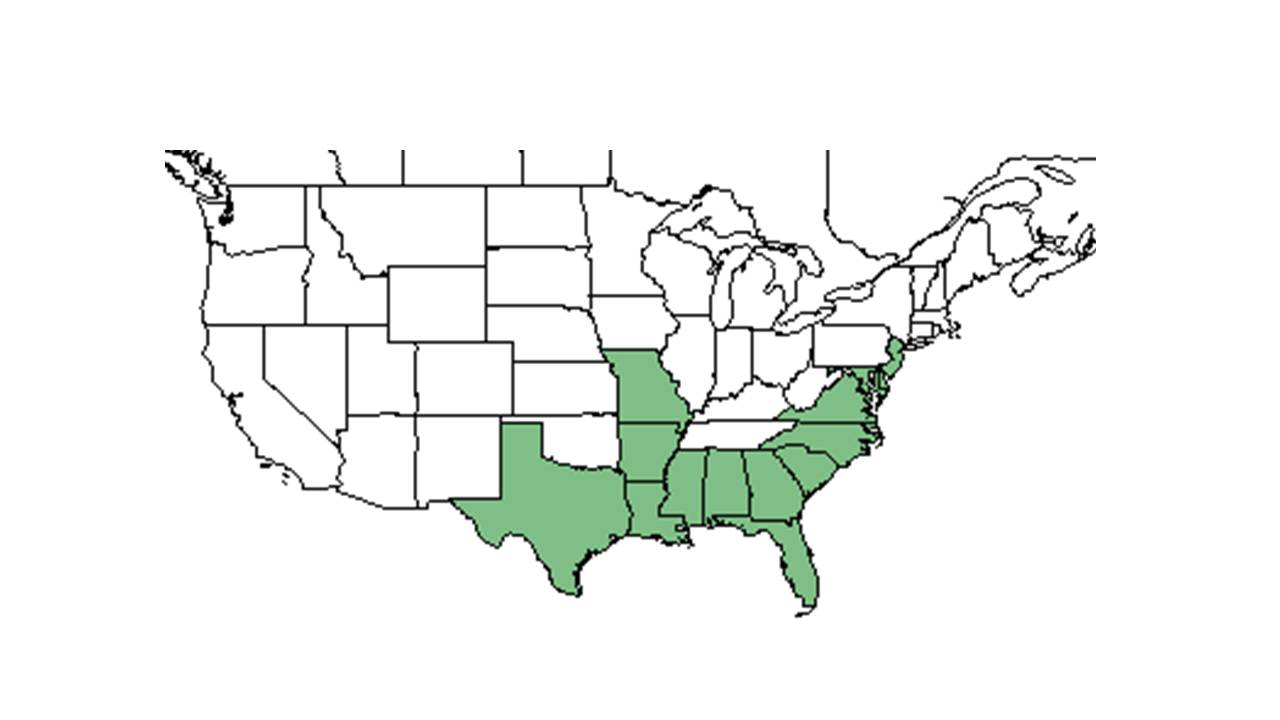
| Natural range of Pluchea foetida from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: stinking camphorweed
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Description
A description of Pluchea foetida is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain in Florida and Georgia, P. foetida can be found at edges of creeks and swampy woodlands, bordering deciduous forests, cypress-sweetgum swamps, cabbage palmetto/ water hickory hammocks, marshy areas, flatwood streams, deeply shaded floodplains, moist depression of sandbars, wet drainage bordering savannas, slash pine-wiregrass flatwoods, wiregrass/saw palmetto with scattered pines and cypress bays, swamp forests, open bogs, and semi shaded mesic woods along creek swamps (FSU Herbarium). It has also been documented to grow in sandy ditches bordering slash pine/gallberry flatwoods, clearings of swampy woodlands, and moist depressions along trails. Associated species include slash pine, gallberry, wiregrass, saw palmetto and cypress trees (FSU Herbarium).
It has been observed to grow in shaded and semi-shaded areas (FSU Herbarium). Soil types can include peaty soils, mucky moist loamy sands, coarse sands of a pond shore, and drying loamy soil (FSU Herbarium).
Phenology
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
Several short-lived perennial forbs also have a seed bank persistent for at least several years (Platt et al 2006).
Fire ecology
Pollination
Use by animals
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Platt, W. J., S. M. Carr, et al. (2006). "Pine savanna overstorey influences on ground-cover biodiversity." Applied Vegetation Science 9: 37-50.