Hypericum crux-andreae
| Hypericum crux-andreae | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Theales |
| Family: | Clusiaceae ⁄ Guttiferae |
| Genus: | Hypericum |
| Species: | H. crux-andreae |
| Binomial name | |
| Hypericum crux-andreae (L.) Crantz | |
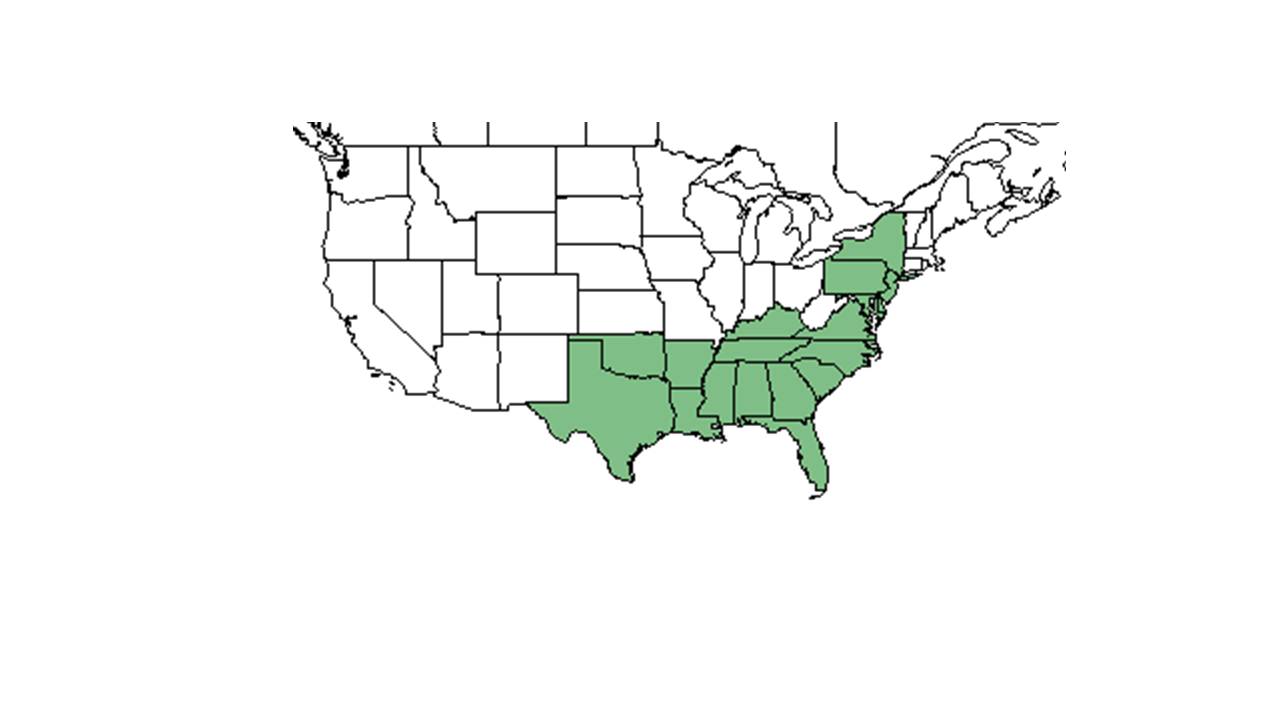
| |
| Natural range of Hypericum crux-andreae from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Description
Common Name: St. Peterswort
Hypericum crux-andreae is a perennial shrub.
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
It is found in flatwoods longleaf pine wiregrass ecosystem.[1]It is found in titi/cypress swamp community type of Florida.[2]
Phenology
Flowering has been observed in August through October, and fruiting has been observed in October (FSU Herbarium).
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
Several short-lived perennial forbs also have a seed bank persistent for at least several years.[3]
Fire ecology
This species has been found in habitat that burns frequently (FSU Herbarium)..
Pollination
Use by animals
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014.
Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Wilson Baker, Andre F. Clewell, M. Davis, R. F. Doren, Robert K. Godfrey, Ann F. Johnson, J. M. Kane, R. A. Norris, and Cecil R. Slaughter.
States and Counties: Florida: Duval, Franklin, Jackson, Leon, Liberty, and Wakulla. Georgia: Baker, Grady, and Thomas. Texas: Hardin.
- ↑ Brockway, D. G. and C. E. Lewis (1997). "Long-term effects of dormant-season prescribed fire on plant community diversity, structure and productivity in a longleaf pine wiregrass ecosystem." Forest Ecology and Management 96: 167-183.
- ↑ Drewa, P., W. Platt, et al. (2002). "Community Structure along Elevation Gradients in Headwater Regions of Longleaf Pine Savannas." Plant Ecology 160(1): 61-78.
- ↑ Platt, W. J., S. M. Carr, et al. (2006). "Pine savanna overstorey influences on ground-cover biodiversity." Applied Vegetation Science 9: 37-50.