Baccharis halimifolia
| Baccharis halimifolia | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by John R. Gwaltney, Southeastern Flora.com | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae ⁄ Compositae |
| Genus: | Baccharis |
| Species: | B. halimifolia |
| Binomial name | |
| Baccharis halimifolia L. | |
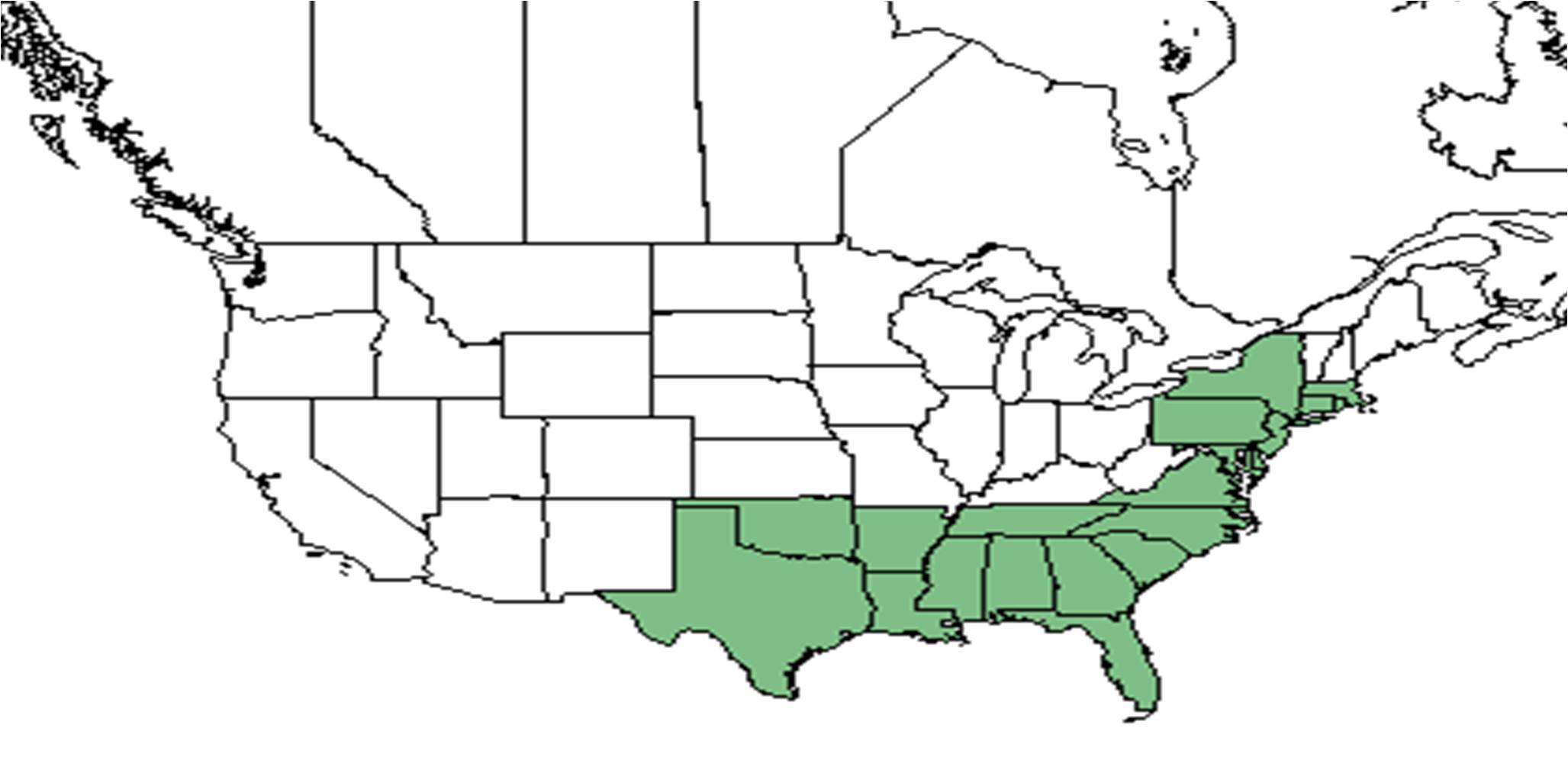
| |
| Natural range of Baccharis halimifolia from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: eastern baccharis
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonym: Baccharis halimifolia var. angustior de Candolle The Flora of North America.
Description
A description of Baccharis halimifolia is provided in The Flora of North America.
Baccharis genus are dioecious, glabrous shrubs. They are rarely small trees. The leaves are alternate, fleshy, toothed or entire. The heads pedunculated or sessile, most of the time in 3-5 glomerules. The involucres are cylindric, 4-5 mm long, 2.5-3.5 mm broad. The bracts are imbricate, sometimes purplish in color, and obtuse. The flowers are discoid and yellowish in color. The nutlets are tan in color, lustrous, cylindric, 10-ribbed, glabrous, and 1.2-1.5 mm long. The pappus bristles are white to tan in color. The capillary is 7-10 mm long.[1] Specifically for B. halimifolia, is a shrub, growing to approximately 1-4 m tall. The leaves are elliptic to obovate, rarely ovate; are coarsely serrate but mostly towards the apex, rarely entire. The leaves grow 3-7 cm long and 1-4 cm wide. The petioles are 5-12 mm long. The involucres are mostly in pedunculated glomerules. [1]
Ecology
Habitat
Phenology
Seed dispersal
According to Kay Kirkman, a plant ecologist, this species disperses by wind. [2]
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
Pollination
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of Baccharis halimifolia' at Archbold Biological Station. [3]
Apidae: Apis mellifera
Apidae: Bombus impatiens
Colletidae: Colletes mandibularis, C. simulans, C. thysanellae
Halictidae: Agapostemon splendens, Augochlora pura, Augochlorella aurata, Augochloropsis metallica, Halictus poeyi, Lasioglossum miniatulus, L. nymphalis, L. puteulanum, Sphecodes heraclei
Leucospidae: Leucospis affinis
Leucospididae: Leucospis affinis, L. robertsoni, L. slossonae
Pompilidae: Anoplius atramentaius, A. parsoni, Episyron conterminus posterus, Poecilopompilus algidus, P. interruptus
Sphecidae: Bicyrtes quadrifasciata, Cerceris blakei, C. flavofasciata floridensis, C. tolteca, Ectemnius decemmaculatus tequesta, E. rufipes ais, Larra bicolor, Oxybelus decorosum, O. laetus fulvipes, Palmodes dimidiatus, Philanthus ventilabris, Tachytes distinctus, T. floridanus, T. pepticus, T. validus
Vespidae: Pachodynerus erynnis, Parancistrocerus salcularis rufulus, Polistes bellicosus, P. dorsalis hunteri, P. fuscatus, P. metricus, P. perplexus, Stenodynerus beameri, S. fundatiformis, S. lineatifrons, Vespula squamosa, Zethus slossonae, Zethus spinipes
Use by animals
Diseases and parasites
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 635-6. Print
- ↑ Kay Kirkman, unpublished data, 2015.
- ↑ Deyrup, M.A. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.