Polypremum procumbens
| Polypremum procumbens | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Scrophulariales |
| Family: | Buddlejaceae |
| Genus: | Polypremum |
| Species: | P. procumbens |
| Binomial name | |
| Polypremum procumbens L. | |
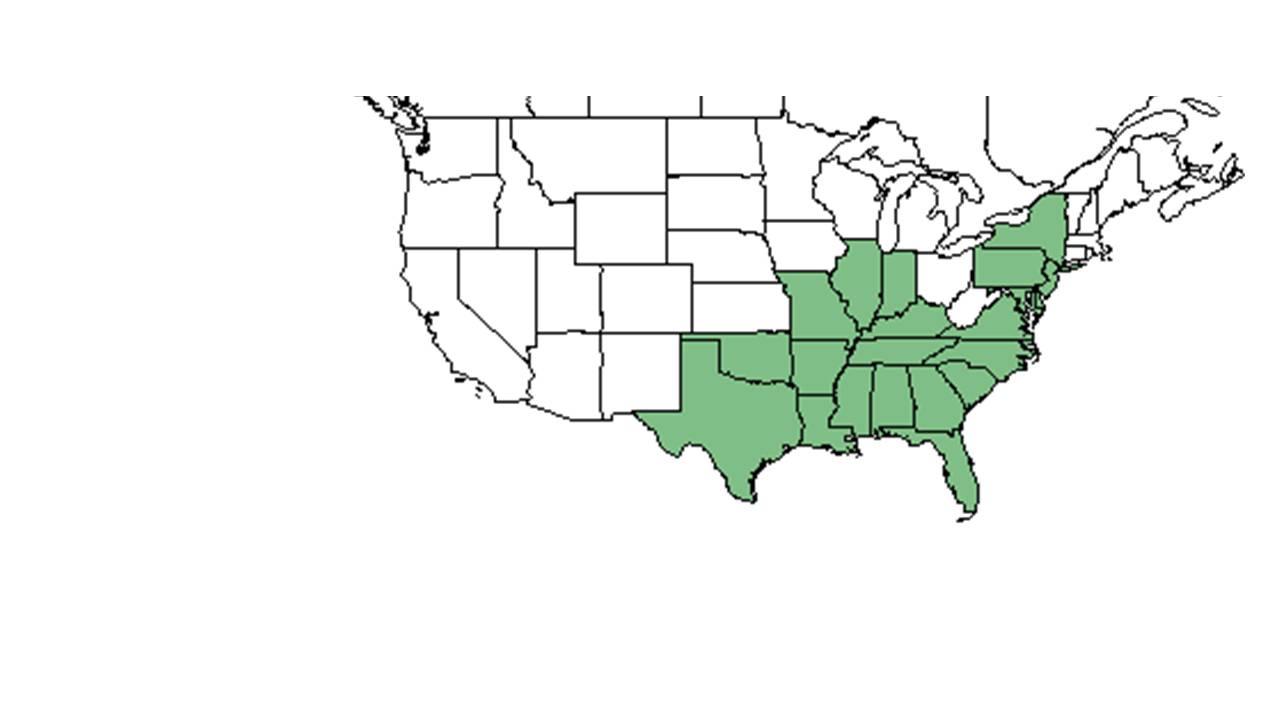
| |
| Natural range of Polypremum procumbens from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Juniper leaf, Rustweed
Contents
[hide]Taxonomic notes
Description
"Perennial, glabrous herb with radially ascending or repent branches from a central crown. Leaves opposite, linear, 1-2.5 cm long, 0.5-2 mm wide, acute. Inflorescence a terminal leafy cyme. Flowers actinomorphic, sessile or on pedicels less than 0.5 mm long. Calyx divided to near the base, teeth 4, subulate, 2-3 mm long; corolla divided 1/3 in length, 4-lobed, white, rotate; stamens 4, included. Capsule 1.5-2.5 mm long; seeds yellow, angulate, more or less square, microscopically pitted, 0.3-0.4 mm long."[1]
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain in Florida and Georgia, P. procumbens can be found near streamlet crossings in open woodlands, well drained sandy soils of citrus furrows, annually burned savannas, sandy shores of karst ponds, annually burned longleaf pinelands, well drained uplands, and coastal dunes.[2] It can also be found in compacted soils of roadways, frequently mowed lawns, and roadside depressions. P. procumbens responds positively to agricultural-based soil disturbance in South Carolina coastal plain communities. This marks it as a possible indicator species for post-agricultural woodland.[3] Associated species include Lindernia, Murdannia, Kyllinga and Sida.[2] It responds positively or not at all to soil disturbance by roller chopping and disturbance by a KG blade in East Texas Loblolly Pine-Hardwood Forests.[4]
Soil types include loamy sand and moist loam.[2]
Phenology
P. procumbens been observed flowering from May to September with peak inflorescence in July.[5][2] Fruiting has been observed in July.[2]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by gravity.[6]
Seed bank and germination
It was found viable in the seed bank of a pine flatwoods in Florida but only one year following fire.[7] Commonly found in seed banks of disturbed areas. [8] In a longleaf pine community in southwestern Georgia and in shrub dominated bays in eastern South Carolina, P. procumbens was found in the seedbank.[9] [10]
Pollination
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of Polypremum procumbens at Archbold Biological Station: [11]
Halictidae: Lasioglossum nymphalis
Megachilidae: Megachile brevis pseudobrevis
Sphecidae: Cerceris blakei, Microbembex monodonta
Vespidae: Stenodynerus fundatiformis
Use by animals
Deyrup observed this bee, Dialictus nymphalis, on P. procumbens.[12] Cover of P. procumbens decreased significantly through time after three grazing treatments (no grazing by deer or cattle, grazing by deer, or grazing by deer and cattle) in thinned and clearcut forested areas. [13]
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- Jump up ↑ Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 835. Print.
- ↑ Jump up to: 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Cecil R Slaughter, Dianne Hall, R. A. Norris, R. Komarek, R. F. Doren, S. W. Leonard, J. Mickel, Thomas E. Miller, Robert K. Godfrey. States and Counties: Florida: Duval, Gadsden, Jefferson, Leon, Polk, St. Johns, Wakulla. Georgia: Grady, Thomas. Mexico. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- Jump up ↑ Brudvig, L.A., E Grman, C.W. Habeck, and J.A. Ledvina. (2013). Strong legacy of agricultural land use on soils and understory plant communities in longleaf pine woodlands. Forest Ecology and Management 310: 944-955.
- Jump up ↑ Stransky, J.J., J.C. Huntley, and Wanda J. Risner. (1986). Net Community Production Dynamics in the Herb-Shrub Stratum of a Loblolly Pine-Hardwood Forest: Effects of CLearcutting and Site Preparation. Gen. Tech. Rep. SO-61. New Orleans, LA: U.S. Dept of Agriculture, Forest Service, Southern Forest Experiment Station. 11 p.
- Jump up ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 12 DEC 2016
- Jump up ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.
- Jump up ↑ Maliakal, S.K., E.S. Menges and J.S. Denslow. 2000. Community composition and regeneration of Lake Wales Ridge wiregrass flatwoods in retlation to time-since-fire. Journal of the Torrey Botanical Society 127:125-138.
- Jump up ↑ Maliakal, S. K., E. S. Menges, et al. (2000). "Community composition and regeneration of Lake Wales Ridge wiregrass flatwoods in relation to time-since-rire " The Journal of the Torrey Botanical Society 127: 125-138
- Jump up ↑ Andreu, M. G., et al. 2009. Can managers bank on seed banks when restoring Pinus taeda L. plantations in southwest Georgia? Restoration Ecology 17:586-596.
- Jump up ↑ Navarra, J. J. and P. F. Quintana-Ascencio 2012. Spatial pattern and composition of the Florida scrub seed bank and vegetation along an anthropegenic disturbance gradient. Applied Vegetation Science 15:349-358.
- Jump up ↑ Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
- Jump up ↑ Deyrup, M. J. E., and Beth Norden (2002). "The diversity and floral hosts of bees at the Archbold Biological Station, Florida (Hymenoptera: Apoidea)." Insecta mundi 16(1-3).
- Jump up ↑ Brockway, D. G. and C. E. Lewis (2003). "Influence of deer, cattle grazing and timber harvest on plant species diversity in a longleaf pine bluestem ecosystem." Forest Ecology and Management 175: 49-69.