Angelica dentata
| Angelica dentata | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo taken by Kevin Robertson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Apiales |
| Family: | Apiaceae ⁄ Umbelliferae |
| Genus: | Angelica |
| Species: | A. dentata |
| Binomial name | |
| Angelica dentata (Chapm.) J.M. Coult. & Rose | |
| |
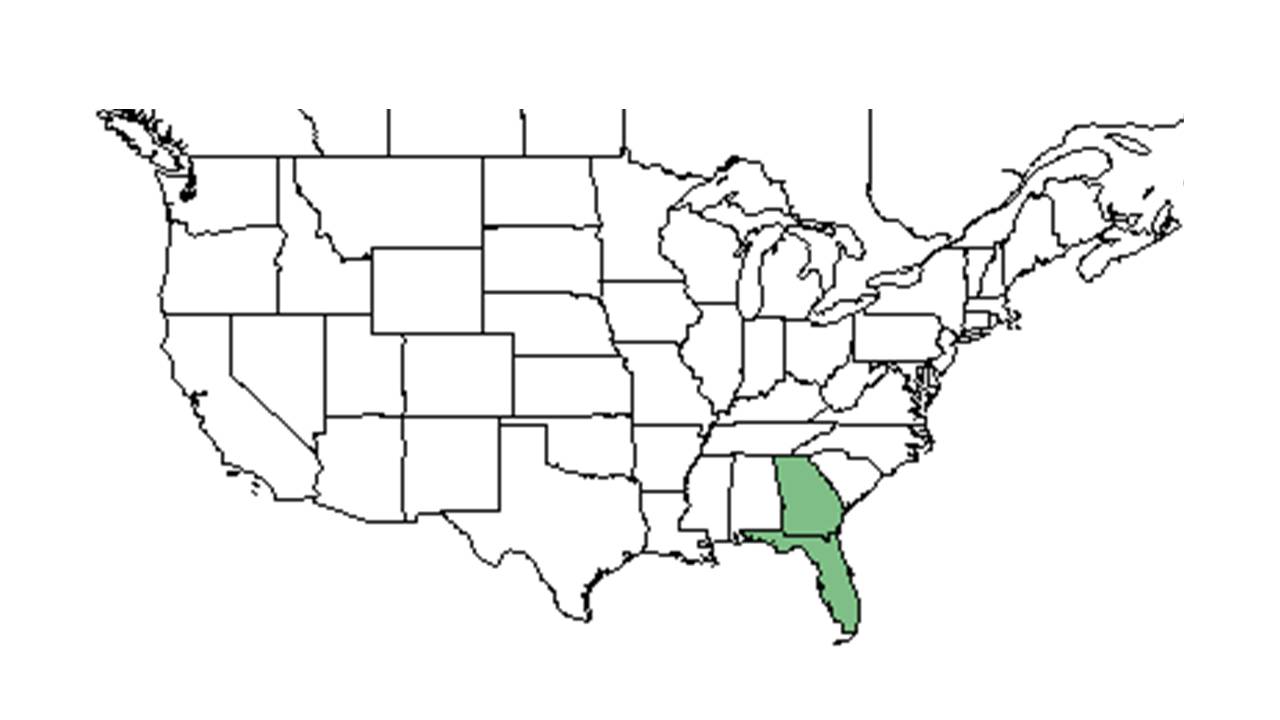
| Natural range of Angelica dentata from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Coastal Plain Angelica, Sandhill Angelica
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Description
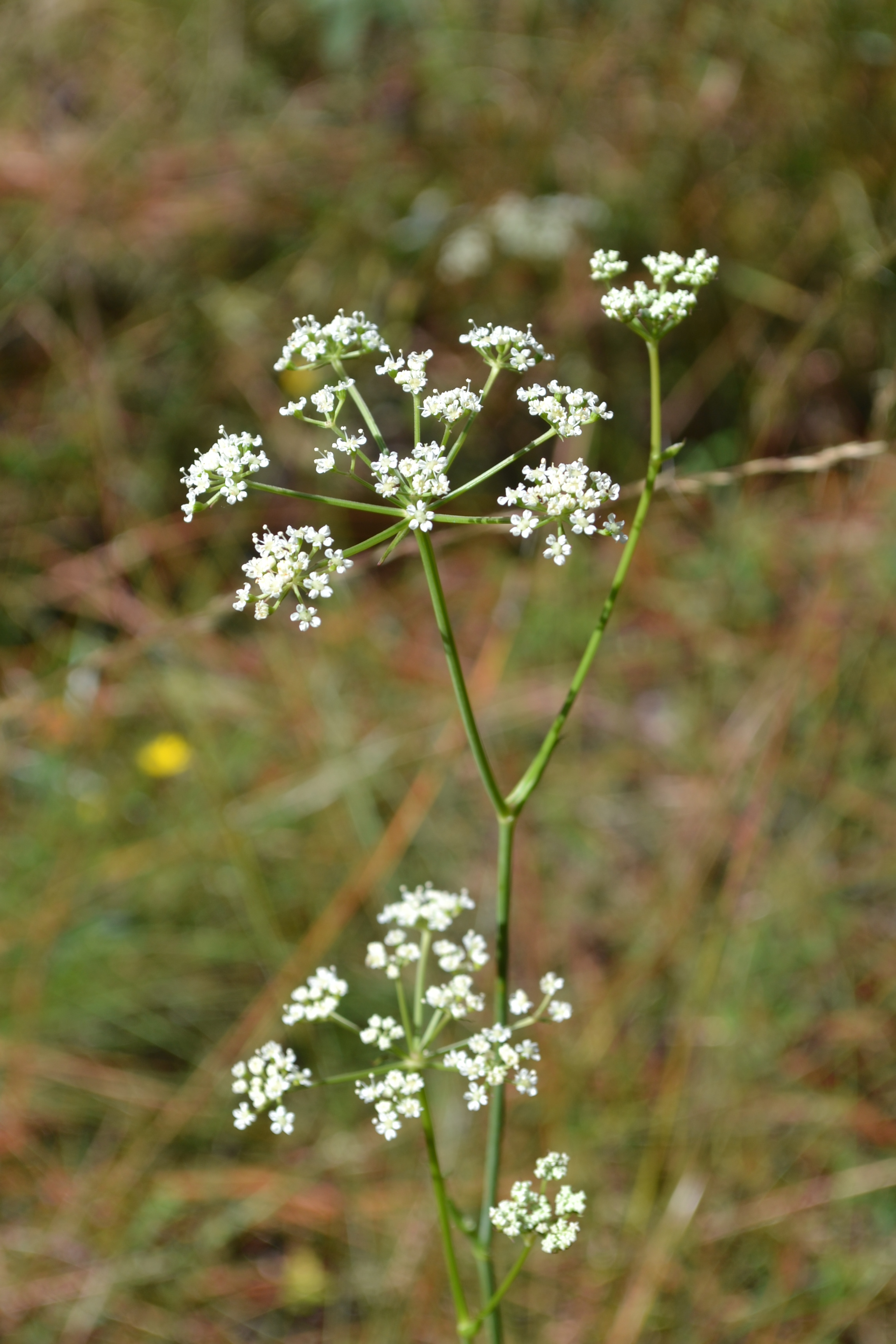
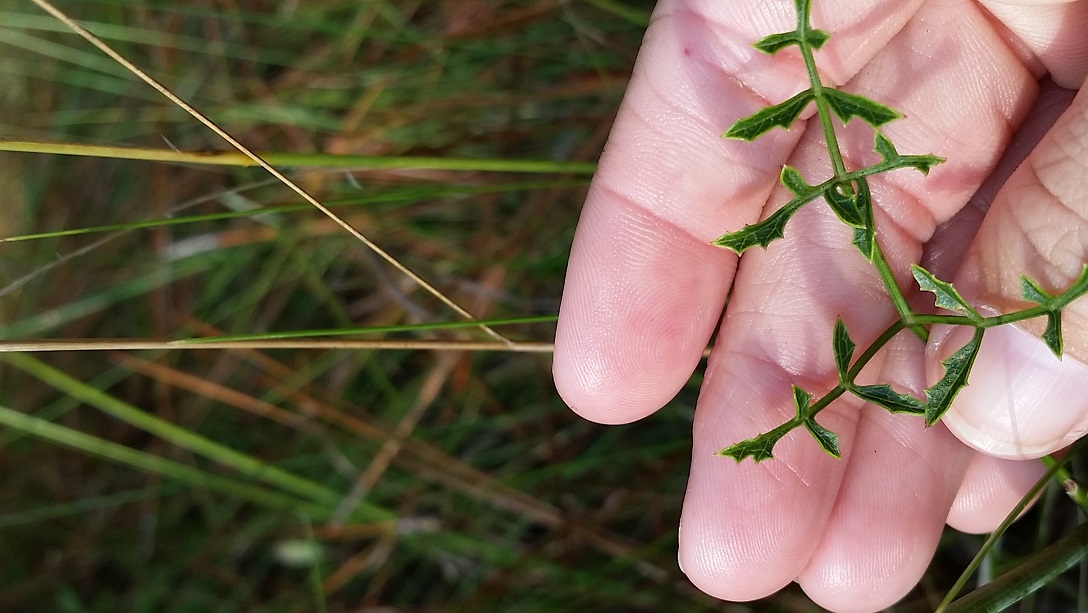
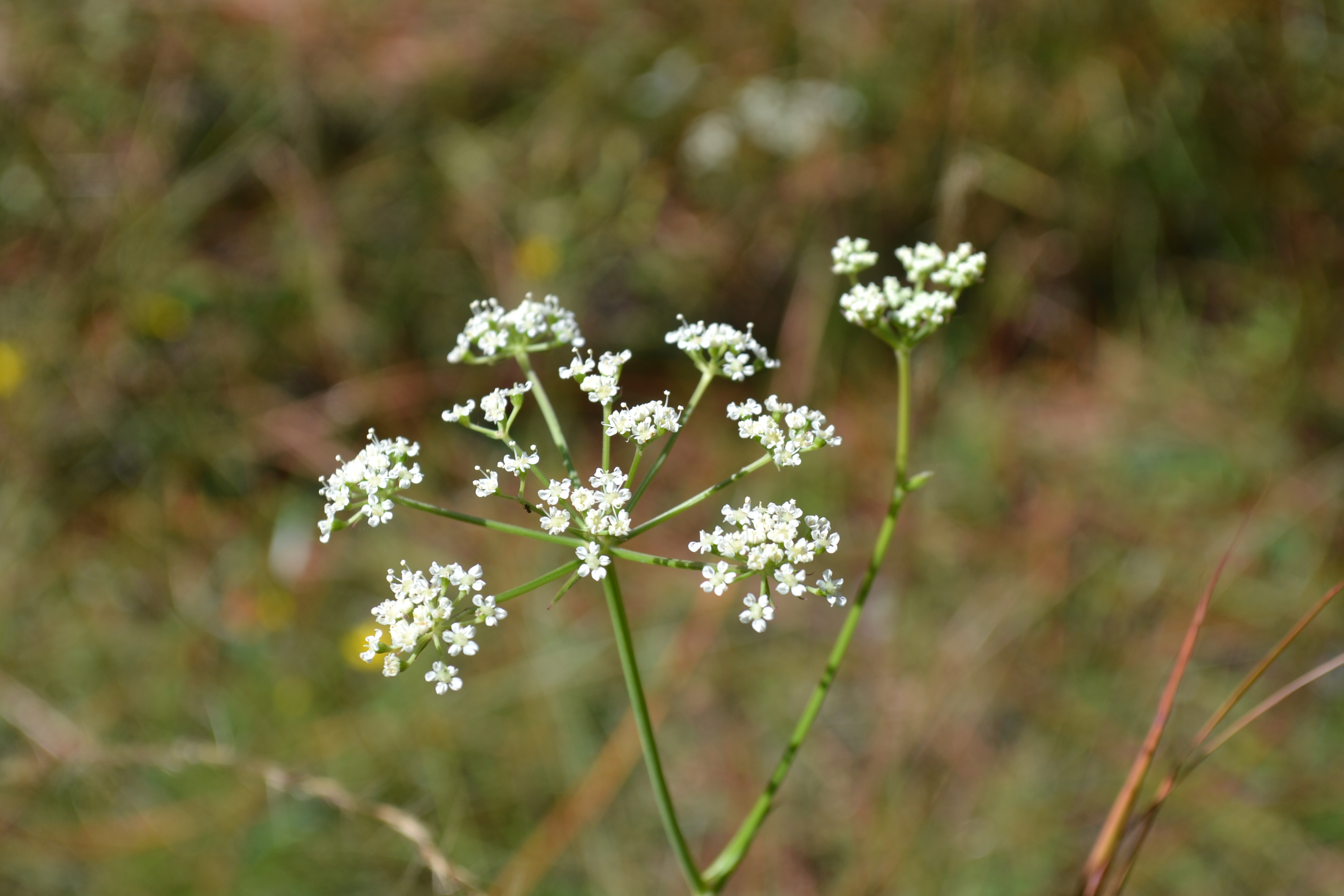
Perennial herb with erect, hairless stems 20 - 40 inches (50 - 100 cm) tall. Leaves with long leaf stalks, each leaf divided into several, leathery, lance-shaped, coarsely toothed leaflets. Flower clusters flat-topped, composed of 5 - 12 smaller clusters of tiny, white flowers; flower stalks hairless. Flowers with 5 white, spreading petals. Fruit about ¼ inch (5 - 6 mm) long, hairless, oval, flattened, ribbed, and winged.[1]
Distribution
It is found in southwest and south-central Georgia and in the eastern part of the panhandle of Florida.[2]
Ecology
Habitat
A. dentata is restricted to native groundcover and is commonly associated with upland pinelands of South Georgia[3]. Habitats include sandhills, longleaf pine-wiregrass savannas, longleaf-scrub oaks, boggy areas, and pine flatwoods. It occurs in disturbed areas such as roadsides and logged fields. Thrives in areas that are open or semi-shaded. Soils include dry sand, gravelly soil, loamy sand and dry and moist loamy soil[4][2].Associated species include Croton, Pinus palustris, Quercus laevis, Q. margaretta, Rhynchosia, Symphyotrichum dumosum, Carphephorus odoratissiumus, C. paniculatus, Chrysopsis spp., and Symphiotrichum dumosum[4].
Phenology
Flowers are arranged in umbels and are compound and bisexual[5]. Flowers June through December[4].
Seed dispersal
Seeds are dispersed by gravity and small animals[1].
Fire ecology
It can be found in frequently burned areas such as longleaf pine savannas.[4]
Pollination
Pollinated by wasps, flies, beetles and bees.[1]
Conservation and management
Threats include conversion of habitat to pine plantations, agriculture, pastures, development and fire suppression.[1]
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 [[1]]Georgia Wildlife. Accessed: March 29, 2016 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "georgia" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ 2.0 2.1 Weakley, Alan S. Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States: Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina Herbarium (NCU). PDF. 1227.
- ↑ Ostertag, T.E., and K.M. Robertson. 2007. A comparison of native versus old-field vegetation in upland pinelands managed with frequent fire, South Georgia, USA. Pages 109–120 in R.E. Masters and K.E.M. Galley (eds.). Proceedings of the 23rd Tall Timbers Fire Ecology Conference: Fire in Grassland and Shrubland Ecosystems.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: L. C. Anderson, W. Baker, B. Boothe, M. Boothe, A. F. Clewell, V. Craig, M. A. Garland, R. K. Godfrey, R. Kral, E. Keppner, L. Keppner, R. Komarek, T. MacClendon, K. MacClendon, R. A. Pursell, H. Roth, and R. White. States and Counties: Florida: Bay, Calhoun, Franklin, Gadsden, Jackson, Leon, Liberty, and Wakulla. Georgia: Decatur, Grady, and Thomas.
- ↑ [[2]]Accessed: March 29, 2016

