Euphorbia discoidalis
| Euphorbia discoidalis | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo taken by Kevin Robertson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Euphorbiales |
| Family: | Euphorbiaceae |
| Genus: | Euphorbia |
| Species: | E. discoidalis |
| Binomial name | |
| Euphorbia discoidalis Chapm. | |
| |
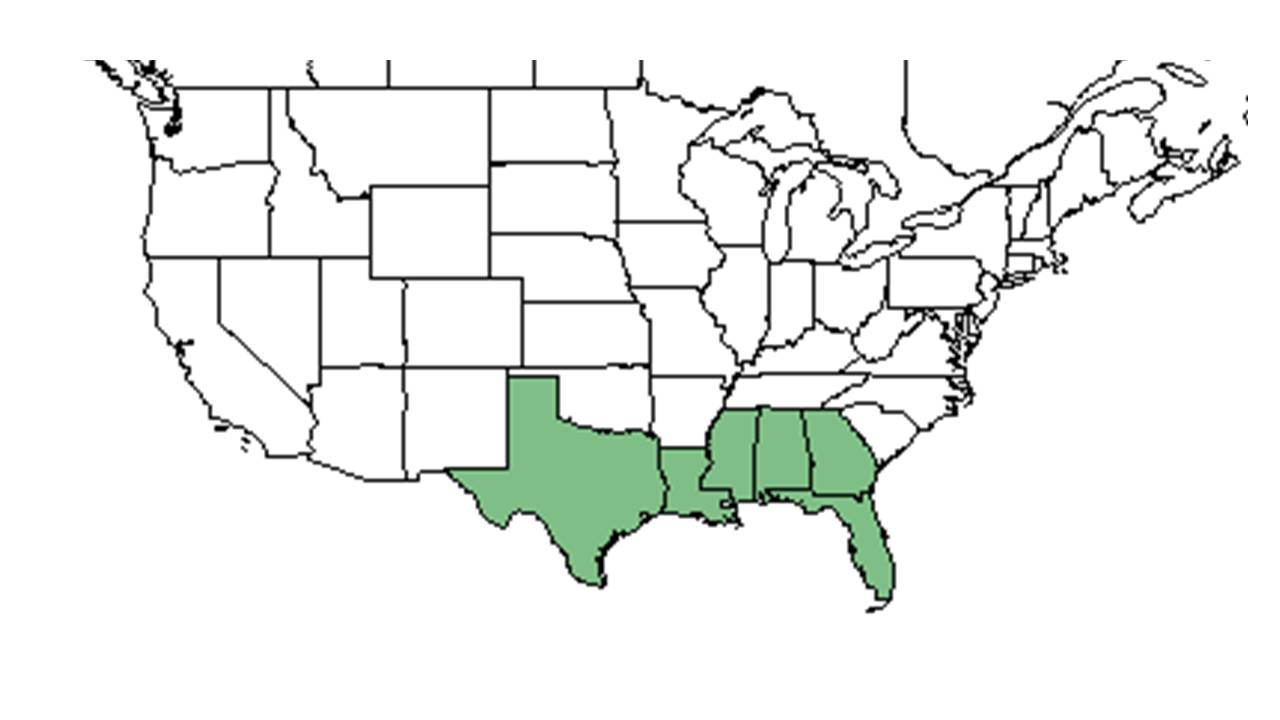
| Natural range of Euphorbia discoidalis from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: summer spurge
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Tithymalopsis discoidalis (Chapman) Small; E. corollata var. corollata[1]
Varieties: none[1]
Description
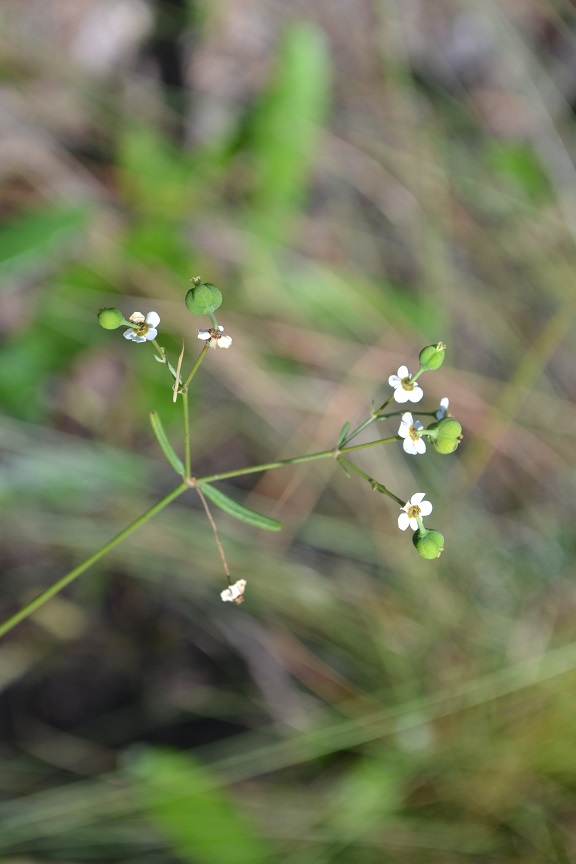
Euphorbia discoidalis is a perennial forb/herb that is a member of the Euphorbiaceae family.[2] It reaches heights of about 18 inches with white colored flowers.[3]
Distribution
Euphorbia discoidalis is distributed from eastern and central Georgia south and west to the Florida panhandle and eastern Texas.[4]
Ecology
Habitat
It is primarily found in sandhills.[4] Other habitats that have been observed of E. discoidalis include pine dominated habitats such as longleaf pine scrubs, sandhills, upland pine, and drained uplands. It prefers areas that have high light level/ open canopies. It also occurs in disturbed habitats such as fallow fields, clearings, and in annually burned pinelands. It likes sandy soil types.[5] Euphorbia discoidalis is restricted to native groundcover with a statistical affinity in upland pinelands of South Georgia.[6]
Populations appear to increase due to disturbance.[7] It is considered an indicator species of the clayhill longleaf woodlands in the western panhandle of Florida.[8] It was found to become absent or decrease in occurrence in response to soil disturbance by agriculture in southwest Georgia. It has shown resistance to regrowth in reestablished pineland habitat that was disturbed by agricultural practices.[6] E. discoidalis was found to be a decreaser in its long-term response following cessation of repeated soil disturbance.[9]
Associated species include longleaf pine, slash pine, shortleaf pine, oaks, red oak, mockernut hickory, magnolia.[5]
Euphorbia discoidalis is an indicator species for the Clayhill Longleaf Woodlands community type as described in Carr et al. (2010).[10]
Phenology
It flowers from late August to frost.[7] This species has been observed flowering in August and September.[5]
Fire ecology
This species is found in areas that are burned annually such as longleaf pine-wiregrass savannas and sandhills.[5] It responds positively to fire, and populations of Euphorbia discoidalis have been known to persist through repeated annual burning.[11] Kral (1983) writes "In naturally stocked uplands it increases as a result of woods fires which reduce competing woody vegetation." [7] It increases in frequency in burned wiregrass habitats rather than fire-surpressed areas or burned bluestem habitats.[12]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
E. discoidalis should avoid soil disturbance by agriculture to conserve its presence in pine communties.[6]
Cultural use
Members of this genus can be used as a laxative in small amounts, but an overdose can cause severe poisoning.[13]
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Weakley, A.S. 2020. Flora of the Southeastern United States. Edition of 20 October 2020. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ USDA, NRCS. (2016). The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 10 May 2019). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ [[1]] Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center. Accessed: May 10, 2019
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: R. A. Norris, R. Komarek, Andre F. Clewell, Robert K. Godfrey, Jefferson, R. Komarek, Loran C. Anderson, Travis MacClendon, Karen McClendon, G. Wilder, Ann F. Johnson, Wilson Baker, and G. Wilder. States and Counties: Florida: Calhoun, Jackson, Leon. Georgia: Thomas.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Ostertag, T.E., and K.M. Robertson. 2007. A comparison of native versus old-field vegetation in upland pinelands managed with frequent fire, South Georgia, USA. Pages 109–120 in R.E. Masters and K.E.M. Galley (eds.). Proceedings of the 23rd Tall Timbers Fire Ecology Conference: Fire in Grassland and Shrubland Ecosystems.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Kral, R. (1983). Euphorbia discoidalis Chapman. A report on some rare, threatened or endangered forest-related vascular plants of the South. R. Kral. Atlanta, USDA Forest Service, Paper 228: 701-705.
- ↑ Carr, S. C., et al. (2010). "A Vegetation Classification of Fire-Dependent Pinelands of Florida." Castanea 75(2): 153-189.
- ↑ Dixon, C. M., K. M. Robertson, A. M. Reid and M. T. Rother. 2024. Mechanical soil disturbance in a pine savanna has multiyear effects on plant species composition. Ecosphere 15(2):e4759.
- ↑ Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.
- ↑ Robertson, K.M. Unpublished data collected from Pebble Hill Fire Plots, Pebble Hill Plantation, Thomasville, Georgia.
- ↑ Rodgers, H. L. and L. Provencher (1999). "Analysis of Longleaf Pine Sandhill Vegetation in Northwest Florida." Castanea 64(2): 138-162.
- ↑ Mueschner, W.C. 1957. Poisonous Plants of the United States. The Macmillan Company, New York.