Difference between revisions of "Andropogon ternarius"
(→Ecology) |
|||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat===<!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat===<!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | In the Coastal Plain in Florida and Georgia, ''Andropogon ternarius'' has been found in pine/oak sandhills, pine scrubs, turkey oak scrubs, upland pine forests, river banks, and pine flatwoods. It can occur in disturbed areas such as roadsides, recreation areas, cut-over pinewoods, gas line corridors, slash pine plantations, old fields and cultivated fields.<ref name="FSU">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: October 2015. Collectors: Jame Amoroso, Loran Anderson, Wilson Baker, Kathleen Craddock Burks, A.F. Clewell, A.H. Curtiss, R. K. Godfrey, D. C. Hunt, R. Komarek, R. Kral, Karen MacClendon, Travis MacClendon, Sidney McDaniel, Marc Minno, Richard S. Mitchell, J. Roche, Cecil R. Slaughter, George Wilder, Jean W. Wooten, Bian Tan. States and Counties: Florida: Baker, Bay, Dixie, Duval, Calhoun, Columbia, Escambia, Franklin, Gadsden, Gilchrist, Jackson, Jefferson, Lake, Leon, Liberty, Madison, Marion, Okaloosa, Taylor, Walton, Wakulla. Georgia: Grady, Thomas. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.</ref> | + | In the Coastal Plain in Florida and Georgia, ''Andropogon ternarius'' has been found in pine/oak sandhills, pine scrubs, turkey oak scrubs, upland pine forests, river banks, and pine flatwoods. It can occur in disturbed areas such as roadsides, recreation areas, cut-over pinewoods, gas line corridors, slash pine plantations, old fields and cultivated fields.<ref name="FSU">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: October 2015. Collectors: Jame Amoroso, Loran Anderson, Wilson Baker, Kathleen Craddock Burks, A.F. Clewell, A.H. Curtiss, R. K. Godfrey, D. C. Hunt, R. Komarek, R. Kral, Karen MacClendon, Travis MacClendon, Sidney McDaniel, Marc Minno, Richard S. Mitchell, J. Roche, Cecil R. Slaughter, George Wilder, Jean W. Wooten, Bian Tan. States and Counties: Florida: Baker, Bay, Dixie, Duval, Calhoun, Columbia, Escambia, Franklin, Gadsden, Gilchrist, Jackson, Jefferson, Lake, Leon, Liberty, Madison, Marion, Okaloosa, Taylor, Walton, Wakulla. Georgia: Grady, Thomas. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.</ref> Soil types include sand, loamy sand, loam, sandy alluvium, and sandy loam.<ref name="FSU"></ref> Where it is found, ''A. ternarius'' is not a large portion of the graminoid plant composition or richness.<ref name= "Gilliam">Gilliam, F. S., et al. (2006). "Natural disturbances and the physiognomy of pine savannas: A phenomenological model." Applied Vegetation Science 9: 83-96.</ref> However, it has been identified as a disturbance indicator.<ref name= "Archer">Archer, J. K., et al. (2007). "Changes in understory vegetation and soil characteristics following silvicultural activities in a southeastern mixed pine forest." Journal of the Torrey Botanical Society 134: 489-504.</ref> |
When exposed to soil disturbance by military training in West Georgia, ''A. ternarius'' responds negatively by way of absence.<ref>Dale, V.H., S.C. Beyeler, and B. Jackson. (2002). Understory vegetation indicators of anthropogenic disturbance in longleaf pine forests at Fort Benning, Georgia, USA. Ecological Indicators 1(3):155-170.</ref> However, it responds positively to soil disturbance by clearcutting and chopping in North Florida flatwoods forests.<ref>Moore, W.H., B.F. Swindel, and W.S. Terry. (1982). Vegetative Response to Clearcutting and Chopping in a North Florida Flatwoods Forest. Journal of Range Management 35(2):214-218.</ref> | When exposed to soil disturbance by military training in West Georgia, ''A. ternarius'' responds negatively by way of absence.<ref>Dale, V.H., S.C. Beyeler, and B. Jackson. (2002). Understory vegetation indicators of anthropogenic disturbance in longleaf pine forests at Fort Benning, Georgia, USA. Ecological Indicators 1(3):155-170.</ref> However, it responds positively to soil disturbance by clearcutting and chopping in North Florida flatwoods forests.<ref>Moore, W.H., B.F. Swindel, and W.S. Terry. (1982). Vegetative Response to Clearcutting and Chopping in a North Florida Flatwoods Forest. Journal of Range Management 35(2):214-218.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Associated species include ''Pteridium, Crataegus lacrimata, Psoralea lupinellus, Aristida purpurascens, Sorghastrum elliottii, Eragrostis hirsuta, Dichanthelium'', and ''Muhlenbergia expansa.''<ref name="FSU"></ref> | ||
''Andropogon ternarius'' is frequent and abundant in the Peninsula Xeric Sandhills community type as described in Carr et al. (2010).<ref>Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.</ref> | ''Andropogon ternarius'' is frequent and abundant in the Peninsula Xeric Sandhills community type as described in Carr et al. (2010).<ref>Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.</ref> | ||
Revision as of 14:42, 21 June 2021
| Andropogon ternarius | |
|---|---|
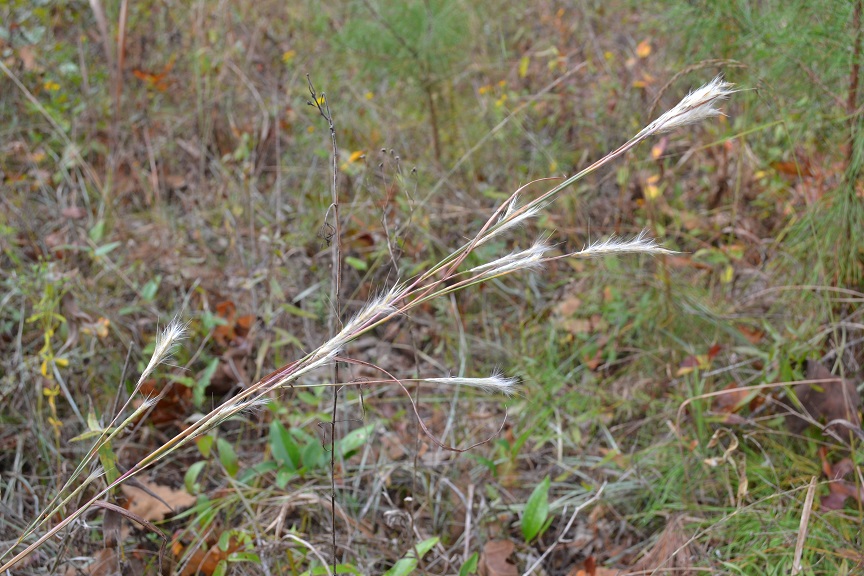

| |
| Andropogon ternarius taken by Kevin Robertson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Moncots or Dicots |
| Order: | Cyperales |
| Family: | Poaceae/Gramineae |
| Genus: | Genus |
| Species: | A. ternarius |
| Binomial name | |
| Andropogon ternarius Michx. | |
| |
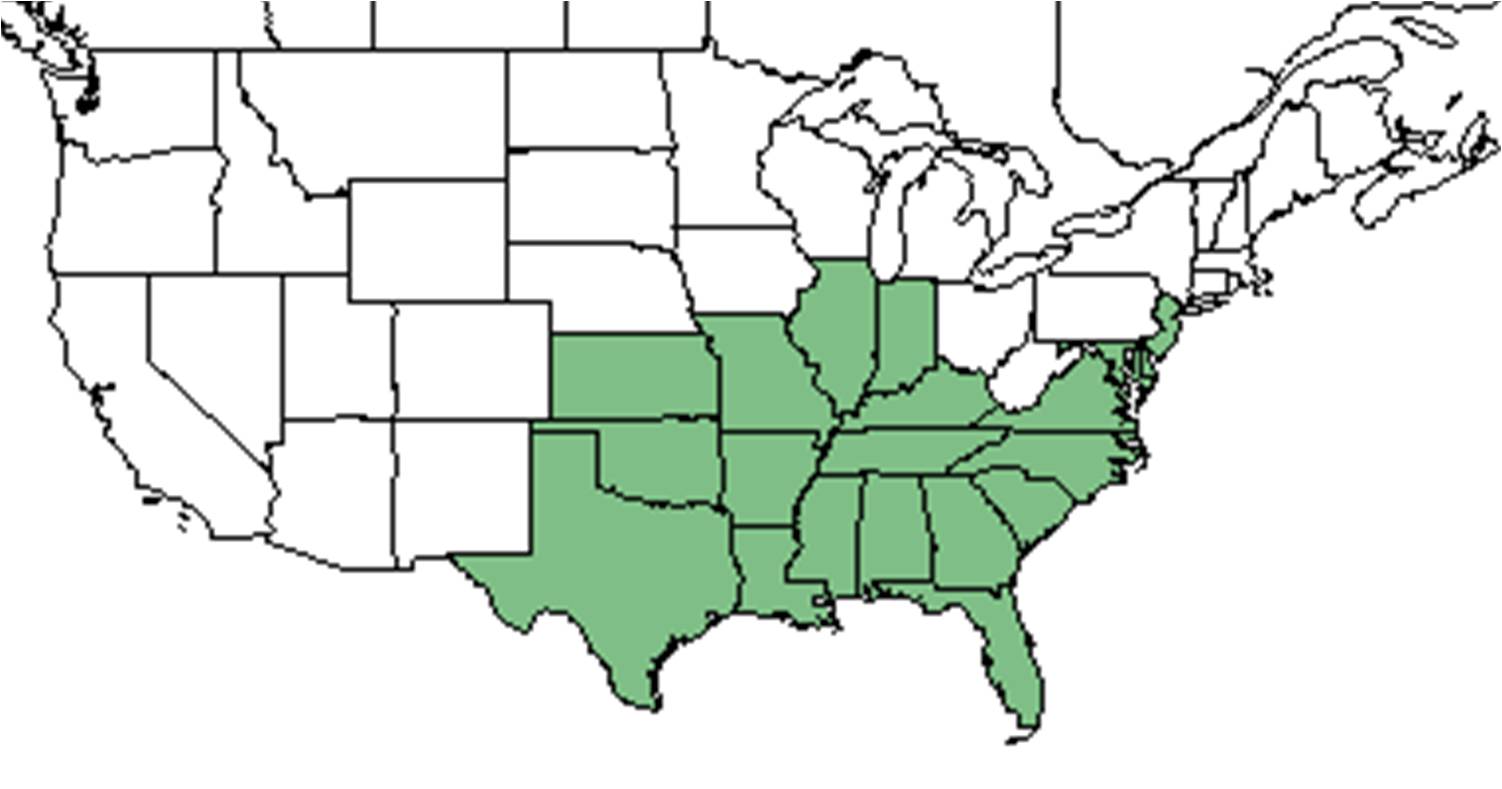
| Natural range of Andropogon ternarius from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Splitbeard bluestem
Contents
[hide]Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: None.[1]
Varieties: None.[1]
Description
Annual, tufted grass, 5 ft tall. NinaRaymond
Cespitose or tufted perennial that comes from hardened bases or short rhizomes. The culms are usually glaucous and sometimes purple in color. The nodes and internodes are usually glabrous. The leaves are basal and cauline. The blades are scaberulous, frequently hirsute or pilose on the upper surface above the ligule. The sheaths are keeled, the margins are scarious, the ligules are membranous, erose or ciliolate, and 0.5-1.5mm long. The collars are glabrous or hirsute. There are numerous racemes that are pedunculated, exserted or inserted in subtending sheaths. The spikelets are in pairs, sessile fertile, pedicellate either staminate, reduced or absent. The glumes are usually scaberulous, subequal, acute to aristate, the first are keeled and somewhat scarious, the second is usually sulcate and somewhat cartilaginous. There are fertile and sterile lemmas hyaline that are subequal that are shorter than glumes. The fertile lemma are awned. The paleas are hyaline and are reduced. The callus beard is usually longer than the spikelet. The grain is purplish or yellowish in color, is linear-ellipsoid in shape, and 2-3mm long.[2]
The culms are 0.7-1.5m tall. The blades are 3dm long and 2-3.5mm wide. There are 2-3 racemes that are villously white and are 1.5-4cm long. The rachis joins and pedicels are densely villous and are 3-10mm long. The peduncles are exserted and are 4-15cm long; sheaths are tight. The fertile spikelet are 5-5mm long, exceeding rachis joint. The lemma awn is slightly twisted and is 1.5-2.5cm long. The sterile spikelet and pedicel are equal and a little longer than the fertile spikelet, the pedicel is flat. Flowers from September to October.[2]
Andropogon ternarius does not have specialized underground storage units apart from its rhizomes.[3] Diaz-Toribio and Putz (2021) recorded this species to have an non-structural carbohydrate concentration of 26.5 mg/g (ranking 90 out of 100 species studied).
Distribution
A. ternarius is native throughout the Southeast United States, ranging as far as Texas and Kansas to the Midwest and the northeast up to New Jersey and Delaware. [4]
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain in Florida and Georgia, Andropogon ternarius has been found in pine/oak sandhills, pine scrubs, turkey oak scrubs, upland pine forests, river banks, and pine flatwoods. It can occur in disturbed areas such as roadsides, recreation areas, cut-over pinewoods, gas line corridors, slash pine plantations, old fields and cultivated fields.[5] Soil types include sand, loamy sand, loam, sandy alluvium, and sandy loam.[5] Where it is found, A. ternarius is not a large portion of the graminoid plant composition or richness.[6] However, it has been identified as a disturbance indicator.[7] When exposed to soil disturbance by military training in West Georgia, A. ternarius responds negatively by way of absence.[8] However, it responds positively to soil disturbance by clearcutting and chopping in North Florida flatwoods forests.[9]
Associated species include Pteridium, Crataegus lacrimata, Psoralea lupinellus, Aristida purpurascens, Sorghastrum elliottii, Eragrostis hirsuta, Dichanthelium, and Muhlenbergia expansa.[5]
Andropogon ternarius is frequent and abundant in the Peninsula Xeric Sandhills community type as described in Carr et al. (2010).[10]
Phenology
Andropogon ternarius has been observed to flower and fruit May through December.[5][11]
Seed bank and germination
It has been recorded germinating in response to fire burning between the months of February to July with the most germination occurring in response to a July burn.[12]
Fire ecology
A. ternarius has been recorded in annually burned upland pines and pine savannas.[5] It has been found that Andropogon species increase in occurrence after prescribed burns in the spring.[13]
Pollination and use by animals
It is used by birds and mammals as cover as well as the seeds as a source of food, and is grazed by cattle in the springtime shortly after growth begins.[4] A. ternarius is also utilized by native bees for nesting materials and structure.[14]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
A. ternarius is not recommended to be included in a cool season species seed mix, and is not common enough to be considered a key management species. It is known to endure periodic controlled burning regiments; annual burning followed by grazing has been found to ultimately eliminate the species from the community over time.[4] Other suggested maintenance includes cutting back the stems in the winter once the grass has gone to seed.[14]
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ Jump up to: 2.0 2.1 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 162-163. Print.
- Jump up ↑ Diaz-Toribio, M.H. and F. E. Putz 2021. Underground carbohydrate stores and storage organs in fire-maintained longleaf pine savannas in Florida, USA. American Journal of Botany 108: 432-442.
- ↑ Jump up to: 4.0 4.1 4.2 USDA Plants Database URL: https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=ANGE
- ↑ Jump up to: 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: October 2015. Collectors: Jame Amoroso, Loran Anderson, Wilson Baker, Kathleen Craddock Burks, A.F. Clewell, A.H. Curtiss, R. K. Godfrey, D. C. Hunt, R. Komarek, R. Kral, Karen MacClendon, Travis MacClendon, Sidney McDaniel, Marc Minno, Richard S. Mitchell, J. Roche, Cecil R. Slaughter, George Wilder, Jean W. Wooten, Bian Tan. States and Counties: Florida: Baker, Bay, Dixie, Duval, Calhoun, Columbia, Escambia, Franklin, Gadsden, Gilchrist, Jackson, Jefferson, Lake, Leon, Liberty, Madison, Marion, Okaloosa, Taylor, Walton, Wakulla. Georgia: Grady, Thomas. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- Jump up ↑ Gilliam, F. S., et al. (2006). "Natural disturbances and the physiognomy of pine savannas: A phenomenological model." Applied Vegetation Science 9: 83-96.
- Jump up ↑ Archer, J. K., et al. (2007). "Changes in understory vegetation and soil characteristics following silvicultural activities in a southeastern mixed pine forest." Journal of the Torrey Botanical Society 134: 489-504.
- Jump up ↑ Dale, V.H., S.C. Beyeler, and B. Jackson. (2002). Understory vegetation indicators of anthropogenic disturbance in longleaf pine forests at Fort Benning, Georgia, USA. Ecological Indicators 1(3):155-170.
- Jump up ↑ Moore, W.H., B.F. Swindel, and W.S. Terry. (1982). Vegetative Response to Clearcutting and Chopping in a North Florida Flatwoods Forest. Journal of Range Management 35(2):214-218.
- Jump up ↑ Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.
- Jump up ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 7 DEC 2016
- Jump up ↑ Shepherd, B. J., et al. (2012). "Fire season effects on flowering characteristics and germination of longleaf pine (Pinus palustris) savanna grasses." Restoration Ecology 20(2): 268-276.
- Jump up ↑ Haywood, J. D., et al. (1995). Responses of understory vegetation on highly erosive Louisiana soils to prescribed burning in May. Asheville, NC, USDA Forest Service, Research Note SO-383: 8.
- ↑ Jump up to: 14.0 14.1 [[1]] Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center. Accessed: March 12, 2019