Difference between revisions of "Leersia virginica"
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
<!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | <!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | ||
| − | ==Conservation and | + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== |
| − | == | + | ==Cultural use== |
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
<gallery widths=180px> | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
Revision as of 16:57, 8 June 2021
Common names: White grass, White cutgrass[1]
| Leersia virginica | |
|---|---|
| File:Leersia virginica IWF.jpg | |
| Photo by the Illinois Wildflowers Database | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Poales |
| Family: | Poaceae |
| Genus: | Leersia |
| Species: | L. virginica |
| Binomial name | |
| Leersia virginica Willd. | |
| |
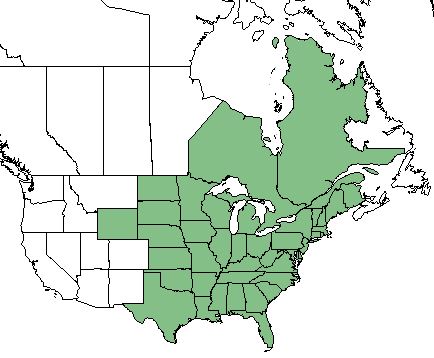
| Natural range of Leersia virginica from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: Homalocenchrus virginicus (Willdenow) Britton.[1]
Varieties: none.[1]
Description
L. virginica is a perennial graminoid of the Poaceae family native to North America.[2]
Distribution
L. virginica is found throughout the Eastern and Midwestern United States, Ontario, and Quebec.[2]
Ecology
Habitat
L. virginica can be found in floodplain forests, swamps, and streambanks.[3] Specimens have been collected in habitats such as shaded wet soils, drying sandy loam, shaded woods, mesic hardwood regions, floodplain bluffs, wet banks of rivers, and hammocks.[4] L. virginica is commonly found in an ideal habitat of partially shaded wet lowlands. It prefers moist soil with a high amount of organic matter that is commonly found along water bodies. It is not tolerant to droughts.[2]
Phenology
This species has been observed flowering July through October.[2][5]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by gravity.[6] Seeds are typically dispersed in the summer through to the fall.[2]
Seed bank and germination
Seeds have bene classified as having medium vigor.[2]
Fire ecology
L. virginica is not fire resistant.[2]
Use by animals
L. virginica can be used by grazing and browsing animals though it is not commonly found in the pasture areas that they inhabit. The Northern Pearly Eye butterfly caterpillar will feed on the foliage of the plant.[2]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 USDA Plant Database
- ↑ Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: Loran Anderson, G. Nelson, W. Baker, R.K.Godfrey, R. Kral, Neal Morar, Lisa Keppner, Annie Schmidt, William Platt, M. Darst, H. Light, D. Johnson, L. Peed. States and counties: Florida (Wakulla, Thomas, Calhoun, Levy, Jefferson, Liberty, Clay, Franklin, Leon, Liberty, Jefferson, Escambia, Suwannee, Washington, Holmes, Dixie) Georgia (Thomas)
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 19 MAY 2021
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.