Difference between revisions of "Rhynchospora harveyi"
(→Seed dispersal) |
|||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| − | + | This species has be observed to flower in August<ref>Nelson, G. [http://www.gilnelson.com/ PanFlora]: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 19 MAY 2021</ref> and fruits May through September.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> | |
===Seed dispersal=== | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
Revision as of 13:28, 8 June 2021
| Rhynchospora harveyi | |
|---|---|
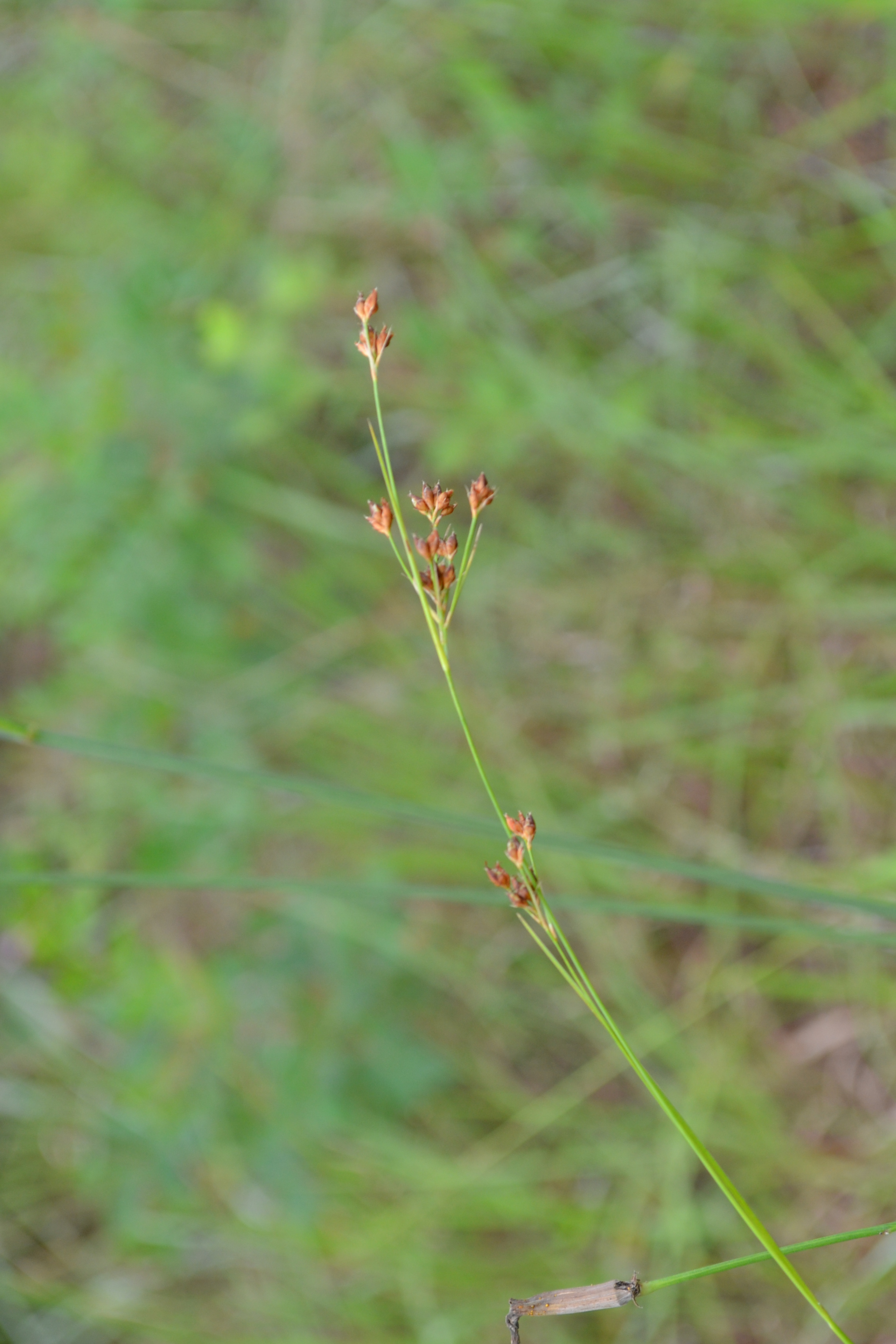

| |
| Photo taken by Kevin Robertson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida – Monocotyledons |
| Order: | Cyperales |
| Family: | Cyperaceae |
| Genus: | Rhynchospora |
| Species: | R. harveyi |
| Binomial name | |
| Rhynchospora harveyi W. Boott | |
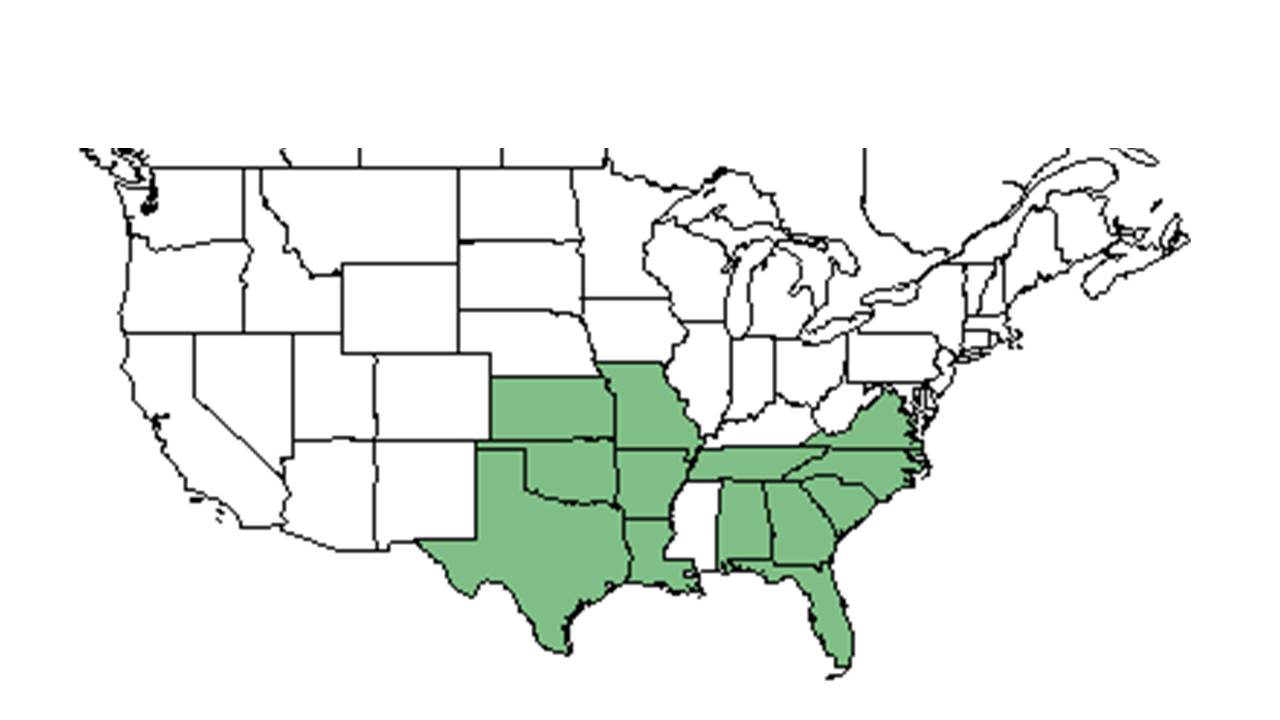
| |
| Natural range of Rhynchospora harveyi from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Harvey's beaksedge
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonym: Rhynchospora harveyi var. harveyi
Description
A description of Rhynchospora harveyi is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain in Florida and Georgia, R. harveyi can be found in longleaf pine forests, drying sandy loam of open pine-oak woodlands, and on dry wiregrass/longleaf pine sandhills.[1] It can also occur in cutover pinewoods with Fimbristylis and Cyperus, sandy loam on pond margins, roadsides, and partially cutover upland longleaf pine savannas. R. harveyi responds negatively to soil disturbance by agriculture in Southwest Georgia.[2]
Associated species include Pinus palustris, Aristida stricta, Quercus, and Fimbristylis, Cyperus.[1]
Phenology
This species has be observed to flower in August[3] and fruits May through September.[1]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by gravity.[4]
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Gary R. Knight, C. Jackson, D. E. Powell, R. A. Norris, Robert K. Godfrey, Andre F. Clewell, Steve L. Orzell. States and Counties: Florida: Franklin, Gadsden, Jackson, Jefferson, Leon, Wakulla. Georgia: Thomas. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ Kirkman, L.K., K.L. Coffey, R.J. Mitchell, and E.B. Moser. Ground Cover Recovery Patterns and Life-History Traits: Implications for Restoration Obstacles and Opportunities in a Species-Rich Savanna. (2004). Journal of Ecology 92(3):409-421.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 19 MAY 2021
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.