Difference between revisions of "Helianthus radula"
(→Distribution) |
|||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | ''H. radula'' can live in loblolly or slash pine communities,<ref name="Yager et al 2007">Yager, L. Y., M. G. Hinderliter, et al. (2007). "Gopher tortoise response to habitat management by prescribed burning." The Journal of Wildlife Management 71: 428-434.</ref> upland longleaf pine communities, <ref>Kirkman, L. K., M. B. Drew, et al. (1998). "Effects of experimental fire regimes on the population dynamics of Schwalbea americana L." Plant Ecology 137: 115-137.</ref><ref name="Gilliam et al 2006"/> pine-oak sandhill woodlands, near the edges of bogs, limestone glades, and mixed oak-cabbage palm hammocks.<ref name=fsu>Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Roomie Wilson, Delzie Demaree, C. Ritchie Bell, F. H. Sargent, Samuel B. Jones, John W. Thieret, Almut G. Jones, A. F. Clewell, R. K. Godfrey, Bruce Hansen, JoAnn Hansen, Robert L. Lazor, R. Kral, J. P. Gillespie, R. E. Perdue, Jr., Paul L. Redfearn, Jr., Kurt E. Blum, D. B. Ward, S. S. Ward, John B. Nelson, G. R. Knight, Cecil R Slaughter, Nancy E. Jordan, R. A. Norris, and R. Komarek. States and Counties: Florida: Bay, Calhoun, Citrus, Flagler, Franklin, Gadsden, Holmes, Jefferson, Lake, Leon, Levy, Liberty, Madison, Nassau, Okaloosa, Orange, Osceola, Putnam, St Johns, Taylor, Wakulla, and Walton. Georgia: Thomas. Louisiana: Tangipahoa and Washington. Mississippi: Jackson, Lamar, and Pearl River. South Carolina: Colleton.</ref> | + | Generally, ''H. radula'' can be found in dryish savannas and sandhills as well as dry pine flatwoods.<ref name= "Weakley"/> It can live in loblolly or slash pine communities,<ref name="Yager et al 2007">Yager, L. Y., M. G. Hinderliter, et al. (2007). "Gopher tortoise response to habitat management by prescribed burning." The Journal of Wildlife Management 71: 428-434.</ref> upland longleaf pine communities, <ref>Kirkman, L. K., M. B. Drew, et al. (1998). "Effects of experimental fire regimes on the population dynamics of Schwalbea americana L." Plant Ecology 137: 115-137.</ref><ref name="Gilliam et al 2006"/> pine-oak sandhill woodlands, near the edges of bogs, limestone glades, and mixed oak-cabbage palm hammocks. Additionally, it occurs in disturbed areas such as roadsides, old fields, power line corridors, by trails, and in lawn and waste areas. This species seems to prefer semi-shaded areas, and occurs on mostly wet to dry sandy soils, or over limestone.<ref name=fsu>Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Roomie Wilson, Delzie Demaree, C. Ritchie Bell, F. H. Sargent, Samuel B. Jones, John W. Thieret, Almut G. Jones, A. F. Clewell, R. K. Godfrey, Bruce Hansen, JoAnn Hansen, Robert L. Lazor, R. Kral, J. P. Gillespie, R. E. Perdue, Jr., Paul L. Redfearn, Jr., Kurt E. Blum, D. B. Ward, S. S. Ward, John B. Nelson, G. R. Knight, Cecil R Slaughter, Nancy E. Jordan, R. A. Norris, and R. Komarek. States and Counties: Florida: Bay, Calhoun, Citrus, Flagler, Franklin, Gadsden, Holmes, Jefferson, Lake, Leon, Levy, Liberty, Madison, Nassau, Okaloosa, Orange, Osceola, Putnam, St Johns, Taylor, Wakulla, and Walton. Georgia: Thomas. Louisiana: Tangipahoa and Washington. Mississippi: Jackson, Lamar, and Pearl River. South Carolina: Colleton.</ref> |
| + | |||
| + | Associated species include ''Pinus palutris, Quercus laevis, Serenoa repens, Sabatia brevifolia, Kalmia hirsuta, Balduina uniflora, Polygala lutea, Sorghastrum secundum, Quercus pumila, Seymeria cassioides, Liatris graminifolia, Helianthus heterophyllus, Cirsium, Bigelowia, Ludwigia, Pinus elliottii, Pityopsis, Baptisia simplicifolia, Ilex glabra, Andropogon, Rynchospora, Phoebanthus tenuifolia, Eupatorium album, Pityopsis, Rhexia alifanus, Liatris gracilis, Carphephorus odoratissimus, Baptisia simplicifolia, Ctenium aromaticum, Vaccinium darrowi, Quercus pumila, Quercus minima, Gaylussacia dumosa,'' and ''Physostegia godfreyi.''<ref name=fsu/> | ||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
Revision as of 13:02, 22 May 2019
| Helianthus radula | |
|---|---|

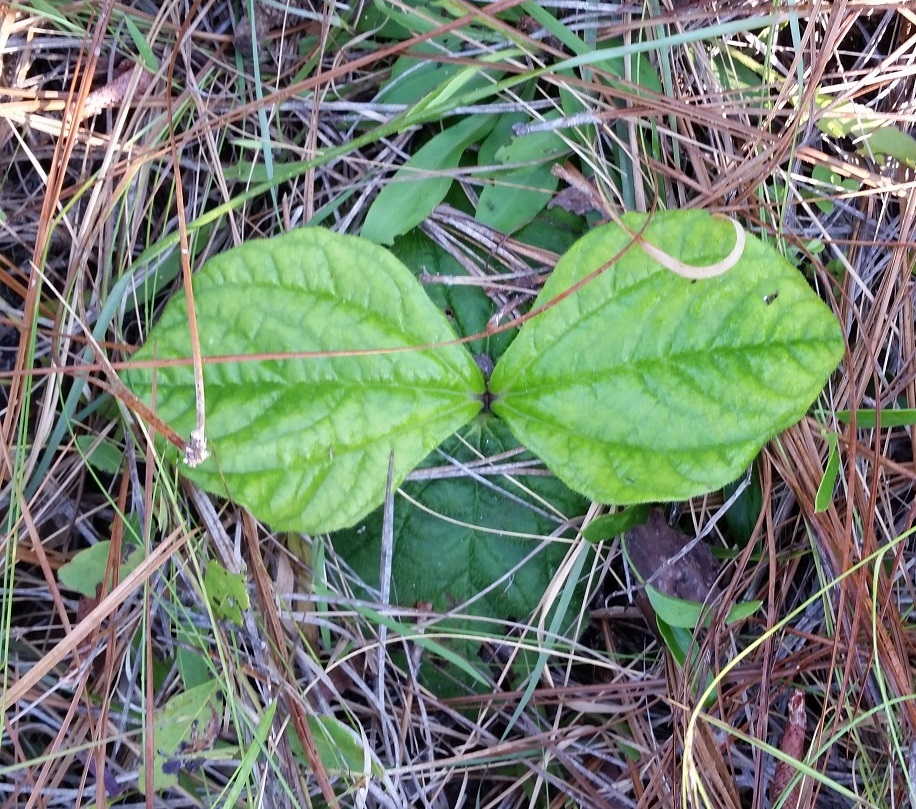
| |
| Photo was taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae ⁄ Compositae |
| Genus: | Helianthus |
| Species: | H. radula |
| Binomial name | |
| Helianthus radula (Pursh) Torr. & A. Gray | |
| |
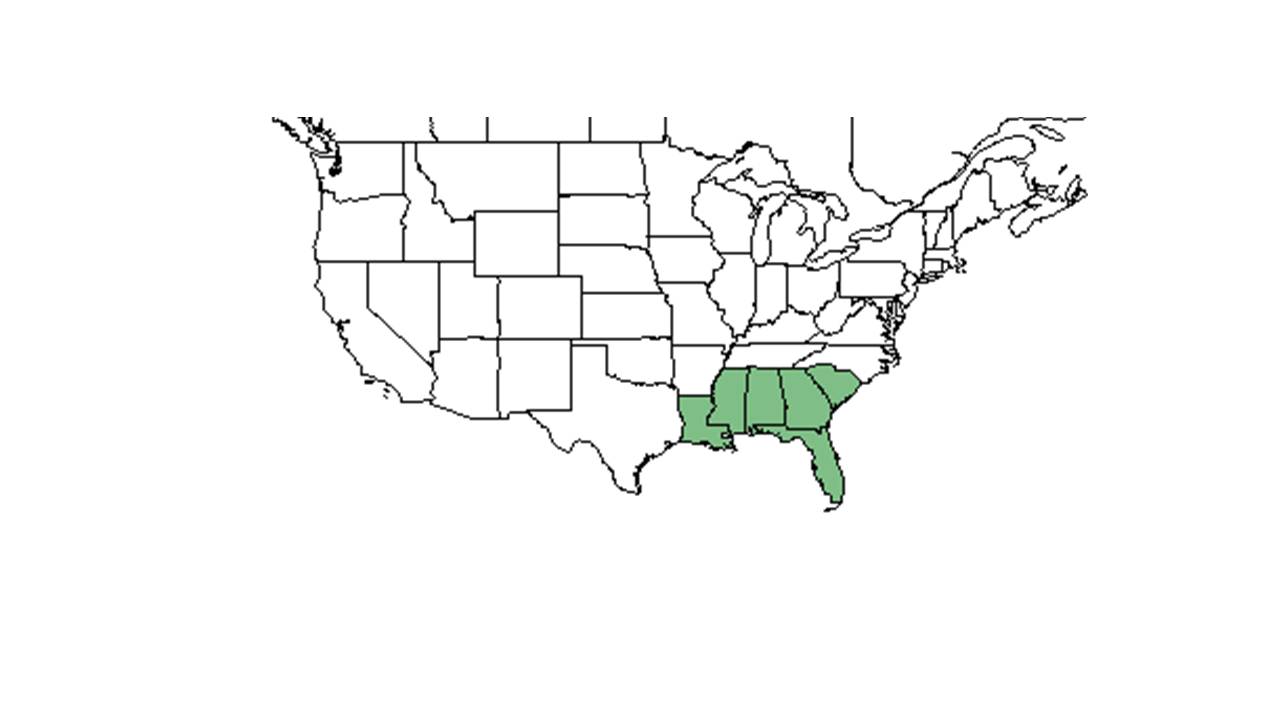
| Natural range of Helianthus radula from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Rayless sunflower; Stiff sunflower; Roundleaf sunflower
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Description
A description of Helianthus radula is provided in The Flora of North America.
Helianthus radula is a perennial herbaceous species.
Distribution
Helianthus radula is found along the southeastern coastal plain from southern South Carolina south to southern peninsular Florida and west to southeastern Louisiana.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
Generally, H. radula can be found in dryish savannas and sandhills as well as dry pine flatwoods.[1] It can live in loblolly or slash pine communities,[2] upland longleaf pine communities, [3][4] pine-oak sandhill woodlands, near the edges of bogs, limestone glades, and mixed oak-cabbage palm hammocks. Additionally, it occurs in disturbed areas such as roadsides, old fields, power line corridors, by trails, and in lawn and waste areas. This species seems to prefer semi-shaded areas, and occurs on mostly wet to dry sandy soils, or over limestone.[5]
Associated species include Pinus palutris, Quercus laevis, Serenoa repens, Sabatia brevifolia, Kalmia hirsuta, Balduina uniflora, Polygala lutea, Sorghastrum secundum, Quercus pumila, Seymeria cassioides, Liatris graminifolia, Helianthus heterophyllus, Cirsium, Bigelowia, Ludwigia, Pinus elliottii, Pityopsis, Baptisia simplicifolia, Ilex glabra, Andropogon, Rynchospora, Phoebanthus tenuifolia, Eupatorium album, Pityopsis, Rhexia alifanus, Liatris gracilis, Carphephorus odoratissimus, Baptisia simplicifolia, Ctenium aromaticum, Vaccinium darrowi, Quercus pumila, Quercus minima, Gaylussacia dumosa, and Physostegia godfreyi.[5]
Phenology
Flowering and fruiting has been observed in January and August through November.[5][6]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by gravity. [7]
Fire ecology
This species has been found in habitat that is burned frequently,[5] even biennially.[4]
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ Yager, L. Y., M. G. Hinderliter, et al. (2007). "Gopher tortoise response to habitat management by prescribed burning." The Journal of Wildlife Management 71: 428-434.
- ↑ Kirkman, L. K., M. B. Drew, et al. (1998). "Effects of experimental fire regimes on the population dynamics of Schwalbea americana L." Plant Ecology 137: 115-137.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Gilliam, F. S., W. J. Platt, et al. (2006). "Natural disturbances and the physiognomy of pine savannas: A phenomenological model." Applied Vegetation Science 9: 83-96.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Roomie Wilson, Delzie Demaree, C. Ritchie Bell, F. H. Sargent, Samuel B. Jones, John W. Thieret, Almut G. Jones, A. F. Clewell, R. K. Godfrey, Bruce Hansen, JoAnn Hansen, Robert L. Lazor, R. Kral, J. P. Gillespie, R. E. Perdue, Jr., Paul L. Redfearn, Jr., Kurt E. Blum, D. B. Ward, S. S. Ward, John B. Nelson, G. R. Knight, Cecil R Slaughter, Nancy E. Jordan, R. A. Norris, and R. Komarek. States and Counties: Florida: Bay, Calhoun, Citrus, Flagler, Franklin, Gadsden, Holmes, Jefferson, Lake, Leon, Levy, Liberty, Madison, Nassau, Okaloosa, Orange, Osceola, Putnam, St Johns, Taylor, Wakulla, and Walton. Georgia: Thomas. Louisiana: Tangipahoa and Washington. Mississippi: Jackson, Lamar, and Pearl River. South Carolina: Colleton.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 12 DEC 2016
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.
