Difference between revisions of "Euphorbia heterophylla"
(→Ecology) |
(→Distribution) |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
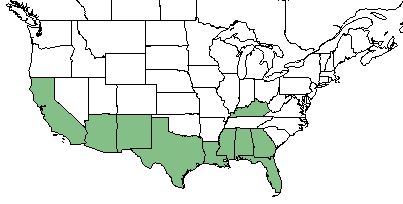
| − | ''E. heterophylla'' is found along the southern United States, from Florida to California. <ref name= "USDA"> [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CEAM USDA Plant Database]</ref> | + | ''E. heterophylla'' is found along the southern United States, from Florida to California, and disjunct in Kentucky. It is also native to Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands, and has been introduced to Hawaii and the Pacific Basin.<ref name= "USDA"> [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CEAM USDA Plant Database]</ref> |
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
Revision as of 12:33, 13 May 2019
Common Names: Fire on the mountain[1]; painted euphorbia; catalina[2]; Fiddler's spurge; Mexican fireplant
| Euphorbia heterophylla | |
|---|---|
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
| |
| Photo from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Euphorbiales |
| Family: | Euphorbiaceae |
| Genus: | Euphorbia |
| Species: | E. heterophylla |
| Binomial name | |
| Euphorbia heterophylla L. | |
| |
| Natural range of Euphorbia heterophylla from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonym: Poinsettia heterophylla (Linnaeus) Klotzsch & Garcke ex Klotzsch; Poinsettia geniculata Ortega
Description
E. heterophylla is a annual/perennial forb/herb of the Euphorbiaceae fmaily native to North America. [1]
Distribution
E. heterophylla is found along the southern United States, from Florida to California, and disjunct in Kentucky. It is also native to Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands, and has been introduced to Hawaii and the Pacific Basin.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
E. heterophylla is largely found in disturbed habitats. [3] It has also been recently found in waste areas in Virginia. [4] It's native habitat is canyons and uplands, though the plant is relatively scarce. [5]
Specimens of this species have been collected from drying loamy sand of roadside, and along fences. [6]
Phenology
This species generally flowers all year round.[3]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 USDA Plant Database
- ↑ Gee, K. L., et al. (1994). White-tailed deer: their foods and management in the cross timbers. Ardmore, OK, Samuel Roberts Noble Foundation.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ Carr, L. G. (1940). "Further notes on coastal floral elements in the bogs of Augusta County, Virginia." Rhodora 42(495): 86-93.
- ↑ Knapp, W. M. and D. Estes (2006). "Gratiola brevifolia (Plantaginaceae) new to the flora of Delaware, the Delmarva Peninsula, and the mid-Atlantic." SIDA Contributions to Botany 22(1): 825-829. Gratiola brevifolia (Plantaginaceae) is reported as a rare and native addition to the 1 lora of Delaware, the Delniarva Peninsula, and to the Mid-Atlantic. This species is disjunct approximately 835 km (520 mi) from the closest known poptilatit^n in Burke Co., Georgia,
- ↑ URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: Loran Anderson States and counties: Florida (Wakulla, Jackson, Liberty, Jefferson, Gulf)