Difference between revisions of "Eragrostis elliottii"
Rwagner914 (talk | contribs) |
(→Distribution) |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
| + | ''E. elliottii'' is distributed along the southeastern Coastal Plain from North Carolina south to Florida and west to Texas.<ref name= "Weakley">Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
Revision as of 19:55, 6 May 2019
| Eragrostis elliottii | |
|---|---|
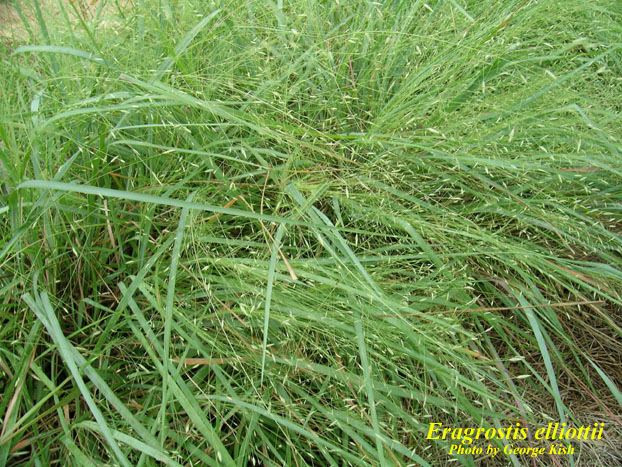

| |
| Photo by George Kish, Atlas of Florida Vascular Plants | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida – Monocotyledons |
| Order: | Poales |
| Family: | Poaceae ⁄ Gramineae |
| Genus: | Eragrostis |
| Species: | E. elliottii |
| Binomial name | |
| Eragrostis elliottii S. Watson | |
| |
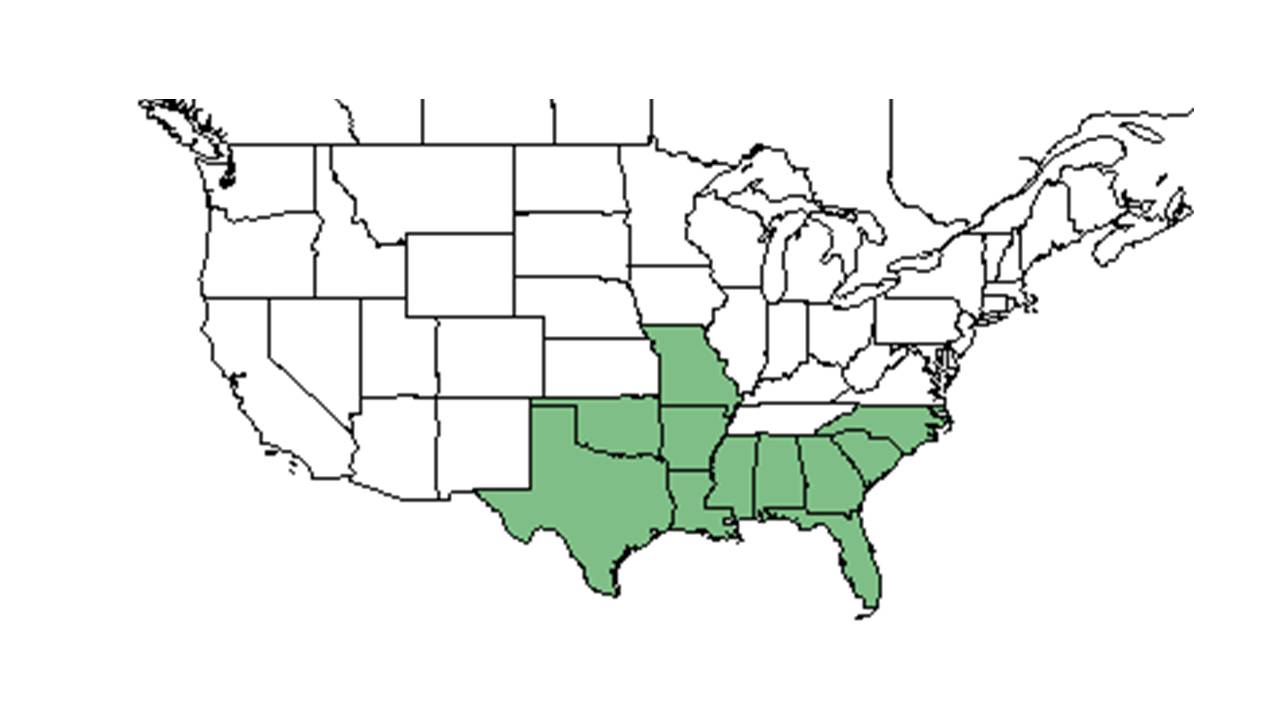
| Natural range of Eragrostis elliottii from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Field lovegrass; Elliott's lovegrass
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Description
This species is strongly glaucous.[1]
Generally, for the Eragrostis genus, they are "annuals or perennials from short rhizomes or hardened bases. Glumes similar, shorter than lowest lemma. Florets more than 2. Lemmas 3-nerved, paleas persistent, ciliate."[2]
Radford (1964) explains that E. elliottii is similar to E. refracta. And states that the "lateral spikeletes shorter than pedicels, not appressed."[2]
Distribution
E. elliottii is distributed along the southeastern Coastal Plain from North Carolina south to Florida and west to Texas.[3]
Ecology
Habitat
It does well in open canopy areas on longleaf pine habitats.[4] Sandhill community.[5] Does not do well in highly disturbed areas (such as clear cutting).[4] This species has also been observed to occur in sand ridges of longleaf pine and turkey oak woodlands, clearings in coastal hammocks, marshy boarders of cypress-gum ponds, oak woodlands, interdune depressions, sandy prairies, and open grassy limestone glades.[1] It does well in areas of high light intensity to partial shade in loamy sands, drying sands, moist shell sands, and peaty sandy soils.
Associated species include Panicum flexile, Eustachya, Habenaria ciliaris, Balduina uniflora, Lilium catesbaei, Eriocaulon decangulare, Rynchospora, Aristia, Eragrostis hirsute, Pinus palustris, Quercus laevis, Stenaria nigricans, Sporobolus junceus, Schoenus nigricans.[1]
Phenology
It has been observed to flower and fruit in October and December.[1]
Fire ecology
This species lives in environments that are burned.[1]
Diseases and parasites
It is a common host plant of the fungus Balansia epichloe in the southeastern United States.[6]
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, A.F. Clewell, R.K. Godfrey, R. Komarek, R. Kral, J. P. Gillespie, William R. Stimson, George R. Cooley, R. J. Eaton, Olga Lakela, Bruce Hansen, JoAnn Hansen, F. C. Craighead, James D. Ray Jr., Herbet L. Monoson, Richard W. Pohl, Robert L. Lazor, Sidney McDaniel, A. H. Curtiss, Allen G. Shuey, J. Harrison, R. Garren, Ann F. Johnson, A. H. Curtiss, Erdman West, Tom Daggy, Steve L. Orzell, Edwin L. Bridges, Grady W. Reinert, Ann F. Johnson, and Wilson Baker. States and Counties: Florida: Bay, Broward, Charlotte, Citrus, Clay, Collier, Dade, Duval, Escambia, Flagler, Franklin, Gadsden, Gulf, Hamilton, Hernando, Hillsborough, Jackson, Lafayette, Lake, Lee, Leon, Levy, Liberty, Madison, Manatee, Monroe, Okaloosa, Palm Beach, Putnam, Santa Rosa, Sarasota, Sumter, Taylor, Volusia, Wakulla, Walton, and Washington. Georgia: Thomas.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 66-71. Print.
- ↑ Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Brockway, D. G. and C. E. Lewis (2003). "Influence of deer, cattle grazing and timber harvest on plant species diversity in a longleaf pine bluestem ecosystem." Forest Ecology and Management 175: 49-69.
- ↑ Downer, M. R. (2012). Plant species richness and species area relationships in a Florida sandhill community. Integrative Biology. Ann Arbor, MI, University of South Florida. M.S.: 52.
- ↑ Phelps, R. A., G. Morgan-Jones, et al. (1993). "Systematic and biological studies in the Balansieae and related anamorphs. 7. Host-pathogen relationship of Eragrostis capillaris and Balansia epichloe." Mycotaxon 49: 117-127.