Difference between revisions of "Callicarpa americana"
(→Seed dispersal) |
(→Pollination) |
||
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
Megachilidae: ''Megachile brevis pseudobrevis'' | Megachilidae: ''Megachile brevis pseudobrevis'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Other Hymenoptera that pollinate ''C. americana'' include ''Dialictus placidensis'' and ''Halictus ligatus''.<ref name= "Deyrup">Deyrup, M. J. E., and Beth Norden (2002). "The diversity and floral hosts of bees at the Archbold Biological Station, Florida (Hymenoptera: Apoidea)." Insecta mundi 16(1-3).</ref> | ||
===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
Revision as of 15:45, 29 March 2019
| Callicarpa americana | |
|---|---|
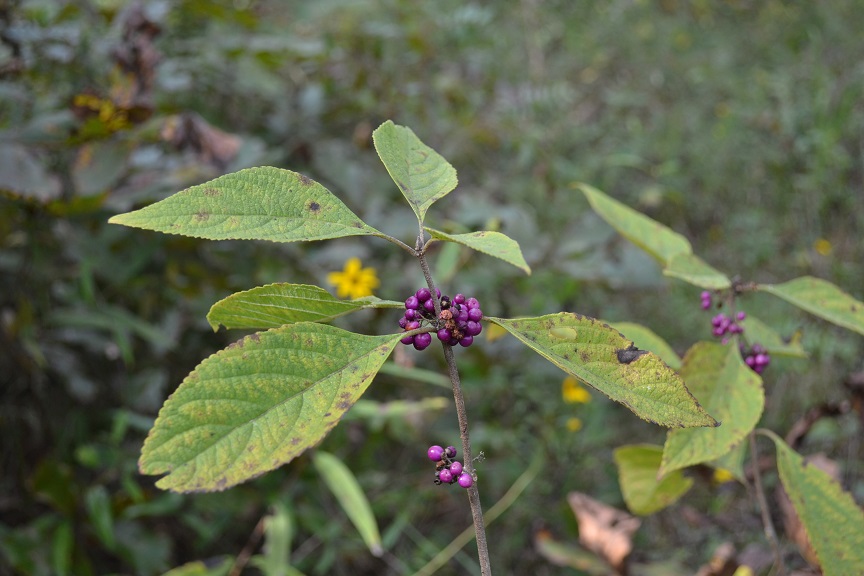

| |
| Photo taken by Kevin Robertson (2015) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Lamiales |
| Family: | Verbenaceae |
| Genus: | Callicarpa |
| Species: | C. americana |
| Binomial name | |
| Callicarpa americana L. | |
| |
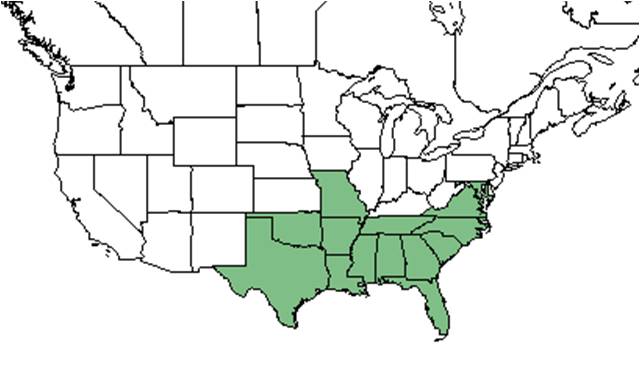
| Natural range of Callicarpa americana from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: American beautyberry; French-mulberry
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: none
Varieties: none
In greek, Callicarpa derives from callos meaning "beauty" and carpos meaning "fruit".[1]
Description
Generally for the Callicarpa genus, they grow up to 1-2.5 m tall with twigs having stellate pubescence while being scrurfy when touched. The leaves are simple, opposite or subopposite, have short pubescent above, and ovate, ovate-lanceolate, or elliptic, acute to acuminate, petiolate in shape. The flowers are in axillary cymes. The calyx is shallowly 5-toothed, grows 0.5-2 mm long. The petals are united ca. 1/2-2/3 their length. The lobes 5, are spreading, are lavender to pinkish in color, grow 3-5 mm long. The stamens are exserted. The stigma is slightly 2-lobed. The drupe is 4-seeded, are lavendar to purple in color, are rarely white in color, and are globose. The seeds are light yellow to brown in color, are ellipsoid to orbicular rounded on the back, and are flattened on the inner surface. [2]
Specifically, for Callicarpa americana, the leaves are ovate to ovate-lanceolate in shape, there are stellate pubescence beneath the leaves, and grow 7-15 cm wide, are crenate to serrate, and at the base are widely cuneate or rounded. The petioles grow 1.5-3.5 cm long, and are scurfy stellate like the twigs. The cymes are shorter than the subtending petioles. The peduncles grow 1-5 mm long. The drupe grows 3-5 mm long. The pyrenes grow 2.3 mm long. [2]
Distribution
C. ameriana is native to the southeastern United States, ranging from Maryland to south Florida and Texas. It can also be found in Mexico and the West Indies.[3]
Ecology
Habitat
The species is associated with longleaf pine forest ecosystems.[4] It can be found in hammocks, maritime forests, other forests (particularly with rocky or sandy soils), and disturbed sites.[3] C. americana has also been observed in sandy soil coastal hammocks, wooded floodplains, calcareous bluffs, margin of creek swamps and swamps, dry sandy slopes, woodland forest edges, understory shrub thickets, flat creeks, and waterfronts.[5] One study found that C. americana was more abundant in tornado-damaged areas containing an open canopy rather than undamaged areas.[6]
Associated species: Quercus sp., Ulmus sp., Ligustrum sp., Liquidambar styraciflua, Prunus sp., Carya sp., Sabal palmetto, and Sabal minor.[5]
Phenology
C. americana has been observed flowering from May to August with peak inflorescence in June.[7] The later blooms and developing fruit persist into the winter.[3]
Seed dispersal
The seeds are dispersed by animals and birds through consumption.[1][8]
Seed bank and germination
Seeds that are planted in the fall commonly germinate in the spring, but C. americana seeds can persist in the seed bank for several years.[1]
Fire ecology
It has been observed growing in sites that were previously burned within the last year.[5] C. americana poses a low wildfire hazard to the wildland-urban interface due to its high foliar moisture content and its low fuel bed bulk density.[9] A study in Arkansas found that C. americana increases in understory cover with a 6 year or 9 year burn cycle.[10]
Pollination
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of Callicarpa americana at Archbold Biological Station: [11]
Apidae: Apis mellifera
Halictidae: Agapostemon splendens, Augochlora pura, Halictus poeyi, Lasioglossum placidensis
Megachilidae: Megachile brevis pseudobrevis
Other Hymenoptera that pollinate C. americana include Dialictus placidensis and Halictus ligatus.[12]
Use by animals
It is a moderate portion of large mammal diets, ranging from 10-25% of their average diet, and a low portion of small mammal and terrestrial bird diets, from 5-10% of their diet.[13][14] Since the fruit is high in moisture content, it is an important source of food for over 40 species of songbirds, like the Brown Thrasher, Purple Finch, American Robin, and Eastern Towhee. The fruit clusters are also eaten by foxes, opossum, armadillo, white tailed deer, squirrels, and raccoon.[1] The Florida marsh rabbit has been observed to browse on the plant.[15] It is also a well known food and cover plant for the northern bobwhite quail.[16] The white tailed deer also browse on the leaves when other preferred food is not available. As well, cattle browse on the twigs in the winter and twigs and leaves in the spring. Historically, C. americana was utilized by Native American tribes for many medicinal purposes, including malarial fevers and rheumatism. As well, the roots were used for stomachaches, dizziness, and dysentry, and the roots and berries were used to treat colic by boiling them and drinking it. Farmers used the plant in the early 20th century as a mosquito repellent for horses and mules by crushing the leaves and placing them under the harnesses, and would use this same method on themselves as well.[1]
Diseases and parasites
Leaf spots (Atractilina callicarpae) and black mold (Meliola cookeana) affect plants in the Callicarpa genus.[1] It is a host plant for Brevipalpus californicus, B. obovatus, and B. phoenicis, which are all false spider mites that cause citrus leprosis.[17]
Conservation and management
It is listed as endangered and extirpated by the Maryland Department of Natural Resources.[18] For ornamental management purposes, pruning the plants in the fall or winter will maintain its form, and old stems should be cut when pruning since only new growth produces fruit.[1]
Cultivation and restoration
While there is no official cultivars of C. americana, there is a variety available (C. americana var. lactea) that produces white fruit that is available at some nurseries.[1]
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Brakie, M. 2010. Plant fact sheet for American beautyberry (Callicarpa americana). USDA-Natural Resources Conservation Service, East Texas Plant Materials Center. Nacogdoches, TX, 75964.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 894. Print.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ Brockway, D. G., et al. (2005). Restoration of longleaf pine ecosystems. F. S. United States Department of Agriculture, Southern Research Station.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: March 2019. Collectors: Harry E. Ahles, Loran C. Anderson, W. R. Anderson, W. P. Adams, Joel A. Barnes, Tom Barnes, Don Blake, H. L. Blomquist, Kurt Blum, J. Bonk, Jane Brockmann, Michael B. Brooks, Kathy Craddock Burks, Burnett, Chris Cooksey, D. S. Correll, Delzie Demaree, R. F. Doren, Patricia Elliot, Joseph Ewan, J. Ferborgh, G. Fleming, Suellen Folensbee, P. Genelle, A. Gholson, Jr., J. P. Gillespie, M. Gillespie, Robert K. Godfrey, C. J. Hansen, Bruce Hansen, JoAnn Hansen, James W. Hardin, Randy Haynes, P. Hilsenbeck, R. Hilsenbeck, Ron Hughes, Samuel B. Jones, Jr., King, Gary R. Knight, R. Komarek, R. Kral, O. Lakela, Robert L. Lazor, Sidney McDaniel, Marc Minno, Richard S. Mitchell, Florence Montgomery, R. Nims, T. Nims, R. Nunan, John C. Ogden, Parker, Laurie Pipkorn, J. Poppleton, Elmer C. Prichard, Gwynn W. Ramsey, Paul L. Redfearn, Jr., Josephine Skehan, Cecil R. Slaughter, William R. Stimson, John W. Thieret, R. E. Weaver, Jr., R. L. Wilbur, Roomie Wilson, Richard P. Wunderlin, and T. Wunderlin. States and Counties: Florida: Broward, Calhoun, Citrus, Dade, Escambia, Franklin, Gadsden, Indian River, Jackson, Jefferson, Leon, Levy, Liberty, Madison, Monroe, Osceola, Seminole, Volusia, and Wakulla. Alabama: Chambers, Houston, Limestone, Lowndes, Monroe, and Pickens. Georgia: Decatur, De Kalb, Grady, McIntosh, Oglethorpe, and Thomas. Mississippi: Forrest, Hancock, Jackson, Pearl River, and Pike. South Carolina: Dorchester, Pickens, and Richland. Louisiana: Evangeline, Iberia, St Landry, and Tangipahoa. Arkansas: Hot Spring and Stone. Texas: Bexar, Jasper, and Van Zandt. North Carolina: Carteret, Dare, Johnston, and Transylvania. Virginia: Norfolk.
- ↑ Brewer, S. J., et al. (2012). "Do natural disturbances or the forestry practices that follow them convert forests to early-successional communities?" Ecological Applications 22: 442-458.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 7 DEC 2016
- ↑ Creech, M. N., et al. (2012). "Alteration and Recovery of Slash Pile Burn Sites in the Restoration of a Fire-Maintained Ecosystem." Restoration Ecology 20(4): 505-516.
- ↑ Behm, A. L., et al. (2004). "Flammability of native understory species in pine flatwood and hardwood hammock ecosystems and implications for the wildland-urban interface." International Journal of Wildland Fire 13: 355-365.
- ↑ Cain, M. D., et al. (1998). "Prescribed fire effects on structure in uneven-aged stands of loblolly and shortleaf pines." Wildlife Society Bulletin 26: 209-218.
- ↑ Deyrup, M.A. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
- ↑ Deyrup, M. J. E., and Beth Norden (2002). "The diversity and floral hosts of bees at the Archbold Biological Station, Florida (Hymenoptera: Apoidea)." Insecta mundi 16(1-3).
- ↑ Miller, J.H., and K.V. Miller. 1999. Forest plants of the southeast and their wildlife uses. Southern Weed Science Society.
- ↑ Yarrow, G.K., and D.T. Yarrow. 1999. Managing wildlife. Sweet Water Press. Birmingham.
- ↑ Blair, W. F. (1936). "The Florida marsh rabbit." Journal of Mammalogy 17(3): 197-207.
- ↑ Chenault, T. P. (1940). "The phenology of some bob-white food and cover plants in Brazos County, Texas." The Journal of Wildlife Management 4(4): 359-368.
- ↑ Childers, C. C., et al. (2003). "Host plants of Brevipalpus californicus, B. obovatus, and B. phoenicis (Acari: Tenuipalpidae) and their potential involvement in the spread of viral diseases vectored by these mites." Experimental & Applied Acarology 30: 29-105.
- ↑ USDA, NRCS. (2016). The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 29 March 2019). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.