Difference between revisions of "Juncus effusus"
(→Ecology) |
|||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
''Juncus effusus'' is found in moist soil, marshes, margins of streams, ponds, lakes, swamps, and low meadows. <ref name= "Weakley 2015"> Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium. </ref> Specimens have been collected from a wet ditch, pine forest in swamp bed, wet flatwoods, flooded pastures, seepage bog, moist sandy loam, shallow water, floodplain forest, and edge of wood. <ref name = "FSU herbarium"> URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: Lisa keppner, Ed Keppner, R.F. Doren, R. Komarek, R.S. Blaisdell, R.K. Godfrey, K.M. Meyer, A. Townesmith, Loran C. Anderson, Cecil Slaughter, Dianne Hall, Kim Ponzio, K. MacClendon, V. Craig, M. Boothe, Alush Shilom Ton, D.E. Breedlove, A. Mast, Chris Buddenhagen, Annie Schmidt, John Kunzer, Peter Zika. States and counties: Florida ( Bay, Marion, Leon, Columbia, Taylor, Brevard, Calhoun, Santa Rosa, Wakulla, Gadsden, Liberty, Holmes, De Soto, washington, Gulf) Oregon (Morrow) Georgia (Grady)</ref> | ''Juncus effusus'' is found in moist soil, marshes, margins of streams, ponds, lakes, swamps, and low meadows. <ref name= "Weakley 2015"> Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium. </ref> Specimens have been collected from a wet ditch, pine forest in swamp bed, wet flatwoods, flooded pastures, seepage bog, moist sandy loam, shallow water, floodplain forest, and edge of wood. <ref name = "FSU herbarium"> URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: Lisa keppner, Ed Keppner, R.F. Doren, R. Komarek, R.S. Blaisdell, R.K. Godfrey, K.M. Meyer, A. Townesmith, Loran C. Anderson, Cecil Slaughter, Dianne Hall, Kim Ponzio, K. MacClendon, V. Craig, M. Boothe, Alush Shilom Ton, D.E. Breedlove, A. Mast, Chris Buddenhagen, Annie Schmidt, John Kunzer, Peter Zika. States and counties: Florida ( Bay, Marion, Leon, Columbia, Taylor, Brevard, Calhoun, Santa Rosa, Wakulla, Gadsden, Liberty, Holmes, De Soto, washington, Gulf) Oregon (Morrow) Georgia (Grady)</ref> | ||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| − | ''J. effusus'' | + | ''J. effusus'' has been observed to flower March through May. <ref name= "PanFlora"> Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 22 MAY 2018 </ref> |
<!--===Seed dispersal===--> | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> | ||
<!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
<!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | <!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| − | <!--===Pollination===--> | + | <!--===Pollination===--> |
| + | |||
===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
''J. effusus'' is readily eaten by marsh rabbits. <ref name= "Blair 1936"> Blair, W. F. (1936). "The Florida marsh rabbit." Journal of Mammalogy 17(3): 197-207. </ref> It is also among the 14 major fall-early winter south Florida deer foods. <ref name= "Quarterly Journal"> Harlow, R. F. (1961). "Fall and winter foods of Florida white-tailed deer." The Quarterly Journal of the Florida Academy of Sciences 24(1): 19-38. </ref> | ''J. effusus'' is readily eaten by marsh rabbits. <ref name= "Blair 1936"> Blair, W. F. (1936). "The Florida marsh rabbit." Journal of Mammalogy 17(3): 197-207. </ref> It is also among the 14 major fall-early winter south Florida deer foods. <ref name= "Quarterly Journal"> Harlow, R. F. (1961). "Fall and winter foods of Florida white-tailed deer." The Quarterly Journal of the Florida Academy of Sciences 24(1): 19-38. </ref> | ||
Revision as of 20:13, 2 November 2018
Common name: lamp rush [1], soft rush [2], common rush [2]
| Juncus effusus | |
|---|---|
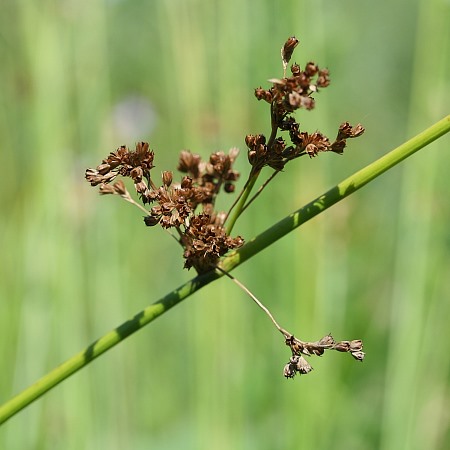

| |
| Photo by the Illinois Wildflowers Database | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Juncales |
| Family: | Juncaceae |
| Genus: | Juncus |
| Species: | J. effusus |
| Binomial name | |
| Juncus effusus L. | |
| |
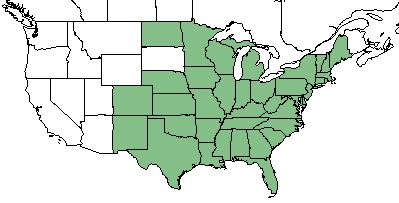
| Natural range of Juncus effusus from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: Juncus effusus L. ssp. solutus (Fernald & Wiegand) Hämet-Ahti; Juncus griscomii Fernald; Juncus effusus Linnaeus var. conglomeratus (Linnaeus) Engelmann
Varieties: none
Description
J. effusus is a perennial graminoid of the Juncaceae family native to North America and introduced in Hawaii. [1]
Distribution
J. effusus is found in the eastern half of the United States from Colorado and New Mexico to Maine, as well as Hawaii. [1]
Ecology
Habitat
Juncus effusus is found in moist soil, marshes, margins of streams, ponds, lakes, swamps, and low meadows. [2] Specimens have been collected from a wet ditch, pine forest in swamp bed, wet flatwoods, flooded pastures, seepage bog, moist sandy loam, shallow water, floodplain forest, and edge of wood. [3]
Phenology
J. effusus has been observed to flower March through May. [4]
Use by animals
J. effusus is readily eaten by marsh rabbits. [5] It is also among the 14 major fall-early winter south Florida deer foods. [6]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 USDA Plant Database https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=JUEFS
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: Lisa keppner, Ed Keppner, R.F. Doren, R. Komarek, R.S. Blaisdell, R.K. Godfrey, K.M. Meyer, A. Townesmith, Loran C. Anderson, Cecil Slaughter, Dianne Hall, Kim Ponzio, K. MacClendon, V. Craig, M. Boothe, Alush Shilom Ton, D.E. Breedlove, A. Mast, Chris Buddenhagen, Annie Schmidt, John Kunzer, Peter Zika. States and counties: Florida ( Bay, Marion, Leon, Columbia, Taylor, Brevard, Calhoun, Santa Rosa, Wakulla, Gadsden, Liberty, Holmes, De Soto, washington, Gulf) Oregon (Morrow) Georgia (Grady)
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 22 MAY 2018
- ↑ Blair, W. F. (1936). "The Florida marsh rabbit." Journal of Mammalogy 17(3): 197-207.
- ↑ Harlow, R. F. (1961). "Fall and winter foods of Florida white-tailed deer." The Quarterly Journal of the Florida Academy of Sciences 24(1): 19-38.