Difference between revisions of "Magnolia grandiflora"
(→Ecology) |
|||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
<!--===Pollination===--> | <!--===Pollination===--> | ||
<!--===Use by animals===--> <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | <!--===Use by animals===--> <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
| − | + | ==Diseases and parasites== | |
| + | A common beetle that can cause death at the tips of branches is ''Xylosandrus campactus'', and ambrosia beetle. <ref name ="FFE">Observation by Craig Bateman comment on Brandi Missouri Griffith post, May 18, Valdosta Fl., posted to Florida Flora and Ecosystematics Facebook Group. </ref> | ||
==Conservation and Management== | ==Conservation and Management== | ||
Revision as of 15:38, 2 July 2018
Common name: southern magnolia [1], bull bay [2]
| Magnolia grandiflora | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by John B | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Magnoliales |
| Family: | Magnoliaceae |
| Genus: | Magnolia |
| Species: | M. grandiflora |
| Binomial name | |
| Magnolia grandiflora L. | |
| |
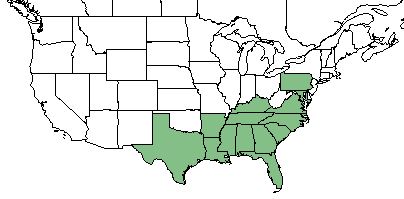
| Natural range of Magnolia grandiflora from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: none
Varieties: Magnolia kobus A.P. de Candolle
Description
M. grandiflora is a perennial tree of the Mangoliaceae family native to North America and introduced to Puerto Rico. [1]
Distribution
M. grandiflora is found along the southeastern coast of the United States from Texas to Pennsylvania, as well as Puerto Rico. [1]
Ecology
Habitat
M. grandiflora is found in suburban woodlands, maritime forests, mesic Coastal Plain bluffs and flats, bottomlands, now also widely naturalized, spreading from cultivation into wet to mesic (and even dry) forests. [2] Specimens have been collected from shore of fresh water spring, dense wooded hammock, sand dunes, mixed hardwood, wet hammock of bottomland, swamp border, and shore of lake. [3]
Phenology
M. grandiflora flowers April-July. [4]
Fire ecology
M. grandiflora is fire resistant, but has a low fire tolerance. [1]
Diseases and parasites
A common beetle that can cause death at the tips of branches is Xylosandrus campactus, and ambrosia beetle. [5]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 USDA Plant Database https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=MAGR4
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, R.K. Godfrey, John Ogden, Patricia Elliot, Richard Mitchell, R. Kral, L.J. Brass, L.B. Trott, Karen MacClendon, Chris Cooksey, R. Komarek, Lisa Keppner, Ed Keppner, Cecil Slaughter, Shirley Wingfield, Elmer C. Prichard. States and counties: Florida (Gadsden, Volusia, Santa Rosa, Leon, Bay, Liberty, Jackson, Levy, Jefferson, Gadsden, Lake, Franklin, Highlands, Wakulla, Calhoun, Washington, Putnam) Georgia (Grady) Louisiana (Oachuita)
- ↑ PanFlora Author: Gil Nelson URL: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Date Accessed: 5/24/18
- ↑ Observation by Craig Bateman comment on Brandi Missouri Griffith post, May 18, Valdosta Fl., posted to Florida Flora and Ecosystematics Facebook Group.