Difference between revisions of "Cornus florida"
(→Diseases and parasites) |
|||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
''C. florida'' is somewhat palatable to browsing animals, not highly palatable to grazing, and inedible for humans. <ref name= "USDA Plant Database"/> | ''C. florida'' is somewhat palatable to browsing animals, not highly palatable to grazing, and inedible for humans. <ref name= "USDA Plant Database"/> | ||
===Diseases and parasites=== | ===Diseases and parasites=== | ||
| − | ''C. florida'' has been impacted since the 1980s by widespread infection by the dogwood anthracnose fungus (''Discula destructive''). <ref name= "Weakley 2015"> | + | ''C. florida'' has been impacted since the 1980s by widespread infection by the dogwood anthracnose fungus (''Discula destructive''). <ref name= "Weakley 2015"/> |
==Conservation and Management== | ==Conservation and Management== | ||
Revision as of 19:31, 18 May 2018
| Cornus florida | |
|---|---|
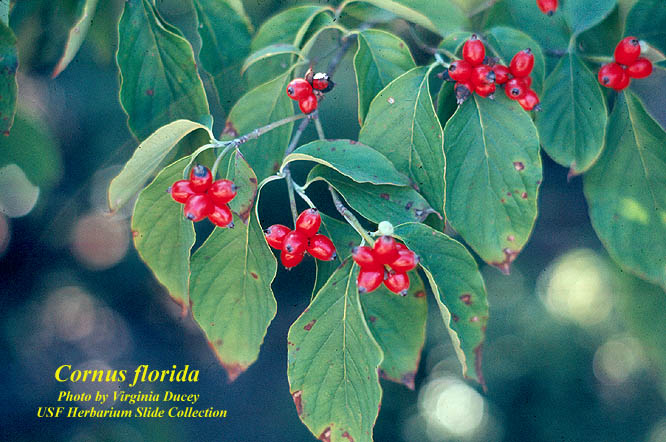

| |
| Photo by the Atlas of Florida Plants Database | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Cornales |
| Family: | Cornaceae |
| Genus: | Cornus |
| Species: | C. florida |
| Binomial name | |
| Cornus florida L. | |
| |
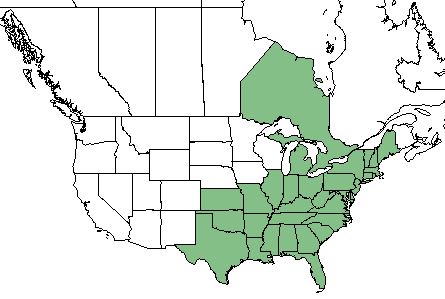
| Natural range of Cornus florida from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: Cynoxylon floridum (Linnaeus) Rafinesque ex B.D. Jackson; Benthamidia florida (Linnaeus) Spach
Varieties: Cornus kousa House
Description
C. florida is a perennial shrub/tree of the Cornaceae family native to North America and Canada. [1]
Distribution
C. florida can be found in the south- and mid-eastern United States, as well as the Ontario region of Canada. [1]
Ecology
Habitat
C. florida thrives in dry to moist forests and wetlands. [2]
Phenology
C. florida flowers February-April, October, and November. [3]
Fire ecology
C. florida is not fire resistant, but has a medium fire tolerance. [1]
Use by animals
C. florida is somewhat palatable to browsing animals, not highly palatable to grazing, and inedible for humans. [1]
Diseases and parasites
C. florida has been impacted since the 1980s by widespread infection by the dogwood anthracnose fungus (Discula destructive). [2]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 USDA Plant Database https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=COFL2
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ PanFlora Author: Gil Nelson URL: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Date Accessed: 5/18/18