Difference between revisions of "Campsis radicans"
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| − | ''C. radicans'' flowers April-August. Its foliage can often be seen in canopies of 30-40 meters high, and with stems of up to 15 centimeters in diameter. ''C. radicans'' is easily recognizable by its tannish, shreddy bark. <ref name= " | + | ''C. radicans'' flowers April-August. <ref name= "PanFlora"> Pan Flora Author: Gil Nelson URL: [http://gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ http://gilnelson.com/PanFlora/] Date Accessed: 5/16/18 </ref> Its foliage can often be seen in canopies of 30-40 meters high, and with stems of up to 15 centimeters in diameter. ''C. radicans'' is easily recognizable by its tannish, shreddy bark. <ref name= "Weakley 2015"> Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium. </ref> |
<!--===Seed dispersal===--> | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> | ||
<!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
<!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | <!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| − | <!--===Pollination===--> | + | <!--===Pollination===--> |
| + | |||
===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
''C. radicans'' is an occasional food source for large mammals and terrestrial birds. <ref name= "USDA Plant Database"> USDA Plant Database [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CARA2 https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CARA2] </ref> | ''C. radicans'' is an occasional food source for large mammals and terrestrial birds. <ref name= "USDA Plant Database"> USDA Plant Database [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CARA2 https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CARA2] </ref> | ||
Revision as of 12:32, 17 May 2018
| Campsis radicans | |
|---|---|
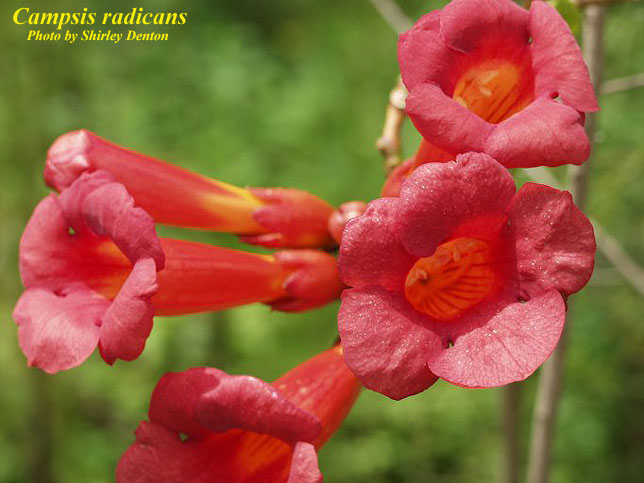

| |
| Photo by the Atlas of Florida Plants Database | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Scrophulariales |
| Family: | Bignoniaceae |
| Genus: | Campsis |
| Species: | C. radicans |
| Binomial name | |
| Campsis radicans L | |
| |
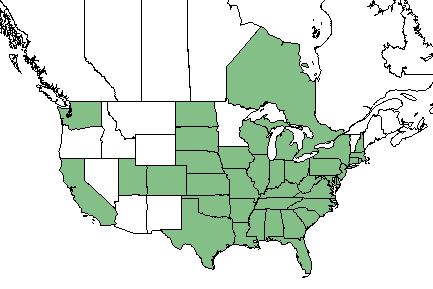
| Natural range of Campsis radicans from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: Bignonia radicans Linnaeus; Tecoma radicans (Linnaeus) Juss
Varieties: none
Description
C. radicans is a perennial vine of the Bignoniaceae family native to North America and Canada. [1]
Distribution
C. radicans is found in the Ontario region of Canada, the eastern half of the United States, California, and Washington. [1]
Ecology
Habitat
C. radicans is found in bottomland forests, swamp forests, fencerows, old fields, forests, thickets, and disturbed areas. It was primarily limited to swamps and bottomlands in the pre-Columbian landscape, and has become a successful colonizer of abandoned farmland, fencerows, and thickets. [2]
Phenology
C. radicans flowers April-August. [3] Its foliage can often be seen in canopies of 30-40 meters high, and with stems of up to 15 centimeters in diameter. C. radicans is easily recognizable by its tannish, shreddy bark. [2]
Use by animals
C. radicans is an occasional food source for large mammals and terrestrial birds. [1]
Conservation and Management
C. radicans is listed as a weedy or invasive species by The University Press of Kentucky, the Cornell University Press, and the Southern Weed Science Society. [1]
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 USDA Plant Database https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CARA2
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ Pan Flora Author: Gil Nelson URL: http://gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Date Accessed: 5/16/18