Difference between revisions of "Solidago gracillima"
(→Taxonomic Notes) |
|||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
==Description== <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ==Description== <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| − | ''Solidago gracillima'' is a dioecious perennial forb/herb.<ref name="USDA"/> | + | ''Solidago gracillima'' is a dioecious perennial forb/herb.<ref name="USDA"/> It has large inflorescences that are very open and have few long branches and smaller compact inflorescence without elongated lower branches.<ref name="Semple 2012">Semple JC (2012) Typification of ''Solidago gracillma'' (Asteraceae: Astereae) and application of the name. Phytoneuron 107:1-10.</ref> |
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
Revision as of 14:23, 18 January 2018
| Solidago gracillima | |
|---|---|
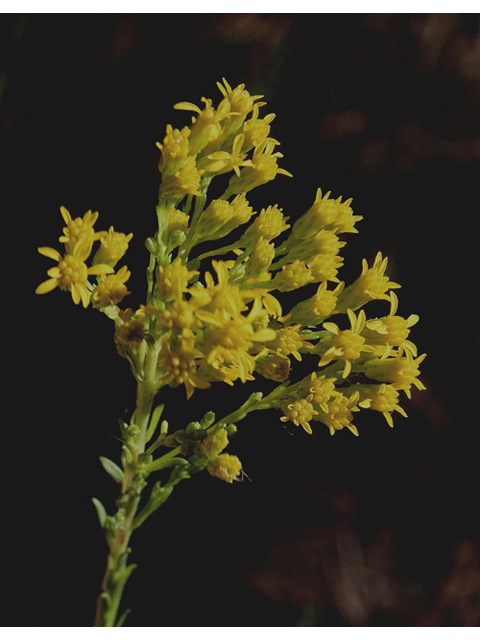

| |
| Photo by RW Smith hosted at Wildflowers.org | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae |
| Genus: | Solidago |
| Species: | S. gracillima |
| Binomial name | |
| Solidago gracillima Torr. and A. Gray | |
| |
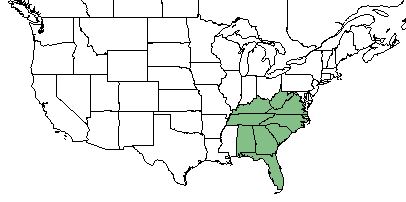
| Natural range of Solidago gracillima from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common Name(s): southern bog goldenrod; graceful goldenrod;[1] Virginia goldenrod[2]
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonym(s): S. austrina; S. perlonga;[1][2] S. flavovirens;[2] S. simulans[1]
Description
Solidago gracillima is a dioecious perennial forb/herb.[2] It has large inflorescences that are very open and have few long branches and smaller compact inflorescence without elongated lower branches.[3]
Distribution
This species is found from east Virginia, south to the central Florida panhandle, westward to south Alabama, and inland to Kentucky.[1][2]
Ecology
Habitat
S. gracillima is found in wet pine savannas and seepage bogs.[1]
Phenology
Flowering occurs from August through November.[1][4]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Weakley AS (2015) Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 USDA NRCS (2016) The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 118 January 2018). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ Semple JC (2012) Typification of Solidago gracillma (Asteraceae: Astereae) and application of the name. Phytoneuron 107:1-10.
- ↑ Nelson G (18 January 2018) PanFlora. Retrieved from gilnelson.com/PanFlora/