Difference between revisions of "Agalinis filifolia"
Krobertson (talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
| range_map_caption = Natural range of ''Agalinis filifolia'' from USDA NRCS [http://www.plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=AGFI2 Plants Database]. | | range_map_caption = Natural range of ''Agalinis filifolia'' from USDA NRCS [http://www.plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=AGFI2 Plants Database]. | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | Common names: Seminole | + | Common names: Seminole false foxglove; Fine-leaf gerardia |
==Taxonomic notes== | ==Taxonomic notes== | ||
Synonym: ''Gerardia filifolia'' Nutt. | Synonym: ''Gerardia filifolia'' Nutt. | ||
Revision as of 13:29, 24 August 2016
| Agalinis filifolia | |
|---|---|
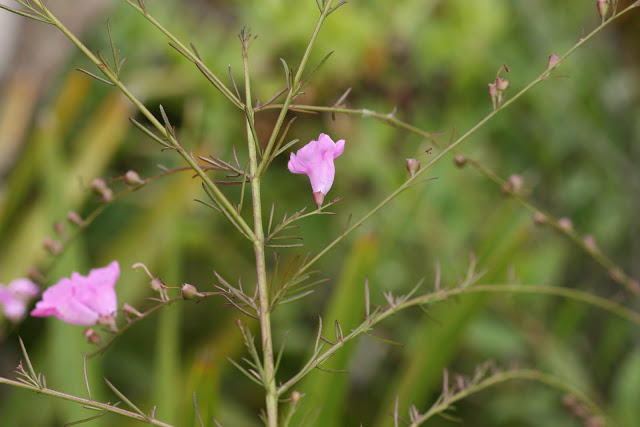

| |
| Photo by Craig Huegel | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Lamiales |
| Family: | Orobanchaceae |
| Genus: | Agalinis |
| Species: | A. filifolia |
| Binomial name | |
| Agalinis filifolia (Nutt.) Raf. | |
| |
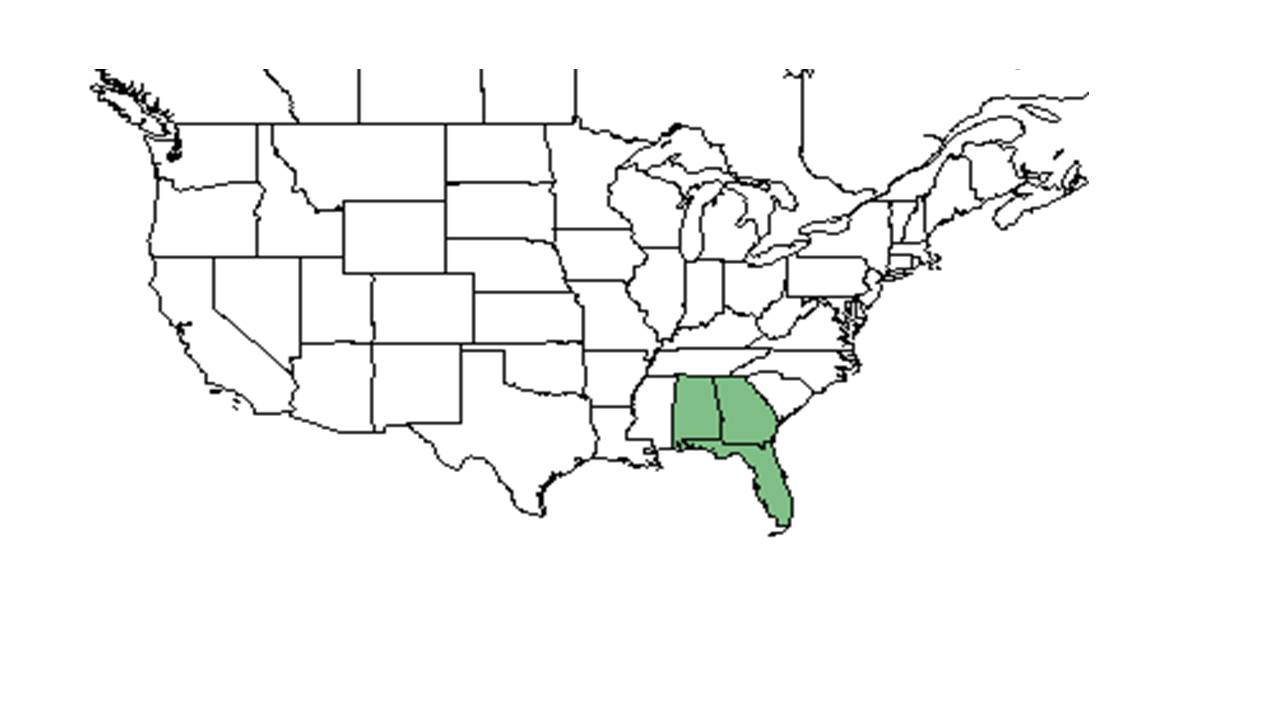
| Natural range of Agalinis filifolia from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Seminole false foxglove; Fine-leaf gerardia
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonym: Gerardia filifolia Nutt.
Description
It is an annual.[1]
Distribution
It is frequent in all of Florida; north to Georgia and Alabama.[1] In Georgia it is listed as critically imperiled.[2]
Ecology
Habitat
This species is found in sandhills and coastal scrub.[3] It is also found in longleaf pine savannas, sandy pinewoods and barrens, and on sand dunes, flats, and interdune hollows. Other habitats includes open stands of evergreen oak shrub, flatwoods, saw-palmetto woods, borders of titi bogs, and in dry sandy scrub that borders mesic woodlands.[4] Agalinis filifolia is somewhat shade tolerant and found in a variety of moisture conditions, from dry to wet.[1] It is observed in mainly sandy soils, including loamy sand. It can also be found in disturbed habitats, including clear-cuts and pine plantations, roadside banks and ditches, and clearings for power lines.[4]
Associated species include Myrica cerifera, Aristida stricta, Myrica pusilo, Aristida spiciformis, Chrysoma, Polygonella, Ceratiola, Conradina, Saw palmetto, Quercus species, and Pinus species.[4]
Phenology
This species has been observed flowering August through October, and fruiting August through November.[4]
Pollination
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of Agalinis filifolia at Archbold Biological Station:[5]
Apidae: Apis mellifera, Bombus impatiens, B. pennsylvanicus
Halictidae: Agapostemon spledens, Augochlorella aurata, A. gratiosa, Lasioglossum coreopsis, L. miniatulus, L. nymphalis, L. placidensis, L. puteulanum
Megachilidae: Megachile brevis psedudobrevis, M. mendica, M. petulans, M. texana
Use by animals
Serves as larval food for the caterpillars of common buckeye butterflies[6]
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Hall, David W. Illustrated Plants of Florida and the Coastal Plain: based on the collections of Leland and Lucy Baltzell. 1993. A Maupin House Book. Gainesville. 341. Print.
- ↑ [[1]]NatureServe. Accessed: March 22, 2016
- ↑ Wunderlin, Richard P. and Bruce F. Hansen. Guide to the Vascular Plants of Florida. Second edition. 2003. University Press of Florida: Gainesville/Tallahassee/Tampa/Boca Raton/Pensacola/Orlando/Miami/Jacksonville/Ft. Myers. 546. Print.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014.Collectors: Sidney M. Daniel, Robert K. Godfrey, R. Kral, Loran C. Anderson, J. B. Hilmon, J. M. Canne, Mark A. Garland, Gary R. Knight, Nancy Endmonson, Cecil R. Slaughter, and Jean W. Wooten. States and Counties: Florida: Wakulla, Franklin, Liberty, Bay, Escambia, Charlotte, Brevard, Nassau, Putnam, Sarasota, Taylor, Manatee, and Lake. Georgia: Thomas
- ↑ Deyrup, M.A. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowering plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
- ↑ [[2]]Native Florida Wildflowers. Accessed: March 22, 2016.