Difference between revisions of "Sabatia brevifolia"
Krobertson (talk | contribs) (→Distribution) |
Krobertson (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | In the Coastal Plain in Florida and Georgia, ''S. brevifolia'' can occur in wet pine flatwoods, moist sand around ephemeral ponds in open flatwoods<ref name="fsu">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: November 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Robert K. Godfrey, R.A. Norris, Annie Schmidt, Cecil R. Slaughter, Rodie White. States and Counties: Florida: Liberty, Osceola. Georgia: Grady. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.</ref> | + | In the Coastal Plain in Florida and Georgia, ''S. brevifolia'' can occur in wet pine flatwoods, moist sand around ephemeral ponds in open flatwoods,<ref name="fsu">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: November 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Robert K. Godfrey, R.A. Norris, Annie Schmidt, Cecil R. Slaughter, Rodie White. States and Counties: Florida: Liberty, Osceola. Georgia: Grady. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.</ref> seepage bogs on pineland slopes, borders of cypress-gum ponds, exposed shores of sinkhole ponds, and sometimes open well-drained woodlands.<ref name="eol"/> Associated species ''Polygala cruciata, P. hookeri, P. lutea, Eupatorium leucolepis.''<ref name="fsu"/> |
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
Revision as of 15:44, 18 August 2016
| Sabatia brevifolia | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Gentianales |
| Family: | Gentianaceae |
| Genus: | Sabatia |
| Species: | S. brevifolia |
| Binomial name | |
| Sabatia brevifolia Raf. | |
| |
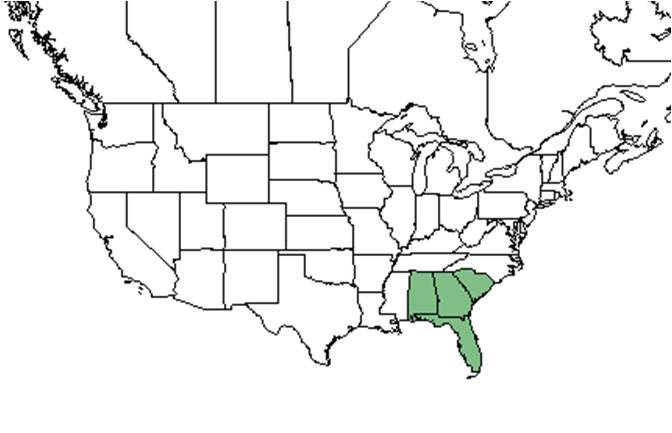
| Natural range of Sabatia brevifolia from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: shortleaf rose gentian
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonym: Sabatia elliottii Steudel
Description
"Glabrous, perennial or annual herbs with erect or ascending stems. Leaves opposite, entire, sessile. Inflorescence terminal, cymose. Calyx 5-13 parted, lobes united at bae, those of first flowers longest, smaller on later flowers; corolla rotate white or pink with yellow eye, lobes 5-13, tube becoming membranous and persistent around the capsule. Capsule ovoid to ellipsoid; seeds small, alveolate." [1]
"Annual, rhizomes absent. Stems freely branched, terete or slightly angled above, 2-5 dm tall. Basal leaves present or absent at anthesis; stems leaves linear to narrowly lanceolate or elliptic-oblanceolate, 1-2.5 cm long, 1-8 mm wide, acute to obtuse. Inflorescence paniculate, branches alternate, to 3 dm long, 0.5-2.5 dm broad. Calyx lobes 5, linear, 2-7 mm long; corolla lobes white, usually white on drying, elliptic to oblanceolate, 1-1.5 cm long, 2-4 mm wide; filaments 1-2 mm long; stigmas 3-4 mm long, style 0-1 mm long. Capsule 4-5 mm long; seeds brown, 0.3-0.4 mm long." [1]
Distribution
Regionally endemic to the Coastal Plain from Virginia south through most of Florida and west to southern Alabama. It is rare in Alabama.[2]
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain in Florida and Georgia, S. brevifolia can occur in wet pine flatwoods, moist sand around ephemeral ponds in open flatwoods,[3] seepage bogs on pineland slopes, borders of cypress-gum ponds, exposed shores of sinkhole ponds, and sometimes open well-drained woodlands.[2] Associated species Polygala cruciata, P. hookeri, P. lutea, Eupatorium leucolepis.[3]
Phenology
White flowers bloom August through November[4].
Pollination
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of Sabatia brevifolia at Archbold Biological Station: [5]
Halictidae: Lasioglossum nymphalis
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: November 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Robert K. Godfrey, R.A. Norris, Annie Schmidt, Cecil R. Slaughter, Rodie White. States and Counties: Florida: Liberty, Osceola. Georgia: Grady. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 836. Print.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 [[1]]Encyclopedia of Life. Accessed: March 15, 2016
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: November 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Robert K. Godfrey, R.A. Norris, Annie Schmidt, Cecil R. Slaughter, Rodie White. States and Counties: Florida: Liberty, Osceola. Georgia: Grady. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ [[2]]Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center. Accessed: March 14, 2016
- ↑ Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.