Difference between revisions of "Dichanthelium strigosum"
(→Cultivation and Restoration) |
Krobertson (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| − | ''Dichanthelium strigosum'' is a perennial graminoid theat tends to grow in thick mats | + | ''Dichanthelium strigosum'' is a perennial graminoid theat tends to grow in thick mats. <ref name="FSU Herbarium>Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Cecil R. Slaughter, Loran C. Anderson, S. W. Leonard, A. E. Radford, H. L. Blomquist, D. S. Correll, Wm. G. Atwater, Robert Kral, O. Lakela, R. Komarek, K. E. Blum, R.K. Godfrey, Ed Tyson, A. F. Clewell, Annie Schmidt, Wilson Baker, Richard W. Pohl, Frank W. Gould, and H. Kurz. States and Counties: Alabama: Convington. Florida: Bay, Brevard, Dade, Escambia, Franklin, Hillsborough, Indian River, Jefferson, Lafayette, Lee, Leon, Madison, Nassau, Okaloosa, Polk, Wakulla, and Washington. Georgia : Baker and Thomas. North Carolina: Brunswick. South Carolina: Greenwood and Jasper. Other Countries: Panama (United States of America).</ref> |
Generally, for the ''Dichanthelium'' genus, they have "spikelets usually in panicles, round or nearly so in cross section, 2-flowered, terminal fertile, basal sterile, neutral or staminate. First glume usually present, 2nd glume and sterile lemma similar; fertile lemma and palea indurate without hyaline margins. Taxonomically our most difficult and least understood genus of grasses, more than 100 species an varieties are ascribed to the Carolinas by some authors. Note general descriptions for species groups (e.g., 1-4, 5-8, 9-13, and 26-62)." <ref name=rad> Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 142-151. Print. </ref> | Generally, for the ''Dichanthelium'' genus, they have "spikelets usually in panicles, round or nearly so in cross section, 2-flowered, terminal fertile, basal sterile, neutral or staminate. First glume usually present, 2nd glume and sterile lemma similar; fertile lemma and palea indurate without hyaline margins. Taxonomically our most difficult and least understood genus of grasses, more than 100 species an varieties are ascribed to the Carolinas by some authors. Note general descriptions for species groups (e.g., 1-4, 5-8, 9-13, and 26-62)." <ref name=rad> Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 142-151. Print. </ref> | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | It can be found in relatively undisturbed areas,<ref>Thaxton, J. M. (2003). Effects of fire intensity on groundcover shrubs in a frequently burned longleaf pine savanna. Ann Arbor, MI, Louisiana State University and Agricultural & Mechanical College. Ph.D.: 146. Kirkman, L. K., K. L. Coffey, et al. (2004). "Ground cover recovery patterns and life-history traits: implications for restoration obstacles and opportunities in a species-rich savanna." Journal of Ecology 92(3): 409-421.</ref> including longleaf pine savannas,<ref name="Thaxton 2003"/> saw palmetto-wax myrtle thickets, sandhill ridges, and bogs | + | It can be found in relatively undisturbed areas,<ref>Thaxton, J. M. (2003). Effects of fire intensity on groundcover shrubs in a frequently burned longleaf pine savanna. Ann Arbor, MI, Louisiana State University and Agricultural & Mechanical College. Ph.D.: 146. Kirkman, L. K., K. L. Coffey, et al. (2004). "Ground cover recovery patterns and life-history traits: implications for restoration obstacles and opportunities in a species-rich savanna." Journal of Ecology 92(3): 409-421.</ref> including longleaf pine savannas,<ref name="Thaxton 2003"/> saw palmetto-wax myrtle thickets, sandhill ridges, and bogs. <ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> However, ''D. strigosum'' also occurs in disturbed areas like power line corridors, roadsides, fields, and clear-cuts. <ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> This species seems to prefer moist sandy soils. <ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> |
Associated species include ''Rhynchospora pusilla, Ludwigia linifolia, Andropogon, Schizachyrium, Eupatorium, Serenoa repens, Juniperus, Schoenus'' (FSU Herbarium). | Associated species include ''Rhynchospora pusilla, Ludwigia linifolia, Andropogon, Schizachyrium, Eupatorium, Serenoa repens, Juniperus, Schoenus'' (FSU Herbarium). | ||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| − | Flowering and fruiting has been observed in February, as well as April through August | + | Flowering and fruiting has been observed in February, as well as April through August. <ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> |
===Seed dispersal=== | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
| − | |||
Revision as of 12:12, 21 June 2016
| Dichanthelium strigosum | |
|---|---|
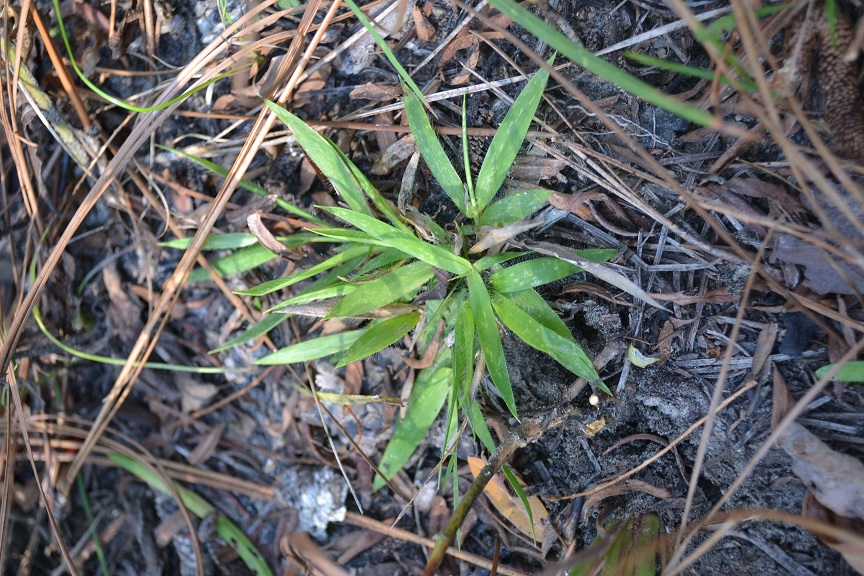

| |
| Photo taken by Kevin Robertson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida – Monocotyledons |
| Order: | Cyperales |
| Family: | Poaceae ⁄ Gramineae |
| Genus: | Dichanthelium |
| Species: | D. strigosum |
| Binomial name | |
| Dichanthelium strigosum (Muhl. ex Elliott) Freckmann | |
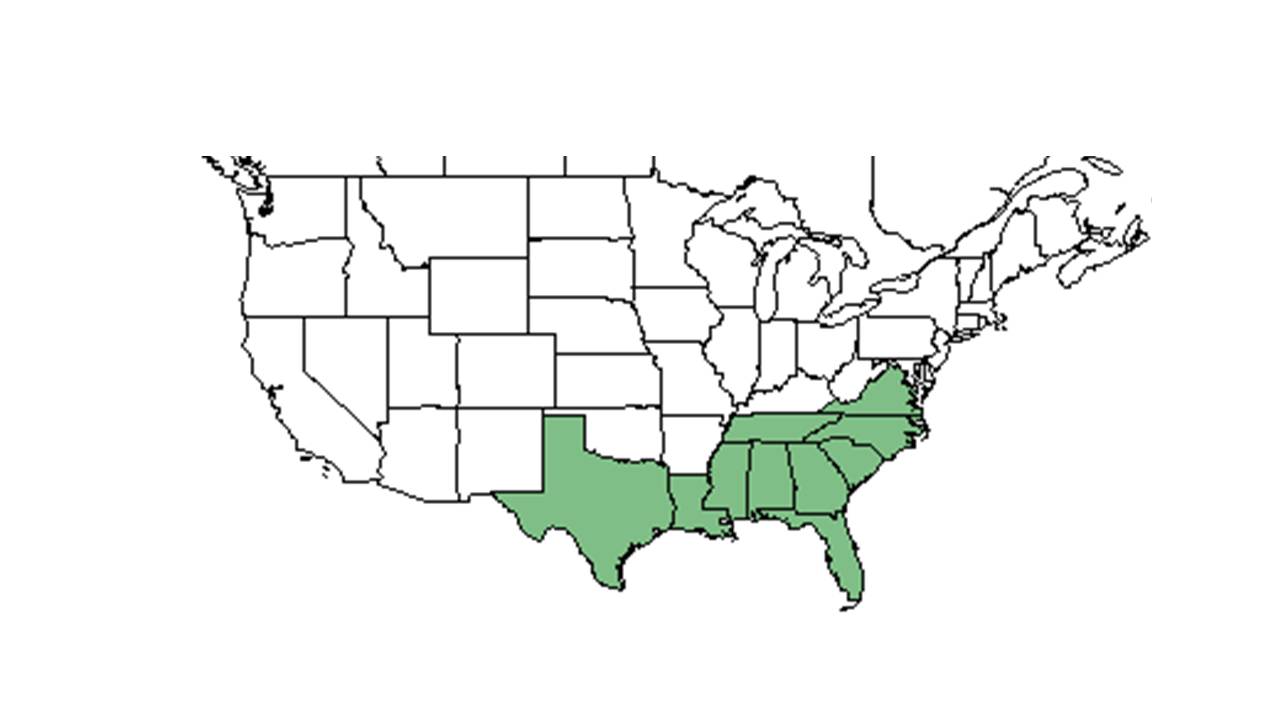
| |
| Natural range of Dichanthelium strigosum from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: roughhair rosette grass
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonym: Panicum strigosum Muhl. ex Elliott The Plant List.org
Description
Dichanthelium strigosum is a perennial graminoid theat tends to grow in thick mats. [1]
Generally, for the Dichanthelium genus, they have "spikelets usually in panicles, round or nearly so in cross section, 2-flowered, terminal fertile, basal sterile, neutral or staminate. First glume usually present, 2nd glume and sterile lemma similar; fertile lemma and palea indurate without hyaline margins. Taxonomically our most difficult and least understood genus of grasses, more than 100 species an varieties are ascribed to the Carolinas by some authors. Note general descriptions for species groups (e.g., 1-4, 5-8, 9-13, and 26-62)." [2]
Specifically, for the D. strigosum species, they are "perennial with distinct basal rosettes; branching, when present, from nodes above basal rosette. Leaves basal and cauline, vernal and autumnal. Culms 1-5 dm tall, nodes bearded, internodes long pilose. Blades to 6 cm long, 2-6 mm wide, softly pilose on both surfaces, margins long ciliate; sheaths pilose to almost glabrous; ligules ciliate, 1-2.5 mm long. Panicle 5-7 cm long, 3-5.5 cm broad; rachis long pilose, branches ascending-spreading, pilose basally. Spikelets obovoid to broadly ellipsoid, 1.2-1.6 mm long; pedicels smoothish. First glume glabrous,, acute, or obtuse, 0.8-1 mm long, 2nd glume and sterile lemma glabrous, acute, 1.2 mm long; fertile lemma and palea 1-1.2 mm long. Grain 0.8-1 mm long, yellowish or purplish, broadly ellipsoid or subglobose." [2]
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
It can be found in relatively undisturbed areas,[3] including longleaf pine savannas,[4] saw palmetto-wax myrtle thickets, sandhill ridges, and bogs. [1] However, D. strigosum also occurs in disturbed areas like power line corridors, roadsides, fields, and clear-cuts. [1] This species seems to prefer moist sandy soils. [1]
Associated species include Rhynchospora pusilla, Ludwigia linifolia, Andropogon, Schizachyrium, Eupatorium, Serenoa repens, Juniperus, Schoenus (FSU Herbarium).
Phenology
Flowering and fruiting has been observed in February, as well as April through August. [1]
Seed dispersal
Seed dispersed by gravity.[5]According to Kay Kirkman, a plant ecologist, this species disperses by gravity. [6]
Fire ecology
It can tolerate biennial, early growing season prescribed fires.[4]
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Cecil R. Slaughter, Loran C. Anderson, S. W. Leonard, A. E. Radford, H. L. Blomquist, D. S. Correll, Wm. G. Atwater, Robert Kral, O. Lakela, R. Komarek, K. E. Blum, R.K. Godfrey, Ed Tyson, A. F. Clewell, Annie Schmidt, Wilson Baker, Richard W. Pohl, Frank W. Gould, and H. Kurz. States and Counties: Alabama: Convington. Florida: Bay, Brevard, Dade, Escambia, Franklin, Hillsborough, Indian River, Jefferson, Lafayette, Lee, Leon, Madison, Nassau, Okaloosa, Polk, Wakulla, and Washington. Georgia : Baker and Thomas. North Carolina: Brunswick. South Carolina: Greenwood and Jasper. Other Countries: Panama (United States of America).
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 142-151. Print.
- ↑ Thaxton, J. M. (2003). Effects of fire intensity on groundcover shrubs in a frequently burned longleaf pine savanna. Ann Arbor, MI, Louisiana State University and Agricultural & Mechanical College. Ph.D.: 146. Kirkman, L. K., K. L. Coffey, et al. (2004). "Ground cover recovery patterns and life-history traits: implications for restoration obstacles and opportunities in a species-rich savanna." Journal of Ecology 92(3): 409-421.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Thaxton, J. M. (2003). Effects of fire intensity on groundcover shrubs in a frequently burned longleaf pine savanna. Ann Arbor, MI, Louisiana State University and Agricultural & Mechanical College. Ph.D.: 146.
- ↑ Kirkman, L. K., K. L. Coffey, et al. (2004). "Ground cover recovery patterns and life-history traits: implications for restoration obstacles and opportunities in a species-rich savanna." Journal of Ecology 92(3): 409-421.
- ↑ Kay Kirkman, unpublished data, 2015.