Difference between revisions of "Gaylussacia dumosa"
(→Pollination) |
|||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | ''Gaylussacia dumosa'' is restricted to native groundcover with a statistical affinity in upland pinelands of South Georgia | + | ''Gaylussacia dumosa'' is restricted to native groundcover with a statistical affinity in upland pinelands of South Georgia. <ref name=or07> Ostertag, T.E., and K.M. Robertson. 2007. A comparison of native versus old-field vegetation in upland pinelands managed with frequent fire, South Georgia, USA. Pages 109–120 in R.E. Masters and K.E.M. Galley (eds.). Proceedings of the 23rd Tall Timbers Fire Ecology Conference: Fire in Grassland and Shrubland Ecosystems.</ref> |
<!--===Phenology===--> <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | <!--===Phenology===--> <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| − | + | ===Seed dispersal=== | |
| + | According to Kay Kirkman, a plant ecologist, this species disperses by being consumed by vertebrates (being assumed). <ref name="KK"> Kay Kirkman, unpublished data, 2015. </ref> | ||
<!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
<!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | <!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| + | |||
===Pollination=== | ===Pollination=== | ||
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of ''Gaylussacia dumosa'' at Archbold Biological Station (Deyrup 2015): | The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of ''Gaylussacia dumosa'' at Archbold Biological Station (Deyrup 2015): | ||
Revision as of 14:43, 8 April 2016
| Gaylussacia dumosa | |
|---|---|
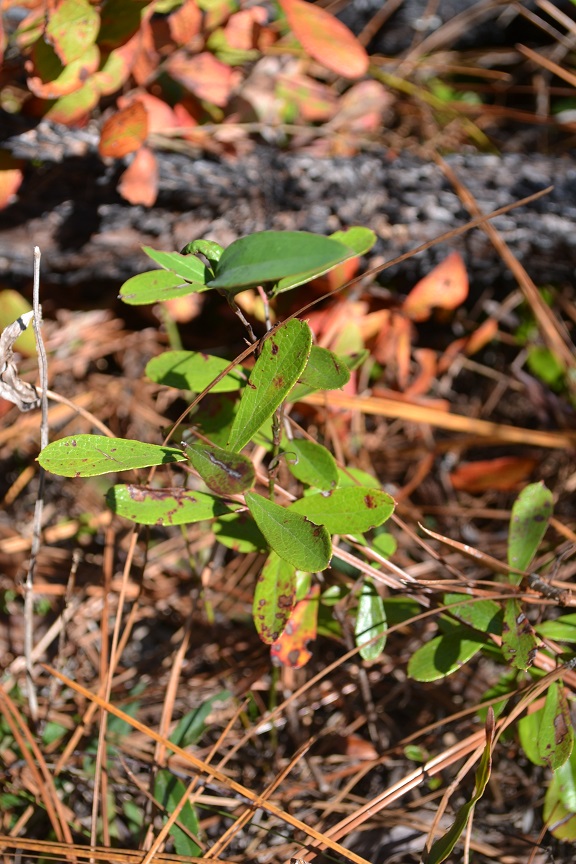

| |
| Photo taken by Kevin Robertson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Ericales |
| Family: | Ericaceae |
| Genus: | Gaylussacia |
| Species: | G. dumosa |
| Binomial name | |
| Gaylussacia dumosa (Andrews) Torr. & A. Gray | |
| |
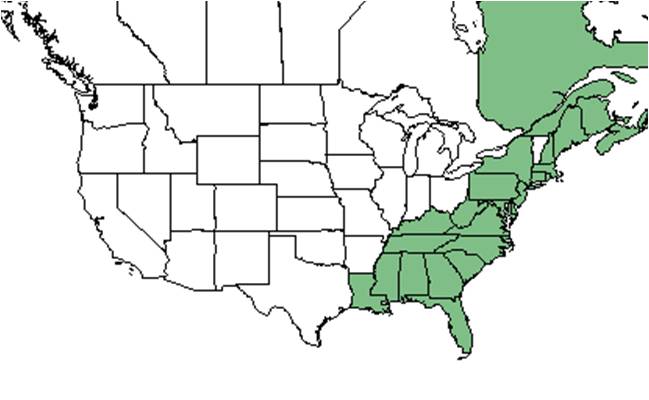
| Natural range of Gaylussacia dumosa from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: dwarf huckleberry
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Gaylussacia dumosa (Andrews) Torrey var. dumosa; Lasiococcus dumosus (Andrews) Small
Description
A description of Gaylussacia dumosa is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
Gaylussacia dumosa is restricted to native groundcover with a statistical affinity in upland pinelands of South Georgia. [1]
Seed dispersal
According to Kay Kirkman, a plant ecologist, this species disperses by being consumed by vertebrates (being assumed). [2]
Pollination
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of Gaylussacia dumosa at Archbold Biological Station (Deyrup 2015):
Apidae: Apis mellifera, Bombus impatiens
Halictidae: Augochlorella aurata, A. gratiosa
Megachilidae: Megachile brevis pseudobrevis, M. integrella
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
Ostertag, T.E., and K.M. Robertson. 2007. A comparison of native versus old-field vegetation in upland pinelands managed with frequent fire, South Georgia, USA. Pages 109–120 in R.E. Masters and K.E.M. Galley (eds.). Proceedings of the 23rd Tall Timbers Fire Ecology Conference: Fire in Grassland and Shrubland Ecosystems.
- ↑ Ostertag, T.E., and K.M. Robertson. 2007. A comparison of native versus old-field vegetation in upland pinelands managed with frequent fire, South Georgia, USA. Pages 109–120 in R.E. Masters and K.E.M. Galley (eds.). Proceedings of the 23rd Tall Timbers Fire Ecology Conference: Fire in Grassland and Shrubland Ecosystems.
- ↑ Kay Kirkman, unpublished data, 2015.