Difference between revisions of "Brickellia eupatorioides"
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) (→Description) |
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
It is common in grassland communities.<ref name="Bahm et al 2011"/> It is especially dominant in the tallgrass prairie.<ref>Towne 2002 cited by Kula et al 2005.More citation needed.</ref> It is also found in loblolly pine communities.<ref name="Miller et al 1999">Miller, J. H. and K. V. Miller (1999). Forest plants of the southeast, and their wildlife uses Champaign, IL, Southern Weed Science Society.</ref> | It is common in grassland communities.<ref name="Bahm et al 2011"/> It is especially dominant in the tallgrass prairie.<ref>Towne 2002 cited by Kula et al 2005.More citation needed.</ref> It is also found in loblolly pine communities.<ref name="Miller et al 1999">Miller, J. H. and K. V. Miller (1999). Forest plants of the southeast, and their wildlife uses Champaign, IL, Southern Weed Science Society.</ref> | ||
| − | In addition, this species occurs in pine-oak woodlands, open pinewoods, limestone glades, sandhills, longleaf pine-wiregrass communities, and hardwood hammocks | + | In addition, this species occurs in pine-oak woodlands, open pinewoods, limestone glades, sandhills, longleaf pine-wiregrass communities, and hardwood hammocks. It can also grow in disturbed areas including railways, roadside embankments, and open fields. ''B. eupatorioides'' appears in a range of light conditions, from semi-shade to full sun, and it prefers rocky or sandy soils. In Florida, it has been found in drying or moist loamy sand; in New Mexico, gravelly sand; in Texas, clay loam; and in Kansas, dry rocky soil<ref name="fsu"/>. |
| − | Associated species include ''Symphyotrichum concolor, Aster linariifolius, Aster phyllolepis, Campanula americana, Ageratina aromatica, Liatris gracilis'', and others | + | Associated species include ''Symphyotrichum concolor, Aster linariifolius, Aster phyllolepis, Campanula americana, Ageratina aromatica, Liatris gracilis'', and others. |
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
Revision as of 17:43, 4 April 2016
| Brickellia eupatorioides | |
|---|---|
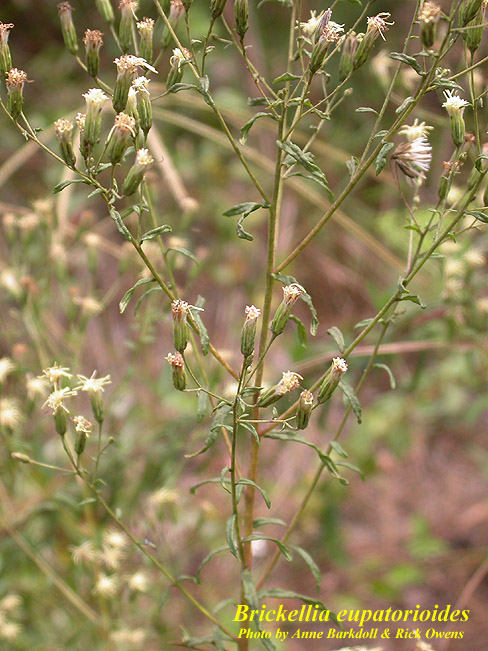

| |
| Photo by Anne Barkdoll and Rick Owens, Atlas of Florida Vascular Plants | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae ⁄ Compositae |
| Genus: | Brickellia |
| Species: | B. eupatorioides |
| Binomial name | |
| Brickellia eupatorioides (L.) Shinners | |
| |
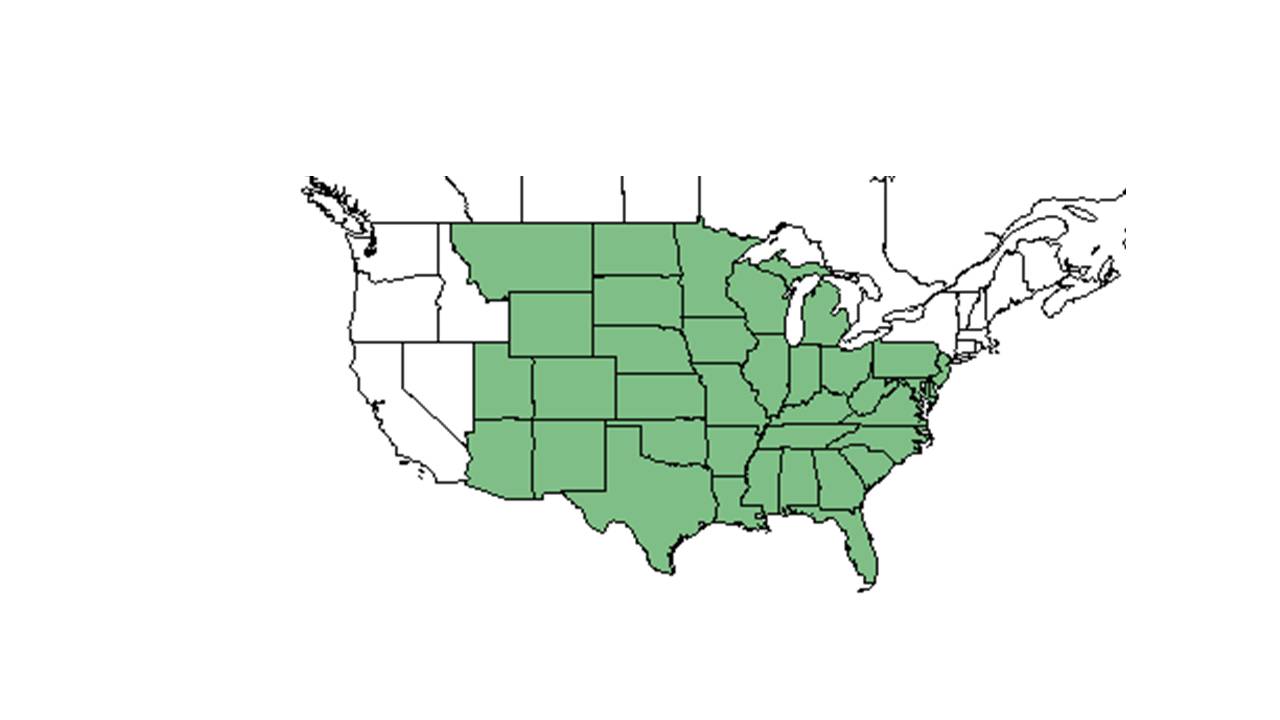
| Natural range of Brickellia eupatorioides from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: false boneset
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Description
A description of Brickellia eupatorioides is provided in The Flora of North America.
Brickellia eupatorioides var. corymbulosa has been documented to be variable in habit, from erect and subvirgatte to decumbent, spreading or distinctly prostrate, arising from a slender deep-seated rootstock[1].
This species is perennial.
Distribution
Ecology
Mycorrhizal relationships seemed to yield significantly higher phosphorous levels.[2]
Habitat
It is common in grassland communities.[3] It is especially dominant in the tallgrass prairie.[4] It is also found in loblolly pine communities.[5]
In addition, this species occurs in pine-oak woodlands, open pinewoods, limestone glades, sandhills, longleaf pine-wiregrass communities, and hardwood hammocks. It can also grow in disturbed areas including railways, roadside embankments, and open fields. B. eupatorioides appears in a range of light conditions, from semi-shade to full sun, and it prefers rocky or sandy soils. In Florida, it has been found in drying or moist loamy sand; in New Mexico, gravelly sand; in Texas, clay loam; and in Kansas, dry rocky soil[1].
Associated species include Symphyotrichum concolor, Aster linariifolius, Aster phyllolepis, Campanula americana, Ageratina aromatica, Liatris gracilis, and others.
Phenology
B. eupatorioides has been observed flowering in July through November, and fruiting in October (FSU Herbarium).
Seed bank and germination
It germinates well at 18-22 degrees Celsius.[2]
Fire ecology
It is fire tolerant.[3]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: L. C. Anderson, W. Baker, E. A. Bartholomew, S. F. Blake, J. R. Bozeman, J. R. Burkhalter, C. Cooksey, D. S. Correll, V. L. Cory, D. Demaree, J. Ewan, N Ewan, W. B. Fox, A. Gholson Jr., R. K. Godfrey, F. R. Hedges, N. C. Henderson, R. Komarek, J. Lazor, R. Lazor, R. Kral, S. McDaniel, J. B. Morrill, G. W. Parmelee, R. E. Perdue Jr., A. E. Radford, G. S. Ramseur, P. L. Redfearn Jr., J. A. Steyermark, B. C. Tharpe, and C. S. Wallis. States and Counties: Alabama: Jefferson and Talladega. Arkansas: Cleburne, Faulkner, and Logan. Colorado: Boulder and Lincoln. Florida: Calhoun, Decatur, Escambia, Gadsden, Jackson, Leon, Liberty, Madison, Suwannee, and Wakulla. Georgia: Decatur, Early, Grady, and Thomas. Iowa: Mills and Pottawatomie. Kansas: Hamilton and Johnson. Kentucky: Madison. Maryland: St. Marys. Michigan: Barry and Kent. Mississippi: Okibbeha. Missouri: Cass, Crawford, Greene, Jackson, Johnson, and Platte. New Mexico: Colfax. North Carolina: Alexander, Buncombe, and Richmond. Tennessee: Davidson. Texas: Crockett, Dallas, Gray, Kern, Milam, Ochiltree, Pecos, Tarrant, Williamson, and Wood. Virginia: Giles. West Virginia: Wirt.
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: L. C. Anderson, W. Baker, E. A. Bartholomew, S. F. Blake, J. R. Bozeman, J. R. Burkhalter, C. Cooksey, D. S. Correll, V. L. Cory, D. Demaree, J. Ewan, N Ewan, W. B. Fox, A. Gholson Jr., R. K. Godfrey, F. R. Hedges, N. C. Henderson, R. Komarek, J. Lazor, R. Lazor, R. Kral, S. McDaniel, J. B. Morrill, G. W. Parmelee, R. E. Perdue Jr., A. E. Radford, G. S. Ramseur, P. L. Redfearn Jr., J. A. Steyermark, B. C. Tharpe, and C. S. Wallis. States and Counties: Alabama: Jefferson and Talladega. Arkansas: Cleburne, Faulkner, and Logan. Colorado: Boulder and Lincoln. Florida: Calhoun, Decatur, Escambia, Gadsden, Jackson, Leon, Liberty, Madison, Suwannee, and Wakulla. Georgia: Decatur, Early, Grady, and Thomas. Iowa: Mills and Pottawatomie. Kansas: Hamilton and Johnson. Kentucky: Madison. Maryland: St. Marys. Michigan: Barry and Kent. Mississippi: Okibbeha. Missouri: Cass, Crawford, Greene, Jackson, Johnson, and Platte. New Mexico: Colfax. North Carolina: Alexander, Buncombe, and Richmond. Tennessee: Davidson. Texas: Crockett, Dallas, Gray, Kern, Milam, Ochiltree, Pecos, Tarrant, Williamson, and Wood. Virginia: Giles. West Virginia: Wirt.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Kula, A. A. R., D. C. Hartnett, et al. (2005). "Effects of mycorrhizal symbiosis on tallgrass prairie plant-herbivore interactions." Ecology Letters 8: 61-69.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Bahm, M. A., T. G. Barnes, et al. (2011). "Herbicide and fire effects on smooth brome (Bromus inermis) and Kentucky bluegrass (Poa pratensis) in invaded prairie remnants." Invasive Plant Science and Management 4: 189-197.
- ↑ Towne 2002 cited by Kula et al 2005.More citation needed.
- ↑ Miller, J. H. and K. V. Miller (1999). Forest plants of the southeast, and their wildlife uses Champaign, IL, Southern Weed Science Society.