Difference between revisions of "Tragia urticifolia"
(→Seed dispersal) |
|||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | In the Coastal Plain in Florida and Georgia, ''T. urticifolia'' can be found in limestone glades, recently burned pine-oak woods, longleaf pine forests, and in pine savannas (FSU Herbarium). It has been recorded to grow in sandy loam and clay loam soils (FSU Herbarium; Miller et al. 1999). Associated species include shortleaf pine, red oak, post oak, mockernut hickory, and longleaf pine (FSU Herbarium). | + | In the Coastal Plain in Florida and Georgia, ''T. urticifolia'' can be found in limestone glades, recently burned pine-oak woods, longleaf pine forests, and in pine savannas (FSU Herbarium). It has been recorded to grow in sandy loam and clay loam soils (FSU Herbarium; <ref name="Miller"> Miller, J. H., R. S. Boyd, et al. (1999). "Floristic diversity, stand structure, and composition 11 years after herbicide site preparation." Canadian Journal of Forest Research 29: 1073-1083. </ref>). Associated species include shortleaf pine, red oak, post oak, mockernut hickory, and longleaf pine (FSU Herbarium). |
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
Revision as of 17:33, 31 March 2016
| Tragia urticifolia | |
|---|---|
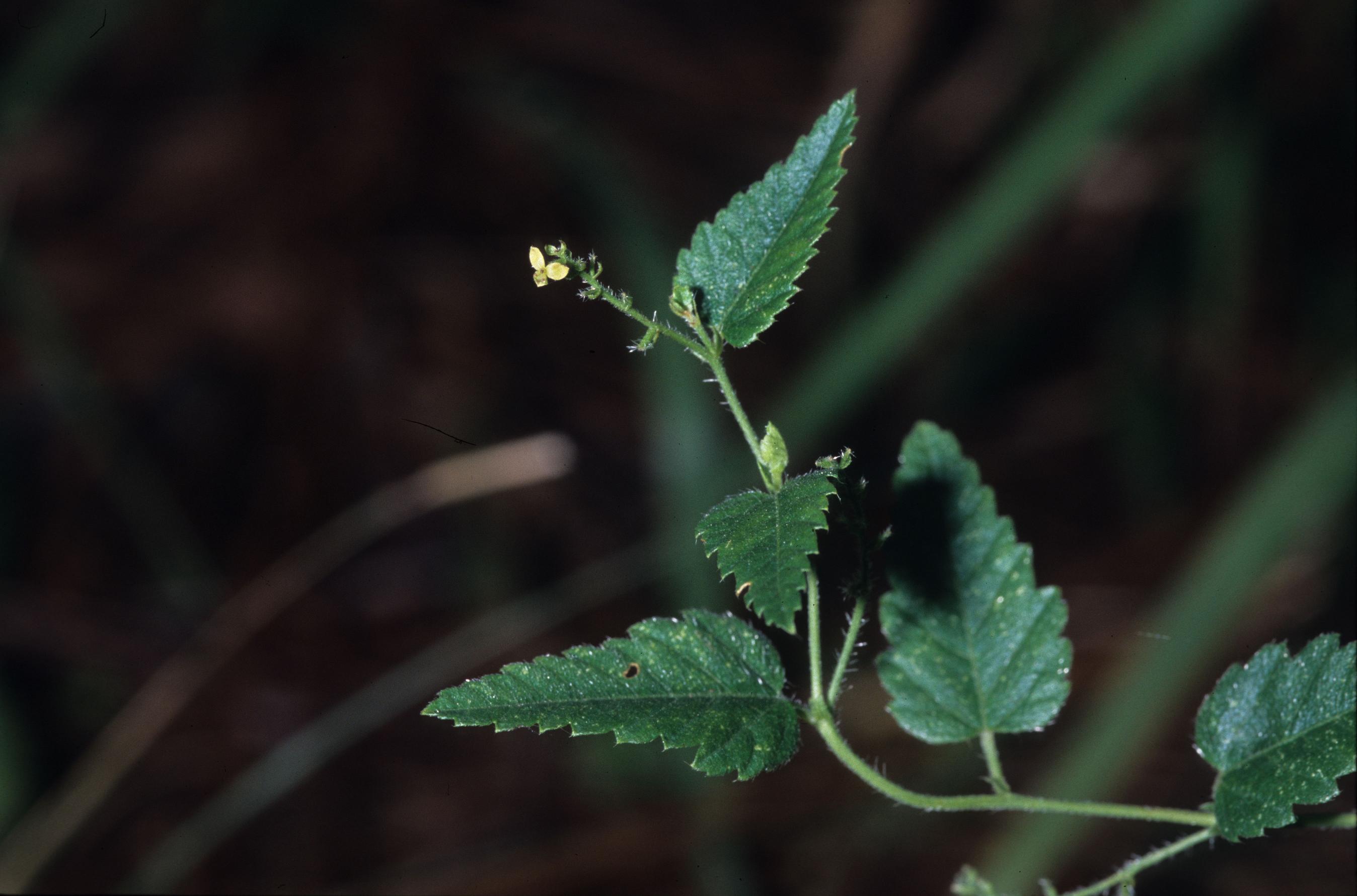

| |
| Photo was taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Euphorbiales |
| Family: | Euphorbiaceae |
| Genus: | Tragia |
| Species: | T. urticifolia |
| Binomial name | |
| Tragia urticifolia Michx. | |
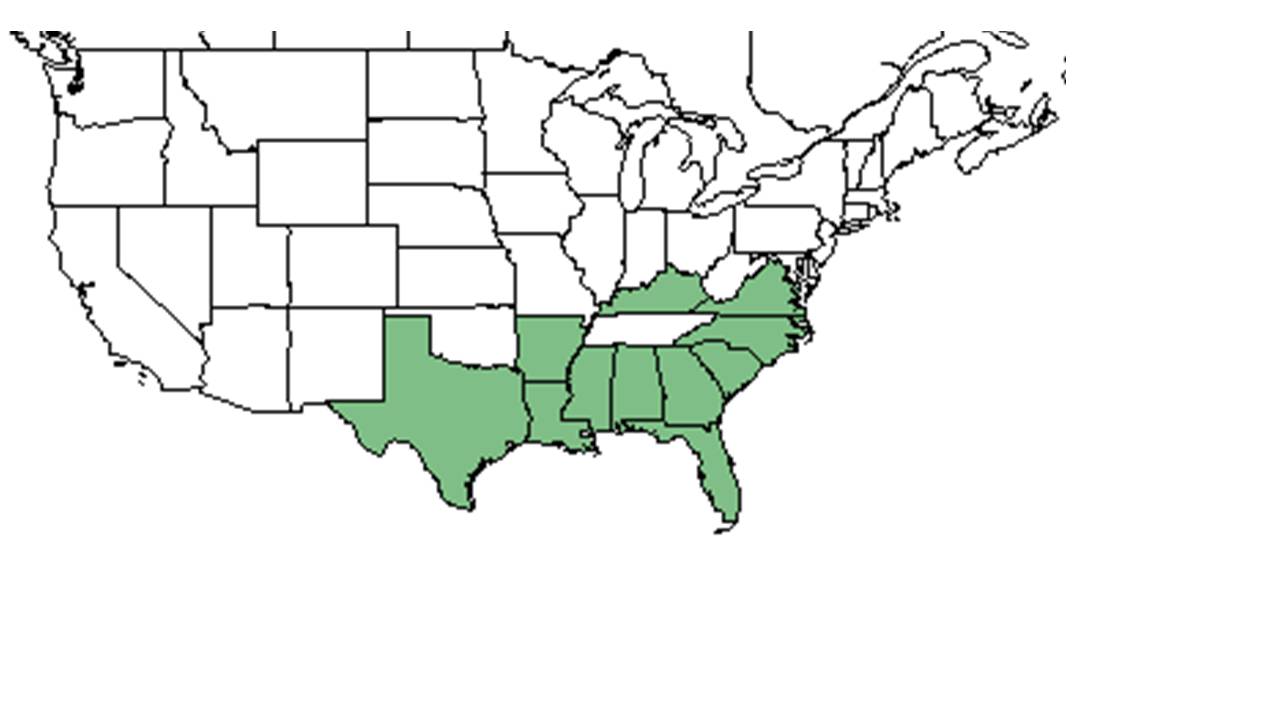
| |
| Natural range of Tragia urticifolia from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: nettleleaf noseburn
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Description
"Monoecious, perennial, rhizomatous herbs, armed with stinging trichomes. Leaves alternate, stipulate. Racemes axillary or terminal, or both, lowest 1 or 2 flowers pistillate, the upper staminate. Flowers greenish or purplish; petals absent; staminate flowers with 3-5 sepals and 2 or 3 stamens; pistillate with 3-8 sepals and 3 stigmas. Capsule 3-locular, 4-5 mm long, 7-8 mm in diam., each locule 1-seeded. Seeds light brown with darker mottling, or entirely dark brown, ovoid, 3-3.5 mm long; caruncle obsolete." [1]
"Plants 2-6 dm tall, stems strict or little branched, often reclining. Leaves triangular-ovate, 2-6 cm long, 0.7-4 cm wide, simply or doubly serrate, base truncate to subcordate; petioles 5-15 mm long. Racemes 1-4 cm long." [1]
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain in Florida and Georgia, T. urticifolia can be found in limestone glades, recently burned pine-oak woods, longleaf pine forests, and in pine savannas (FSU Herbarium). It has been recorded to grow in sandy loam and clay loam soils (FSU Herbarium; [2]). Associated species include shortleaf pine, red oak, post oak, mockernut hickory, and longleaf pine (FSU Herbarium).
Phenology
Flowering and fruiting have been observed June and September (FSU Herbarium).
Seed dispersal
According to Kay Kirkman, a plant ecologist, this species disperses by explosion mechanisms or by ants. [3]
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
Pollination
Use by animals
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Ann F. Johnson, Wilson Baker, R. A. Norris, Andre F. Clewell, Robert K. Godfrey, Loran C. Anderson, Annie Schmidt, A. Johnson, M. Jenkins. States and Counties: Florida: Gadsden, Jackson, Leon, Washington. Georgia: Decatur, Lowndes, Thomas. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
Miller, J. H., R. S. Boyd, et al. (1999). "Floristic diversity, stand structure, and composition 11 years after herbicide site preparation." Canadian Journal of Forest Research 29: 1073-1083.
Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 667. Print.
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 665. Print.
- ↑ Miller, J. H., R. S. Boyd, et al. (1999). "Floristic diversity, stand structure, and composition 11 years after herbicide site preparation." Canadian Journal of Forest Research 29: 1073-1083.
- ↑ Kay Kirkman, unpublished data, 2015.