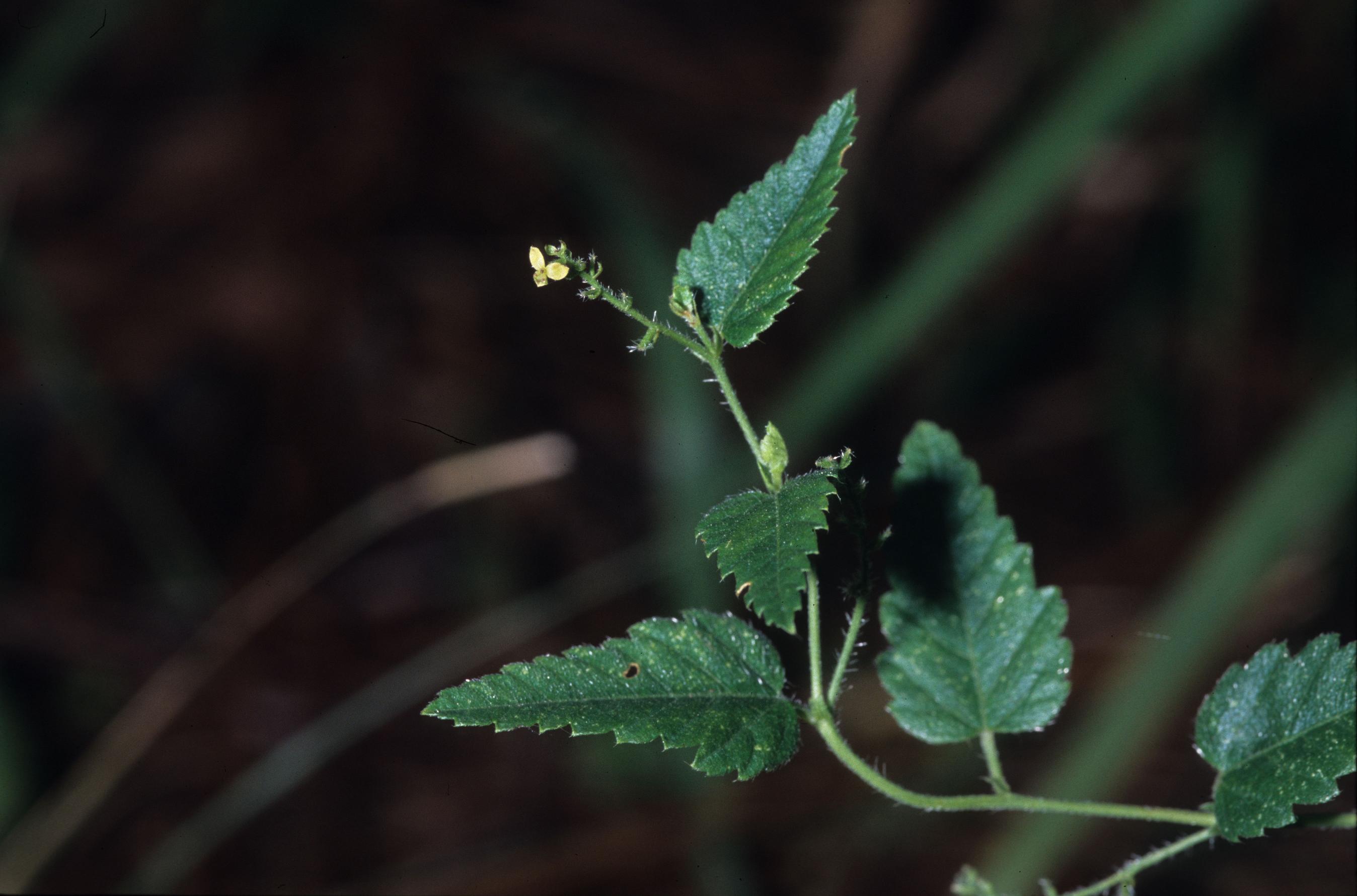
Tragia urticifolia
| Tragia urticifolia | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo was taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Euphorbiales |
| Family: | Euphorbiaceae |
| Genus: | Tragia |
| Species: | T. urticifolia |
| Binomial name | |
| Tragia urticifolia Michx. | |
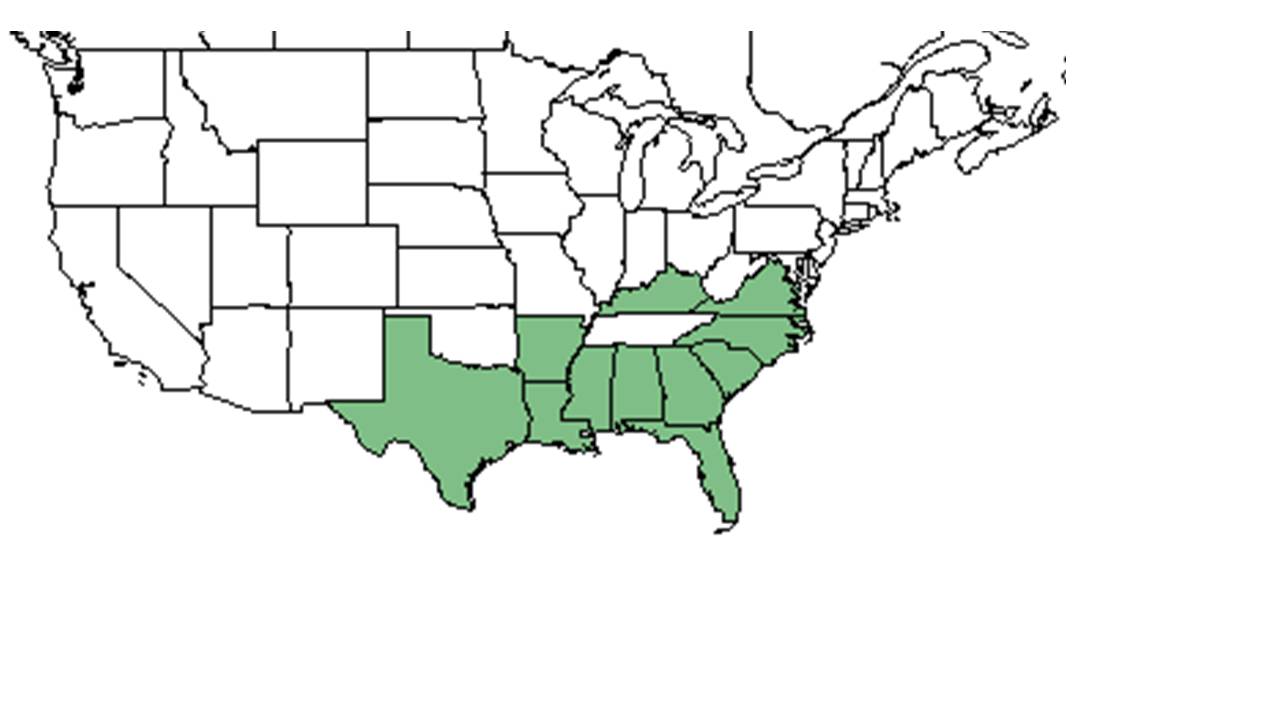
| |
| Natural range of Tragia urticifolia from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Nettleleaf noseburn
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonym: T. urticaefolia.[1]
Description
"Monoecious, perennial, rhizomatous herbs, armed with stinging trichomes. Leaves alternate, stipulate. Racemes axillary or terminal, or both, lowest 1 or 2 flowers pistillate, the upper staminate. Flowers greenish or purplish; petals absent; staminate flowers with 3-5 sepals and 2 or 3 stamens; pistillate with 3-8 sepals and 3 stigmas. Capsule 3-locular, 4-5 mm long, 7-8 mm in diam., each locule 1-seeded. Seeds light brown with darker mottling, or entirely dark brown, ovoid, 3-3.5 mm long; caruncle obsolete."[2]
"Plants 2-6 dm tall, stems strict or little branched, often reclining. Leaves triangular-ovate, 2-6 cm long, 0.7-4 cm wide, simply or doubly serrate, base truncate to subcordate; petioles 5-15 mm long. Racemes 1-4 cm long."[2]
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain in Florida and Georgia, T. urticifolia can be found in limestone glades, recently burned pine-oak woods, longleaf pine forests, and in pine savannas.[3] It has been recorded to grow in sandy loam and clay loam soils.[3][4]
Associated species include shortleaf pine, red oak, post oak, mockernut hickory, and longleaf pine.[3]
Phenology
T. urticifolia has been observed flowering May through July and in September and fruiting in June and September.[3][5]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by ants and/or explosive dehiscence.[6]
Fire ecology
Populations of Tragia urticifolia have been known to persist through repeated annual burning.[7]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draf of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 665. Print.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Ann F. Johnson, Wilson Baker, R. A. Norris, Andre F. Clewell, Robert K. Godfrey, Loran C. Anderson, Annie Schmidt, A. Johnson, M. Jenkins. States and Counties: Florida: Gadsden, Jackson, Leon, Washington. Georgia: Decatur, Lowndes, Thomas. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ Miller, J. H., R. S. Boyd, et al. (1999). "Floristic diversity, stand structure, and composition 11 years after herbicide site preparation." Canadian Journal of Forest Research 29: 1073-1083.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 14 DEC 2016
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.
- ↑ Platt, W.J., R. Carter, G. Nelson, W. Baker, S. Hermann, J. Kane, L. Anderson, M. Smith, K. Robertson. 2021. Unpublished species list of Wade Tract old-growth longleaf pine savanna, Thomasville, Georgia.