Difference between revisions of "Eupatorium album"
(→Description) |
|||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| + | A description of ''Eupatorium album'' is provided in [http://www.efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=1&taxon_id=250066731 The Flora of North America]. | ||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
Revision as of 14:35, 14 August 2015
| Eupatorium album | |
|---|---|
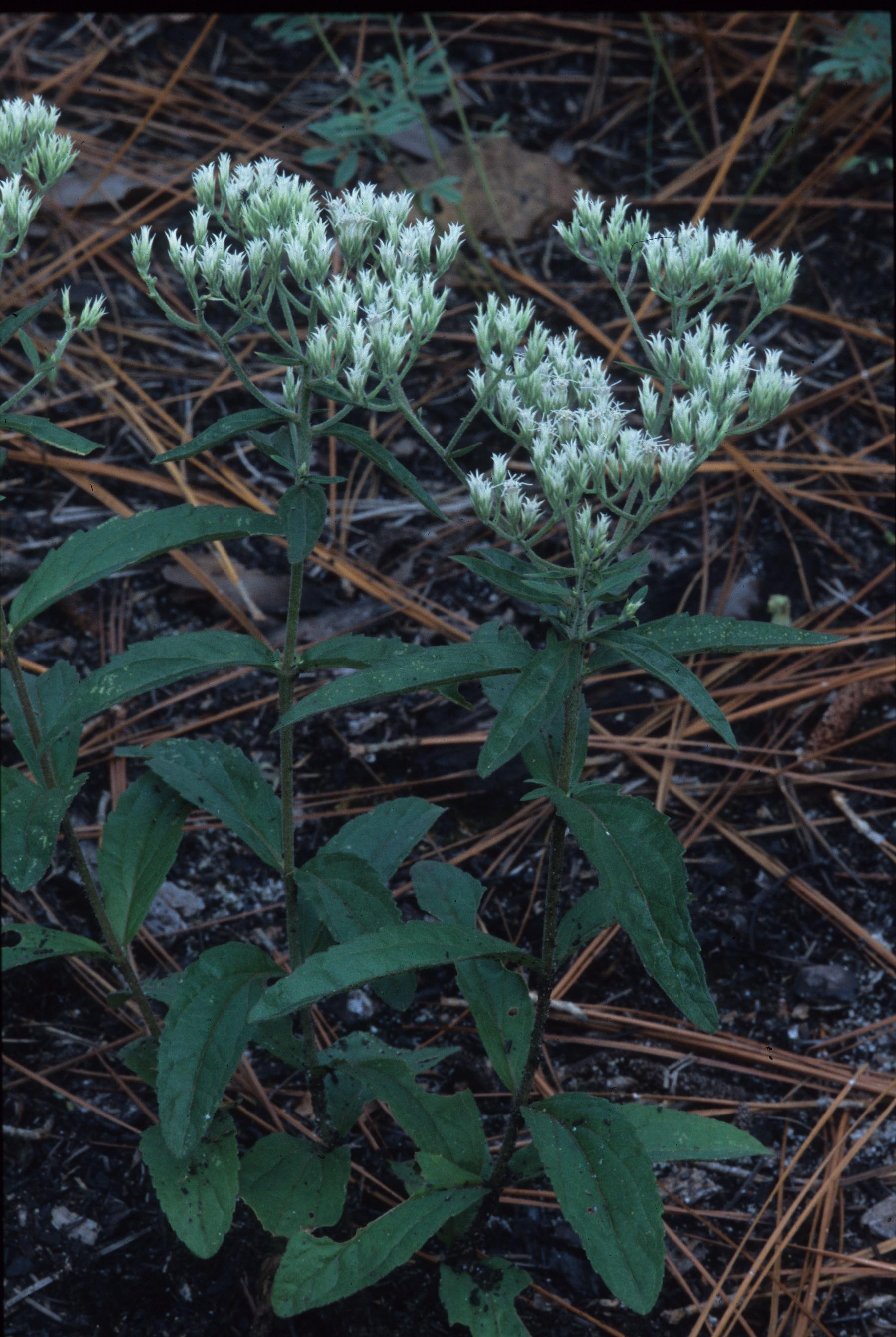

| |
| Photo was taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae ⁄ Compositae |
| Genus: | Eupatorium |
| Species: | E. album |
| Binomial name | |
| Eupatorium album L. | |
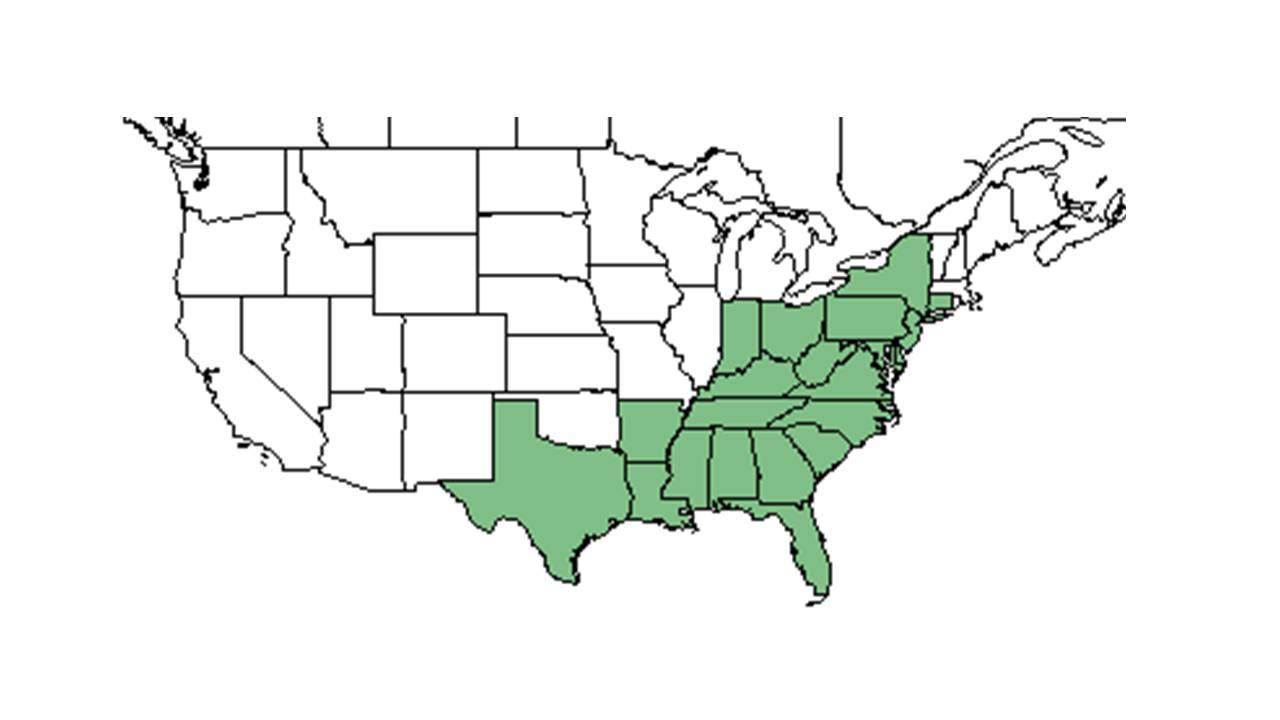
| |
| Natural range of Eupatorium album from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: White thoroughwort
Contents
Description
A description of Eupatorium album is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
It is found in sandhills, Longleaf pine-wiregrass savannas, evergreen scrub oak sand ridges, pine flatwoods, old fields, flatwoods, hammocks, seepage slopes, pine-palmetto flatwoods, in woods adjacent to sinkholes, and in well-drained Longleaf pinelands (FSU Herbarium). It is also found in human disturbed areas such as roadsides, areas that have been clear cut, clobbered, bulldozed, and in powerline corridors (FSU Herbarium). it requires open to semi-shaded areas (FSU Herbarium). It is associated with areas that have drying-loamy sand, wet-sandy loam, dry sand, gray-sand loam, dry-sparsely loamy sand soil types (FSU Herbarium). It does well in open canopy areas on longleaf pine habitats and does okay in areas that have been clear cut.[1] It is found in longleaf pine sandhill communities.[2]
Phenology
It has been observed flowering from July to November (FSU Herbarium).
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
It flowers within three months of burning in the early spring to early summer.KMR
Pollination
Use by animals
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, R.K. Godfrey, Robert L. Lazor, John Lazor, J. P. Gillespie, R. Kral, Victoria I. Sullivan, Brenda Herring, Don Herring, Delzie Demaree, Nancy E. Jordan, R. F. Doren, R. E. Perdue, S. C. Hood, Paul L. Redfearn, Jr., R. A. Norris, and R. Komarek. States and Counties: Florida: Bay, Calhoun, Citrus, Clay, Columbia, Escambia, Franklin, Gadsden, Gulf, Jackson, Jefferson, Lafayette, Leon, Levy, Liberty, Madison, Marion, Okaloosa, Santa Rosa, Taylor, Wakulla, and Washington. Georgia: Thomas.
- ↑ Brockway, D. G. and C. E. Lewis (2003). "Influence of deer, cattle grazing and timber harvest on plant species diversity in a longleaf pine bluestem ecosystem." Forest Ecology and Management 175: 49-69.
- ↑ Heuberger, K. A. and F. E. Putz (2003). "Fire in the suburbs: ecological impacts of prescribed fire in small remnants of longleaf pine (Pinus palustris) sandhill." Restoration Ecology 11: 72-81.